
French Polynesia is an overseas collectivity of France and its sole overseas country. It comprises 121 geographically dispersed islands and atolls stretching over more than 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi) in the South Pacific Ocean. The total land area of French Polynesia is 3,521 square kilometres (1,359 sq mi), with a population of 278,786 of which at least 205,000 live in the Society Islands and the remaining population lives in the rest of the archipelago.
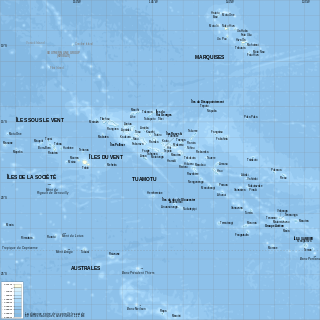
French Polynesia is located in Oceania. It is a group of six archipelagos in the South Pacific Ocean, about halfway between South America and Australia. Its area is about 4,167 km2, of which 3,827 km2 is land and 340 km2 is (inland) water. It has a coastline of 2,525 km but no land borders with other countries.

The Marquesas Islands are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in the southern Pacific Ocean. Their highest point is the peak of Mount Oave on Ua Pou island, at 1,230 m (4,035 ft) above sea level.

The administrative divisions of France are concerned with the institutional and territorial organization of French territory. These territories are located in many parts of the world. There are many administrative divisions, which may have political, electoral (districts), or administrative objectives. All the inhabited territories are represented in the National Assembly, Senate and Economic and Social Council and their citizens have French citizenship and elect the President of France.

The Tuamotu Archipelago or the Tuamotu Islands are a French Polynesian chain of just under 80 islands and atolls in the southern Pacific Ocean. They constitute the largest chain of atolls in the world, extending over an area roughly the size of Western Europe. Their combined land area is 850 square kilometres. This archipelago's major islands are Anaa, Fakarava, Hao and Makemo.

Legislative elections were held in French Polynesia on 23 May 2004 to elect members of the Assembly.

The Windward Islands are the eastern group of the Society Islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in the southern Pacific Ocean. These islands were also previously named the Georgian Islands in honour of King George III of the United Kingdom.

The Leeward Islands are the western part of the Society Islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France, in the South Pacific Ocean. They lie south of the Line Islands, east of the Cooks and north of the Austral Islands. Their area is around 404 km2 (156 sq mi) and their population is over 36,000.

The Îles Tuamotu-Gambier is an administrative division in French Polynesia. It consists of the Tuamotus and the Gambier Islands which are geographically located closely together.

The Assembly of French Polynesia is the unicameral legislature of French Polynesia, an overseas country of the French Republic. It is located at Place Tarahoi in Papeete, Tahiti. It was established in its current form in 1996 although a Tahitian Assembly was first created in 1824. It consists of 57 members who are elected by popular vote for five years; the electoral system is based upon proportional representation in six multi-seat constituencies. Every constituency is represented by at least three representatives. Since 2001, the parity bill binds that the number of women matches the number of men elected to the assembly.

In French Polynesia, there are two levels of administrative divisions: five administrative subdivisions and 48 communes. Many of the communes are further subdivided into communes associées. The breakdown into administrative subdivisions was as a result of the law #71-1028, dated December 24, 1971. The compositions of the administrative subdivisions and the communes were defined in the decrees #72-408 and #72-407 of May 17, 1972, respectively. These subdivisions were confirmed in the decree #2005-1611 of December 20, 2005. Below are several lists of the divisions, according to different sorting schemes.

The Society Islands are an archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean that includes the major islands of Tahiti, Moʻorea, Raiatea, Bora Bora and Huahine. Politically, they are part of French Polynesia, an overseas country of the French Republic. Geographically, they form part of Polynesia.

Arutua, or Ngaru-atua is an atoll in the Tuamotu group in French Polynesia. It is located 40 km SW of Rangiroa. The closest land is Apataki Atoll, only 16 km to the East.

Tatakoto is an atoll in the Tuamotu group in French Polynesia.

Overseas France consists of 13 French territories outside Europe, mostly the remnants of the French colonial empire that remained a part of the French state under various statuses after decolonisation. Most, but not all, are part of the European Union.

The 1st constituency of French Polynesia is a French legislative constituency in French Polynesia.

Gambier is a commune of French Polynesia in the administrative subdivision of the Tuamotu-Gambier Islands. The commune includes the Gambier Islands as well as several atolls in the Tuamotu Archipelago. All the Tuamotu atolls belonging to the commune are uninhabited except for Marutea Sud, and are sometimes mistakenly included among the Gambier Islands themselves. The commune population was 1,570 at the 2022 census. Its total land area is 45.97 km2.

French Polynesia's 2nd constituency is a French legislative constituency in French Polynesia. It is currently represented by Nicole Sanquer of A here ia Porinetia.

The annexation of the Leeward Islands or the Leewards War was a series of diplomatic and armed conflicts between the French Third Republic and the native kingdoms of Raiatea-Tahaa, Huahine and Bora Bora, which resulted in the conquest of the Leeward Islands, in the South Pacific archipelago of the Society Islands in modern-day French Polynesia.



















