
Polythionates are oxyanions with the formula −O3S−Sn−SO−3 (n ≥ 0). They occur naturally and are the products of redox reactions of thiosulfate. Polythionates are readily isolable, unlike the parent polythionic acids. [2]

Polythionates are oxyanions with the formula −O3S−Sn−SO−3 (n ≥ 0). They occur naturally and are the products of redox reactions of thiosulfate. Polythionates are readily isolable, unlike the parent polythionic acids. [2]
Many members of the polythionates have been characterized: dithionate, trithionate, tetrathionate, pentathionate, etc.
These salts are often generated by oxidation of thiosulfate. For example, tetrathionate is obtained by oxidation of thiosulfate ion with iodine (reaction is used in iodometry):
More specialized routes involve reactions of sulfur chlorides with bisulfite salts:
Potassium pentathionate ion has been obtained from SCl2, sodium thiosulfate, and potassium acetate. Initially prismatic crystals of potassium tetrathionate appear, then lamellar crystals of potassium pentathionate, from which the influence of tartaric acid makes an aqueous solution of pentathionic acid. [3]
Potassium hexathionate K2S6O6 has been synthesized by combining KNO2 and K2S2O3 in concentrated HCl at low temperatures. [4]

The chalcogens are the chemical elements in group 16 of the periodic table. This group is also known as the oxygen family. Group 16 consists of the elements oxygen (O), sulfur (S), selenium (Se), tellurium (Te), and the radioactive elements polonium (Po) and livermorium (Lv). Often, oxygen is treated separately from the other chalcogens, sometimes even excluded from the scope of the term "chalcogen" altogether, due to its very different chemical behavior from sulfur, selenium, tellurium, and polonium. The word "chalcogen" is derived from a combination of the Greek word khalkόs (χαλκός) principally meaning copper, and the Latinized Greek word genēs, meaning born or produced.
Selenic acid is the inorganic compound with the formula H2SeO4. It is an oxoacid of selenium, and its structure is more accurately described as O2Se(OH)2. It is a colorless compound. Although it has few uses, one of its salts, sodium selenate is used in the production of glass and animal feeds.

In chemistry tellurate is a compound containing an oxyanion of tellurium where tellurium has an oxidation number of +6. In the naming of inorganic compounds it is a suffix that indicates a polyatomic anion with a central tellurium atom.

Telluric acid, or more accurately Orthotelluric acid, is a chemical compound with the formula Te(OH)6, often written as H6TeO6. It is a white crystalline solid made up of octahedral Te(OH)6 molecules which persist in aqueous solution. In the solid state, there are two forms, rhombohedral and monoclinic, and both contain octahedral Te(OH)6 molecules, containing one hexavalent tellurium (Te) atom in the +6 oxidation state, attached to six hydroxyl (–OH) groups, thus, it can be called tellurium(VI) hydroxide. Telluric acid is a weak acid which is dibasic, forming tellurate salts with strong bases and hydrogen tellurate salts with weaker bases or upon hydrolysis of tellurates in water. It is used as tellurium-source in the synthesis of oxidation catalysts.

Lead(IV) oxide, commonly known as lead dioxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula PbO2. It is an oxide where lead is in an oxidation state of +4. It is a dark-brown solid which is insoluble in water. It exists in two crystalline forms. It has several important applications in electrochemistry, in particular as the positive plate of lead acid batteries.
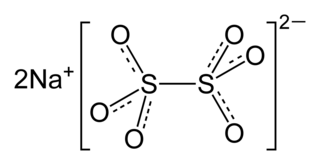
Sodium dithionate Na2S2O6 is an important compound for inorganic chemistry. It is also known under names disodium dithionate, sodium hyposulfate, and sodium metabisulfate. The sulfur can be considered to be in its +5 oxidation state.

Selenite refers to the anion with the chemical formula SeO2−3. It is the oxyanion of selenium. It is the selenium analog of the sulfite ion, SO2−3. Thus selenite is pyramidal and selenium is assigned oxidation state +4. Selenite also refers to compounds that contains this ion, for example sodium selenite Na2SeO3 which is a common source of selenite. Selenite also refers to the esters of selenous acid, for example dimethyl selenite (CH3)2SeO3.

The bisulfite ion (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogensulfite) is the ion HSO−
3. Salts containing the HSO−
3 ion are also known as "sulfite lyes". Sodium bisulfite is used interchangeably with sodium metabisulfite (Na2S2O5). Sodium metabisulfite dissolves in water to give a solution of Na+HSO−
3.

Sodium thioantimoniate or sodium tetrathioantimonate(V) is an inorganic compound with the formula Na3SbS4. The nonahydrate of this chemical, Na3SbS4·9H2O, is known as Schlippe's salt, named after Johann Karl Friedrich von Schlippe (1799–1867). These compounds are examples of sulfosalts. They were once of interest as species generated in qualitative inorganic analysis.
Selenium trioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula SeO3. It is white, hygroscopic solid. It is also an oxidizing agent and a Lewis acid. It is of academic interest as a precursor to Se(VI) compounds.

Peroxydisulfuric acid is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula (HO3SO)2. Also called Marshall's acid after Professor Hugh Marshall, who discovered it in 1891.

Potassium bisulfite (or potassium hydrogen sulfite) is a chemical mixture with the approximate chemical formula KHSO3. Potassium bisulfite in fact is not a real compound, but a mixture of salts that dissolve in water to give solutions composed of potassium ions and bisulfite ions. It is a white solid with an odor of sulfur dioxide. Attempts to crystallize potassium bisulfite yield potassium metabisulfite, K2S2O5.
Thiosulfuric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula H2S2O3. It has attracted academic interest as a simple, easily accessed compound that is labile. It has few practical uses.

A disulfite, commonly known as metabisulfite or pyrosulfite, is a chemical compound containing the ion S
2O2−
5. It is a colorless dianion that is primarily marketed in the form of sodium metabisulfite or potassium metabisulfite. When dissolved in water, these salts release the hydrogensulfite HSO−
3 anion. These salts act equivalently to sodium hydrogensulfite or potassium hydrogensulfite.

Polythionic acid is an oxoacid which has a straight chain of sulfur atoms and has the chemical formula Sn(SO3H)2 (n > 2). Trithionic acid (H2S3O6), tetrathionic acid (H2S4O6) are simple examples. They are the conjugate acids of polythionates. The compounds of n < 80 are expected to exist, and those of n < 20 have already been synthesized. Dithionic acid (H2S2O6) does not belong to the polythionic acids due to strongly different properties.
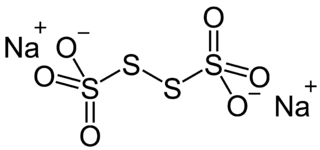
Sodium tetrathionate is a salt of sodium and tetrathionate with the formula Na2S4O6.xH2O. The salt normally is obtained as the dihydrate (x = 2). It is a colorless, water-soluble solid. It is a member of the polythionates, which have the general formula [Sn(SO3)2]2-. Other members include trithionite (n = 1), pentathionate (n = 3), hexathionate (n = 4).

Polonium dioxide (also known as polonium(IV) oxide) is a chemical compound with the formula PoO2. It is one of three oxides of polonium, the other two being polonium monoxide (PoO) and polonium trioxide (PoO3). It is a pale yellow crystalline solid at room temperature. Under lowered pressure (such as a vacuum), it decomposes into elemental polonium and oxygen at 500 °C. It is the most stable oxide of polonium and is an interchalcogen.
Tellurium compounds are compounds containing the element tellurium (Te). Tellurium belongs to the chalcogen family of elements on the periodic table, which also includes oxygen, sulfur, selenium and polonium: Tellurium and selenium compounds are similar. Tellurium exhibits the oxidation states −2, +2, +4 and +6, with +4 being most common.

Sulfoxylic acid (H2SO2) (also known as hyposulfurous acid or sulfur dihydroxide) is an unstable oxoacid of sulfur in an intermediate oxidation state between hydrogen sulfide and dithionous acid. It consists of two hydroxy groups attached to a sulfur atom. Sulfoxylic acid contains sulfur in an oxidation state of +2. Sulfur monoxide (SO) can be considered as a theoretical anhydride for sulfoxylic acid, but it is not actually known to react with water.
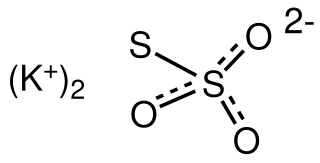
Potassium thiosulfate, commonly abbreviated KTS, is an inorganic compound with the formula K2S2O3. This salt can form multiple hydrates, such as the monohydrate, dihydrate, and the pentahydrate, all of which are white or colorless solids. It is used as a fertilizer.