
Meconium aspiration syndrome (MAS) also known as neonatal aspiration of meconium is a medical condition affecting newborn infants. It describes the spectrum of disorders and pathophysiology of newborns born in meconium-stained amniotic fluid (MSAF) and have meconium within their lungs. Therefore, MAS has a wide range of severity depending on what conditions and complications develop after parturition. Furthermore, the pathophysiology of MAS is multifactorial and extremely complex which is why it is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in term infants.

A pulmonary alveolus, also known as an air sac or air space, is one of millions of hollow, distensible cup-shaped cavities in the lungs where pulmonary gas exchange takes place. Oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide at the blood–air barrier between the alveolar air and the pulmonary capillary. Alveoli make up the functional tissue of the mammalian lungs known as the lung parenchyma, which takes up 90 percent of the total lung volume.

Infant respiratory distress syndrome (IRDS), also known as surfactant deficiency disorder (SDD), and previously called hyaline membrane disease (HMD), is a syndrome in premature infants caused by developmental insufficiency of pulmonary surfactant production and structural immaturity in the lungs. It can also be a consequence of neonatal infection and can result from a genetic problem with the production of surfactant-associated proteins.
Transient tachypnea of the newborn is a respiratory problem that can be seen in the newborn shortly after delivery. It is caused by retained fetal lung fluid due to impaired clearance mechanisms. It is the most common cause of respiratory distress in term neonates. It consists of a period of tachypnea. Usually, this condition resolves over 24–72 hours. Treatment is supportive and may include supplemental oxygen and antibiotics. The chest x-ray shows hyperinflation of the lungs including prominent pulmonary vascular markings, flattening of the diaphragm, and fluid in the horizontal fissure of the right lung.

Pulmonary surfactant is a surface-active complex of phospholipids and proteins formed by type II alveolar cells. The proteins and lipids that make up the surfactant have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions. By adsorbing to the air-water interface of alveoli, with hydrophilic head groups in the water and the hydrophobic tails facing towards the air, the main lipid component of surfactant, dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC), reduces surface tension.
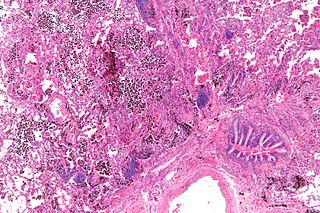
Pulmonary hemorrhage is an acute bleeding from the lung, from the upper respiratory tract and the trachea, and the pulmonary alveoli. When evident clinically, the condition is usually massive. The onset of pulmonary hemorrhage is characterized by a cough productive of blood (hemoptysis) and worsening of oxygenation leading to cyanosis. Treatment should be immediate and should include tracheal suction, oxygen, positive pressure ventilation, and correction of underlying abnormalities such as disorders of coagulation. A blood transfusion may be necessary.
Antenatal steroids, also known as antenatal corticosteroids, are medications administered to pregnant women expecting a preterm birth. When administered, these steroids accelerate the maturation of the fetus' lungs, which reduces the likelihood of infant respiratory distress syndrome and infant mortality. The effectiveness of this corticosteroid treatment on humans was first demonstrated in 1972 by Sir Graham Liggins and Ross Howie, during a randomized control trial using betamethasone.
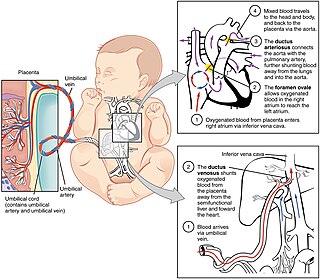
In humans, the circulatory system is different before and after birth. The fetal circulation is composed of the placenta, umbilical blood vessels encapsulated by the umbilical cord, heart and systemic blood vessels. A major difference between the fetal circulation and postnatal circulation is that the lungs are not used during the fetal stage resulting in the presence of shunts to move oxygenated blood and nutrients from the placenta to the fetal tissue. At birth, the start of breathing and the severance of the umbilical cord prompt various changes that quickly transform fetal circulation into postnatal circulation.

Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC) is a phospholipid (and a lecithin) consisting of two C16 palmitic acid groups attached to a phosphatidylcholine head-group.

Surfactant protein B is an essential lipid-associated protein found in pulmonary surfactant. Without it, the lung would not be able to inflate after a deep breath out. It rearranges lipid molecules in the fluid lining the lung so that tiny air sacs in the lung, called alveoli, can more easily inflate.
Lucinactant is a liquid medication used to treat infant respiratory distress syndrome. It is a pulmonary surfactant for infants who lack enough natural surfactant in their lungs. Whereas earlier medicines of the class, such as beractant, calfactant (Infasurf), and poractant (Curosurf), are derived from animals, lucinactant is synthetic. It was approved for use in the United States by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on March 6, 2012.
Surfactant metabolism dysfunction is a condition where pulmonary surfactant is insufficient for adequate respiration. Surface tension at the liquid-air interphase in the alveoli makes the air sacs prone to collapsing post expiration. This is due to the fact that water molecules in the liquid-air surface of alveoli are more attracted to one another than they are to molecules in the air. For sphere-like structures like alveoli, water molecules line the inner walls of the air sacs and stick tightly together through hydrogen bonds. These intermolecular forces put great restraint on the inner walls of the air sac, tighten the surface all together, and unyielding to stretch for inhalation. Thus, without something to alleviate this surface tension, alveoli can collapse and cannot be filled up again. Surfactant is essential mixture that is released into the air-facing surface of inner walls of air sacs to lessen the strength of surface tension. This mixture inserts itself among water molecules and breaks up hydrogen bonds that hold the tension. Multiple lung diseases, like ISD or RDS, in newborns and late-onsets cases have been linked to dysfunction of surfactant metabolism.
Beractant, also known by the trade name of Survanta, is a modified bovine pulmonary surfactant containing bovine lung extract, to which synthetic DPPC, tripalmitin and palmitic acid are added. The composition provides 25 mg/mL phospholipids, 0.5 to 1.75 mg/mL triglycerides, 1.4 to 3.5 mg/mL free fatty acids, and <1.0 mg/mL total surfactant proteins. As an intratracheal suspension, it can be used for the prevention and treatment of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome. Survanta is manufactured by Abbvie.
Surfactant therapy is the medical administration of exogenous surfactant. Surfactants used in this manner are typically instilled directly into the trachea. When a baby comes out of the womb and the lungs are not developed yet, they require administration of surfactant in order to process oxygen and survive. This condition that the baby has is called newborn respiratory distress syndrome, and it is treatable. Surfactant coat the smallest parts of the lungs called the alveoli and helps for oxygen to go in and for carbon dioxide to go out. How surfactant does this is by not allowing the alveoli to collapse and to retain their inflated shape when the baby exhales.

Henrik Verder is a pediatrician and the inventor of the INSURE and LISA methods combined with nasal CPAP. In 1989 he used this pioneering method to successfully treat the first premature infant with severe RDS. Verder is a significant researcher within the field of paediatrics, with more than 50 publications and over 500 citations.
Chiesi Farmaceutici S.p.A. is an Italian family controlled global pharmaceutical company based in Parma, Emilia-Romagna. Chiesi has 31 affiliates in the world, nearly 6,500 total employees and provides medicines to patients in 100 nations. Chiesi currently has revenues of 3 billion euros. According to 2020 official data from the European Patent Office (EPO), Chiesi Group, with 42 patents filed, is confirmed as the first Italian Pharmaceutical Company and third among Italian Companies across all sectors for filing the highest number of patents.

Pulmonary surfactant is used as a medication to treat and prevent respiratory distress syndrome in newborn babies.

Bengt A. Robertson was a Swedish physician and perinatal pathologist. Robertson was primarily known for the development of the synthetic lung surfactant known as Corusurf that brought relief to very small babies suffering from infant respiratory distress syndrome (RDS). From 1974 to 2000 he was the director of the division for experimental perinatal pathology in the department of women and child Health at the Karolinska Institute.
Christian P. Speer is a German pediatrician and Professor of Pediatrics specialized in neonatology at the Julius Maximilian University of Würzburg. Speer is known for his scientific and educational contributions in neonatal medicine.

Henry Lewis Halliday was a British-Irish paediatrician and neonatologist. In 2021, Halliday was awarded the James Spence Medal for research into neonatology, for coordinating two of the largest neonatal multicentre trials for prevention and treatment of a number of neonatal respiratory illnesses and for a breakthrough in the development of a new lung surfactant that brought relief to very small babies suffering from infant respiratory distress syndrome (RDS).











