Related Research Articles

A straitjacket is a garment shaped like a jacket with long sleeves that surpass the tips of the wearer's fingers. Its most typical use is restraining people who may cause harm to themselves or others. Once the wearer slides their arms into the sleeves, the person restraining the wearer crosses the sleeves against the chest and ties the ends of the sleeves to the back of the jacket, ensuring the arms are close to the chest with as little movement as possible.

Nasogastric intubation is a medical process involving the insertion of a plastic tube through the nose, past the throat, and down into the stomach. Orogastric intubation is a similar process involving the insertion of a plastic tube through the mouth. Abraham Louis Levin invented the NG tube. Nasogastric tube is also known as Ryle's tube in Commonwealth countries, after John Alfred Ryle.

A gait belt or transfer belt is a device put on a patient who has mobility issues, by a caregiver prior to that caregiver moving the patient. Patients may have problems with balance and a gait belt may be used to aid in the safe movement of a patient, from a standing position to a wheelchair, for example. The gait belt has been customarily made out of cotton webbing, with a durable metal buckle on one end. Cleanable vinyl gait belts were introduced due to the tendency of webbing to harbor supergerms.

Bondage, in BDSM, is the activity of tying or restraining people using equipment such as chains, cuffs, or collars for mutual erotic pleasure. According to the Kinsey Institute, 12% of females and 22% of males respond erotically to BDSM.
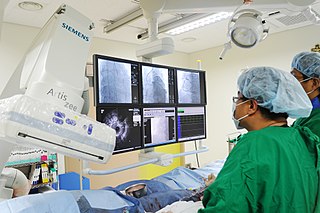
A coronary catheterization is a minimally invasive procedure to access the coronary circulation and blood filled chambers of the heart using a catheter. It is performed for both diagnostic and interventional (treatment) purposes.

A crutch is a mobility aid that transfers weight from the legs to the upper body. It is often used by people who cannot use their legs to support their weight, for reasons ranging from short-term injuries to lifelong disabilities.
Nursing theory is defined as "a creative and rigorous structuring of ideas that project a tentative, purposeful, and systematic view of phenomena". Through systematic inquiry, whether in nursing research or practice, nurses are able to develop knowledge relevant to improving the care of patients. Theory refers to "a coherent group of general propositions used as principles of explanation".

A hospital gown, sometimes called a johnny gown or johnny, especially in Canada and New England, is "a long loose piece of clothing worn in a hospital by someone doing or having an operation". It can be used as clothing for bedridden patients.
Medical restraints are physical restraints used during certain medical procedures to restrain patients with (supposedly) the minimum of discomfort and pain and to prevent them from injuring themselves or others.

In medicine, Fowler's position is a standard patient position in which the patient is seated in a semi-sitting position and may have knees either bent or straight. Variations in the angle are denoted by high Fowler, indicating an upright position at approximately 90 degrees and semi-Fowler, 30 to 45 degrees; and low Fowler, where the head is slightly elevated." It is an intervention used to promote oxygenation via maximum chest expansion and is implemented during events of respiratory distress. Fowler's position facilitates the relaxing of tension of the abdominal muscles, allowing for improved breathing. In immobile patients and infants, the Fowler's position alleviates compression of the chest that occurs due to gravity. Fowler's position increases comfort during eating and other activities, is used in postpartum women to improve uterine drainage, and in infants when signs of respiratory distress are present. Fowler's position is also used when oral or nasal gastric feeding tubes have been implemented as it minimizes the risk of aspiration. Peristalsis and swallowing are aided by the effect of gravitational pull.

Sims' position, named after the gynaecologist J. Marion Sims, is usually used for rectal examination, treatments, enemas, and examining women for vaginal wall prolapse.
An adjustable bed is a bed which has a multi-hinged lying surface which can be profiled to a number of different positions. Common adjustments include inclining the upper body and raising the lower body independently of each other. Other common features include height adjustment and tilting the bed to raise the upper body or the lower body into the Trendelenburg or reverse Trendelenburg positions.

Limb restraints can be physical restraints that inhibit an individual's movement in their arms or legs. The most common limb restraint is physical, whereby restraints are fixed to the individual in order to prevent movement of the limbs. They're most commonly used within the field of medicine. However, opposed to physical restraints, chemical restraints are forms of psychoactive medication that intentionally inhibit an individual's behaviour or movement.
A chemical restraint is a form of medical restraint in which a drug is used to restrict the freedom or movement of a patient or in some cases to sedate the patient. Chemical restraint is used in emergency, acute, and psychiatric settings to reduce agitation, aggression or violent behaviours; it may also be used to control or punish unruly behaviours. Chemical restraint is also referred to as a "Psychopharmacologic Agent", "Psychotropic Drug" or "Therapeutic Restraints" in certain legal writing.

A hospital bed or hospital cot is a bed specially designed for hospitalized patients or others in need of some form of health care. These beds have special features both for the comfort and well-being of the patient and for the convenience of health care workers. Common features include adjustable height for the entire bed, the head, and the feet, adjustable side rails, and electronic buttons to operate both the bed and other nearby electronic devices.
A draw sheet is a small bed sheet placed crosswise over the middle of the bottom sheet of a mattress to cover the area between the person's upper back and thighs, often used by medical professionals to move patients. It can be made of plastic, rubber, or cotton, and is about half the size of a regular sheet. It can be used in place of a mattress pad if a rubber mattress is used. The draw sheet may or may not be tucked into the sides of the bed. When a draw sheet is used to move patients, it is sometimes known as a lift sheet. Nursing manuals recommend that, when a plastic or rubber draw sheet is used, a cotton drawsheet is placed over it. If a folded sheet is used as a draw sheet, the folded edge of the sheet is positioned at the person's upper body. Draw sheets used as lift sheets are generally not tucked in, though sometimes after the move, they are.
Surgical positioning is the practice of placing a patient in a particular physical position during surgery. The goal in selecting and adjusting a particular surgical position is to maintain the patient's safety while allowing access to the surgical site. Often a patient must be placed in an unnatural position to gain access to the surgical site.

J. B. Lippincott & Co. was an American publishing house founded in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania in 1836 by Joshua Ballinger Lippincott. It was incorporated in 1885 as J. B. Lippincott Company.
Heat intolerance is a symptom characterized by feeling overheated in warm environments or when the surrounding environment's temperature rises. Typically, the person feels uncomfortably hot and sweats excessively.
Assisting in activities of daily living (ADL) are skills required in nursing and other professions such as nursing assistants.
References
- ↑ Special care units for people with Alzheimer's and other dementias : consumer education, research, regulatory, and reimbursement issues. DIANE Publishing. 1992. ISBN 9781428928176.
- ↑ Allen, James E. (2003-01-01). Nursing Home Administration: Fourth Edition. Springer Publishing Company. ISBN 9780826153937.
- ↑ Accreditation Issues for Emergency Departments. Joint Commission Resources. 2003-01-01. ISBN 9780866887922.
- ↑ Wilkins, Lippincott Williams & (2007-01-01). Best Practices: Evidence-based Nursing Procedures. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 9781582555324.