Bosnia and Herzegovina is a country in Southeast Europe, in the Balkans, bordering Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to the north and southwest. In the south it has a 20 kilometres long coast on the Adriatic Sea, with the town of Neum being its only access to the sea. Bosnia has a moderate continental climate with hot summers and cold, snowy winters. In the central and eastern regions, the geography is mountainous, in the northwest it is moderately hilly, and in the northeast it is predominantly flat. Herzegovina, the smaller, southern region, has a Mediterranean climate and is mostly mountainous. Sarajevo is the capital and the largest city.

Sarajevo is the capital and largest city of Bosnia and Herzegovina, with a population of 275,524 in its administrative limits. The Sarajevo metropolitan area including Sarajevo Canton, East Sarajevo and nearby municipalities is home to 555,210 inhabitants. Located within the greater Sarajevo valley of Bosnia, it is surrounded by the Dinaric Alps and situated along the Miljacka River in the heart of the Balkans, a region of Southern Europe.

The Siege of Sarajevo was a prolonged blockade of Sarajevo, the capital of Bosnia and Herzegovina, during the Bosnian War. After it was initially besieged by the forces of the Yugoslav People's Army, the city was then besieged by the Army of Republika Srpska. Lasting from 5 April 1992 to 29 February 1996, it was three times longer than the Battle of Stalingrad, more than a year longer than the siege of Leningrad, and was the longest siege of a capital city in the history of modern warfare.
"Muslims" is a designation for the ethnoreligious group of Serbo-Croatian-speaking Muslims and people of Muslim heritage, inhabiting mostly the territory of the former Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. The term, adopted in the 1971 Constitution of Yugoslavia, groups together a number of distinct South Slavic communities of Islamic ethnocultural tradition. Prior to 1993, a vast majority of present-day Bosniaks self-identified as ethnic Muslims, along with some smaller groups of different ethnicity, such as Gorani and Torbeši. This designation did not include Yugoslav non-Slavic Muslims, such as Turks, some Romani people and majority of Albanians.

The Bosnian War was an international armed conflict that took place in Bosnia and Herzegovina between 1992 and 1995. The war is commonly seen as having started on 6 April 1992, following a number of earlier violent incidents. The war ended on 14 December 1995 when the Dayton accords were signed. The main belligerents were the forces of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina and those of Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia and Republika Srpska, proto-states led and supplied by Croatia and Serbia, respectively.

Centar is a municipality of the city of Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is located between the older parts of the city under Stari Grad, and the newer more modern parts of the city under the municipalities Novi Grad and Novo Sarajevo.

Novi Grad is a municipality of the city of Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is the westernmost of the four municipalities that make up the city of Sarajevo. The municipality also consists of the villages Bojnik and Rečica.

The Sarajevo Canton, officially the Canton of Sarajevo, is one of the ten cantons of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Its cantonal seat is the city of Sarajevo, also the capital city of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
The population of the city of Sarajevo's four municipalities is 275,524, whereas the Sarajevo Canton population is estimated at 413,593.

This article is about the Demographic history of Bosnia and Herzegovina, and deals with the country's documented demographics over time. For an overview of the various ethnic groups and their historical development, see Ethnic groups in Bosnia and Herzegovina.

Ahmići is a village in central Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is located in the municipality of Vitez in the Lašva river valley.
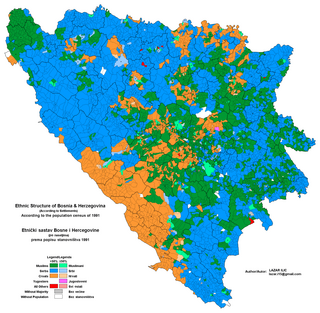
The 1991 population census in Bosnia and Herzegovina was the last census of the population undertaken in the Socialist Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina before the Bosnian War. It was conducted during the final week of March 1991. For the 1991 census there were 109 municipalities of which ten were part of Sarajevo.
Bjelovac is a village in the municipality of Bratunac, Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Duhri is a village in the municipality of Kiseljak, Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Smoluća Gornja is a village in the municipality of Lukavac, Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina.

Ethnic cleansing occurred during the Bosnian War (1992–95) as large numbers of Bosnian Muslims (Bosniaks) and Bosnian Croats were forced to flee their homes or were expelled by the Army of Republika Srpska and Serb paramilitaries. Bosniaks and Bosnian Serbs had also been forced to flee or were expelled by Bosnian Croat forces, though on a restricted scale and in lesser numbers. The UN Security Council Final Report (1994) states while Bosniaks also engaged in "grave breaches of the Geneva Conventions and other violations of international humanitarian law", they "have not engaged in "systematic ethnic cleansing"". According to the report, "there is no factual basis for arguing that there is a 'moral equivalence' between the warring factions".
Around 2:30 p.m. on Sunday, 1 March 1992, a Bosnian Serb wedding procession in Sarajevo's old Muslim quarter of Baščaršija was attacked, resulting in the death of the father of the groom, Nikola Gardović, and the wounding of a Serbian Orthodox priest. The attack took place on the last day of a controversial referendum on Bosnia and Herzegovina's independence from Yugoslavia, in the early stages of the breakup of Yugoslavia and the Yugoslav Wars.

The siege of Goražde refers to engagements during the Bosnian War (1992–95) in and around the town of Goražde in eastern Bosnia.
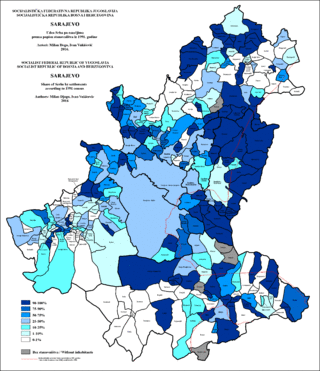
The Exodus of Sarajevo Serbs was the migration of ethnic Serbs from Sarajevo, the capital of Bosnia and Herzegovina, between January and March 1996 after the Dayton Agreement that concluded the Bosnian War (1992–95).

The Kazani pit killings were the mass murder of predominantly ethnic Serbs living inside besieged Sarajevo by the forces of Mušan Topalović, commander of the 10th Mountain Brigade in the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina during the Bosnian War.