External links
| Power plants |
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reactor types |
| ||||
| Research locations | |||||
| Fuel cycle locations | |||||
| Organizations | |||||
| Public discourse | |||||
Pool Test Reactor (PTR) was a 10 kWt ordinary (light) water moderated pool-type reactor fueled with highly enriched uranium built at Chalk River in 1957. It used 93% enriched uranium-aluminum plate-type fuel. The reactor, was used for burnup measurement of fissile samples from NRX. The reactor was designed and built by Canadair.
On November 29, 1957 the reactor attained first criticality and shortly took over the function of ZEEP for measuring reactivity effects of materials, particularly after irradiation. It was shut down and defueled in 1990.

A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a fission nuclear chain reaction or nuclear fusion reactions. Nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in nuclear marine propulsion. Heat from nuclear fission is passed to a working fluid, which in turn runs through steam turbines. These either drive a ship's propellers or turn electrical generators' shafts. Nuclear generated steam in principle can be used for industrial process heat or for district heating. Some reactors are used to produce isotopes for medical and industrial use, or for production of weapons-grade plutonium. As of 2022, the International Atomic Energy Agency reports there are 422 nuclear power reactors and 223 nuclear research reactors in operation around the world.
Enriched uranium is a type of uranium in which the percent composition of uranium-235 has been increased through the process of isotope separation. Naturally occurring uranium is composed of three major isotopes: uranium-238, uranium-235, and uranium-234. 235U is the only nuclide existing in nature that is fissile with thermal neutrons.

A fast-neutron reactor (FNR) or fast-spectrum reactor or simply a fast reactor is a category of nuclear reactor in which the fission chain reaction is sustained by fast neutrons, as opposed to slow thermal neutrons used in thermal-neutron reactors. Such a fast reactor needs no neutron moderator, but requires fuel that is relatively rich in fissile material when compared to that required for a thermal-neutron reactor. Around 20 land based fast reactors have been built, accumulating over 400 reactor years of operation globally. The largest of this was the Superphénix Sodium cooled fast reactor in France that was designed to deliver 1,242 MWe. Fast reactors have been intensely studied since the 1950s, as they provide certain decisive advantages over the existing fleet of water cooled and water moderated reactors. These are:

The High Flux Australian Reactor (HIFAR) was Australia's first nuclear reactor. It was built at the Australian Atomic Energy Commission Research Establishment at Lucas Heights, Sydney. The reactor was in operation between 1958 and 2007, when it was superseded by the Open-pool Australian lightwater reactor, also in Lucas Heights.

The light-water reactor (LWR) is a type of thermal-neutron reactor that uses normal water, as opposed to heavy water, as both its coolant and neutron moderator; furthermore a solid form of fissile elements is used as fuel. Thermal-neutron reactors are the most common type of nuclear reactor, and light-water reactors are the most common type of thermal-neutron reactor.
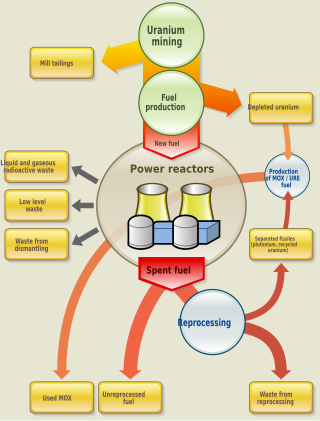
Nuclear fuel is material used in nuclear power stations to produce heat to power turbines. Heat is created when nuclear fuel undergoes nuclear fission.

Aqueous homogeneous reactors (AHR) is a two (2) chamber reactor consisting of an interior reactor chamber and an outside cooling and moderating jacket chamber. They are a type of nuclear reactor in which soluble nuclear salts are dissolved in water. The fuel is mixed with heavy or light water which partially moderates and cools the reactor. The outside layer of the reactor has more water which also partially cools and acts as a moderator,. The water can be either heavy water or ordinary (light) water, which slows neutrons and helps facilitate a stable reaction, both of which need to be very pure.

Research reactors are nuclear fission-based nuclear reactors that serve primarily as a neutron source. They are also called non-power reactors, in contrast to power reactors that are used for electricity production, heat generation, or maritime propulsion.

The SLOWPOKE is a family of low-energy, tank-in-pool type nuclear research reactors designed by Atomic Energy of Canada Limited (AECL) beginning in the late 1960s. John W. Hilborn is the scientist most closely associated with their design. They are beryllium-reflected with a very low critical mass, but provide neutron fluxes higher than available from a small particle accelerator or other radioactive sources.
The Chinese built Miniature Neutron Source reactor (MNSR) is a small and compact research reactor modeled on the Canadian HEU SLOWPOKE-2 design.

A swimming pool reactor, also called an open pool reactor, is a type of nuclear reactor that has a core immersed in an open pool usually of water.


SAFARI-1 is a 20 MW light water-cooled, beryllium reflected, pool-type research reactor, initially used for high level nuclear physics research programmes and was commissioned in 1965.
There are two nuclear research reactors that serve the Texas A&M University Nuclear Science Center. The older of the two is the AGN-201M model, a low-power teaching reactor. The newer reactor, the TRIGA Mark I, is focused strongly towards research.
A gas-cooled reactor (GCR) is a nuclear reactor that uses graphite as a neutron moderator and a gas as coolant. Although there are many other types of reactor cooled by gas, the terms GCR and to a lesser extent gas cooled reactor are particularly used to refer to this type of reactor.

The Maria reactor is Poland's second nuclear research reactor and is the only one still in use. It is located at Narodowe Centrum Badań Jądrowych (NCBJ) at Świerk-Otwock, near Warsaw and named in honor of Maria Skłodowska-Curie. It is the only reactor of Polish design.
RA-1 Enrico Fermi is a research reactor in Argentina. It was the first nuclear reactor to be built in that country and the first research reactor in the southern hemisphere.

Iran's nuclear program is made up of a number of nuclear facilities, including nuclear reactors and various nuclear fuel cycle facilities.

A traveling-wave reactor (TWR) is a proposed type of nuclear fission reactor that can convert fertile material into usable fuel through nuclear transmutation, in tandem with the burnup of fissile material. TWRs differ from other kinds of fast-neutron and breeder reactors in their ability to use fuel efficiently without uranium enrichment or reprocessing, instead directly using depleted uranium, natural uranium, thorium, spent fuel removed from light water reactors, or some combination of these materials. The concept is still in the development stage and no TWRs have ever been built.
A pressurized heavy-water reactor (PHWR) is a nuclear reactor that uses heavy water (deuterium oxide D2O) as its coolant and neutron moderator. PHWRs frequently use natural uranium as fuel, but sometimes also use very low enriched uranium. The heavy water coolant is kept under pressure to avoid boiling, allowing it to reach higher temperature (mostly) without forming steam bubbles, exactly as for a pressurized water reactor. While heavy water is very expensive to isolate from ordinary water (often referred to as light water in contrast to heavy water), its low absorption of neutrons greatly increases the neutron economy of the reactor, avoiding the need for enriched fuel. The high cost of the heavy water is offset by the lowered cost of using natural uranium and/or alternative fuel cycles. As of the beginning of 2001, 31 PHWRs were in operation, having a total capacity of 16.5 GW(e), representing roughly 7.76% by number and 4.7% by generating capacity of all current operating reactors.