
Transportation in Boston includes roadway, subway, regional rail, air, and sea options for passenger and freight transit in Boston, Massachusetts. The Massachusetts Port Authority (Massport) operates the Port of Boston, which includes a container shipping facility in South Boston, and Logan International Airport, in East Boston. The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) operates bus, subway, short-distance rail, and water ferry passenger services throughout the city and region. Amtrak operates passenger rail service to and from major Northeastern cities, and a major bus terminal at South Station is served by varied intercity bus companies. The city is bisected by major highways I-90 and I-93, the intersection of which has undergone a major renovation, nicknamed the Big Dig.

Interstate 27 (I-27) is an Interstate Highway, entirely in the US state of Texas, running north from Lubbock to I-40 in Amarillo. These two cities are the only control cities on I-27; other cities and towns served by I-27 include New Deal, Abernathy, Hale Center, Plainview, Kress, Tulia, Happy, and Canyon. In Amarillo, I-27 is commonly known as the Canyon Expressway, although it is also called Canyon Drive on its access roads. I-27 was officially designated the Marshall Formby Memorial Highway after former attorney and State Senator Marshall Formby in 2005. The entire length of I-27 replaced US Highway 87 (US 87) for through traffic. An extension of I-27 north to Raton, New Mexico, and south to Laredo, Texas, was approved in 2022.

Forgottonia, also spelled Forgotonia, is the name given to a 16-county region in Western Illinois in the late 1960s and early 1970s. This geographic region forms the distinctive western bulge of Illinois that is roughly equivalent to "The Tract", the Illinois portion of the Military Tract of 1812, along and west of the Fourth Principal Meridian. Since this wedge-shaped region lies between the Illinois and Mississippi rivers, it has historically been isolated from the eastern portion of Central Illinois.

Highway 41, officially named Buffalo Trail, is a 686-kilometre (426 mi) north-south highway in eastern Alberta, Canada. It extends from the United States border at Wild Horse to Highway 55 in the hamlet of La Corey north of Bonnyville. Highway 41, along with Highway 36 and Highway 63, is part of the Eastern Alberta Trade Corridor, an economic development corridor that links the oil sands with Texas and Mexico, and works in association with the North American Ports-to-Plains Alliance.

Montana Highway 16 is a 152.371-mile-long (245.217 km) state highway in the U.S. state of Montana. It begins in West Glendive at a Business Loop of Interstate 94 (I-94), and ends at the Port of Raymond on the Saskatchewan border. The northern portion from U.S. Route 2 at Culbertson to the Canada–United States border is proposed as part of the Theodore Roosevelt Expressway.

Louisiana Highway 1 (LA 1) is a state highway in Louisiana. At 431.88 miles (695.04 km), it is the longest numbered highway of any class in Louisiana. It runs diagonally across the state, connecting the oil and gas fields near the island of Grand Isle with the northwest corner of the state, north of Shreveport.
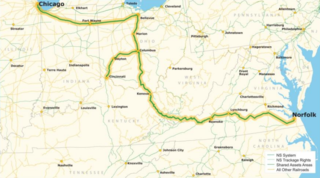
The Heartland Corridor is a public-private partnership between the Norfolk Southern Railway (NS) and the Federal Highway Administration and three U.S. states to improve railroad freight operations.

Southern Manitoba is the southernmost area of the Canadian province of Manitoba. Southern Manitoba encompasses the Winnipeg Metropolitan Region, Westman Region, Central Plains Region, Eastman Region, and Pembina Valley Region, as well as the Manitoba portion of Red River Valley. Holding a population of over one million, seven of the ten cities in Manitoba are located in this area, including Winnipeg, Brandon, Portage la Prairie, Selkirk, Morden, Winkler, and Steinbach.
Port Alberta is a joint venture between Edmonton Global and Edmonton International Airport (EIA) based in the Edmonton Metropolitan Region in Alberta, Canada. Port Alberta provides transportation, logistics and supply chain solutions to connect Alberta's economy to worldwide markets. Its office is located in Edmonton.
The Ports to Plains Corridor, also known as National Highway System High Priority Corridor 38, is a highway corridor between the United States Mexico border at Laredo, Texas and Denver, Colorado. It is the southern third of the Ports-to-Plains Alliance. The reason for proposed improvements to this corridor is to expedite the transportation of goods and services from Mexico in the United States and vice versa. The proposed improvements gained momentum with the signing of the FY22 Omnibus Appropriations bill, which designated a section of the highway part of the interstate system. The Ports-To-Plains Corridor starts in South Texas and traverses through Texas, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and ends in Denver, Colorado.
The Puget Sound Regional Council (PSRC) is a metropolitan planning organization that develops policies and makes decisions about transportation planning, economic development, and growth management throughout the four-county Seattle metropolitan area surrounding Puget Sound. It is a forum for cities, towns, counties, transit agencies, port districts, Native American tribes, and state agencies to address regional issues.
National Gateway is a multi-stage railroad construction project in the United States promoted by CSX Transportation, a unit of CSX Corporation. It is designed to improve rail connections between ports in the U.S. mid-Atlantic seaboard and the Midwest by upgrading bridges and tunnels to allow taller freight trains. In 2008 the company announced its plans to invest $300 million, and is seeking investment from state governments and the U.S. federal government of an additional $400 million as a public-private partnership. Phase 1 of the $850 million project, between CSX's existing terminal in Chambersburg, Pennsylvania, and its hub facility in Northwest Ohio. was completed in September 2013.

The Theodore Roosevelt Expressway, is made up of several existing highways between Rapid City, South Dakota and the Port of Raymond between Saskatchewan and Montana. It is the northern third of the Ports-to-Plains Alliance. The corridor is approximately 445 miles (716 km) long with the majority of the highway two lanes. Congress designated the route as one of 80 National Highway System High-Priority Corridors in 2005 by the Intermodal Surface Transportation Efficiency Act. The designation did not create new design standards or create new eligibility for any additional federal funding.
The Leduc-Nisku Economic Development Association (EDA) was an economic development partnership founded in 1984. It marketed Alberta's International Region, and became dissolved at the end of 2019.
The National Highway System in Canada is a federal designation for a strategic transport network of highways and freeways. The system includes but is not limited to the Trans-Canada Highway, and currently consists of 38,098 kilometres (23,673 mi) of roadway designated under one of three classes: Core Routes, Feeder Routes, and Northern and Remote Routes.
CentrePort Canada is a tri-modal dry port and Foreign Trade Zone located partly in northwest Winnipeg, Manitoba and partly in the Rural Municipality of Rosser, and situated adjacent to the Winnipeg James Armstrong Richardson International Airport (YWG). With 20,000 acres (81 km2) of industrial land, it is the largest tri-modal inland port and foreign trade zone in North America.

The East Coast Economic Corridor (ECEC) is India’s first coastal economic corridor, covering 2500 km of India's coastline, to be developed with the help of the Asian Development Bank (ADB). The ADB is to invest $500 million in infrastructural development of the project. Since late 2013, ADB has been supporting studies on transport corridors in India. Phase 1 of the ECEC is Visakhapatnam-Chennai Industrial Corridor (VCIC) which had been approved by the ADB board in October 2016. The ECEC running along the entire east coast of India from Kolkata to Kanyakumari, is a multimodal, regional maritime corridor that can play a vital role in unifying the large domestic market, as well as integrating the Indian economy with the dynamic global value chains of Southeast and East Asia. It would play a crucial role in the Government of India’s (GoI) Make in India campaign and also supports the port-led industrialization strategy under the Sagar Mala initiative and the Act East Policy by linking domestic companies with the vibrant global production networks of East and Southeast Asia.

U.S. Route 385 (US 385) is a part of the United States Numbered Highway System that travels from Big Bend National Park in Texas to US 85 in Deadwood, South Dakota. Within the state of Nebraska, the highway is known as the Gold Rush Byway, one of nine scenic byways across the state. The highway follows along the old Sidney-Black Hills trail which played a crucial role during the Black Hills Gold Rush in the late 1870s. It served as the primary route to transport gold and mining gear between Sidney, Nebraska and the Black Hills to the north. Today, the highway enters Nebraska in the southeastern portion of the Nebraska Panhandle on the state line with Colorado northeast of Julesburg and continues in a northerly direction to the South Dakota state line north of Chadron.
The Heartland Expressway is a federally-designated High Priority Corridor between Limon, Colorado, and Rapid City, South Dakota in the US. The proposed four-lane corridor is currently under construction, and when completed, will function as the central third of the Ports-to-Plains Alliance, connecting the Ports to Plains Corridor and Theodore Roosevelt Expressway via the Nebraska Panhandle. When completed, the highway will provide multi-lane, divided-highway access to cities including Alliance, Nebraska; Scottsbluff, Nebraska; and Brush, Colorado, bringing long-term economic development and reducing travel times in the region.











