Related Research Articles

The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is an archipelago lying to the north of the Canadian continental mainland, excluding Greenland and Iceland.
The Dominion Range is a broad mountain range, about 30 nautical miles long, forming a prominent salient at the juncture of the Beardmore and Mill glaciers in Antarctica. The range is part of the Queen Maud Mountains The range was discovered by the British Antarctic Expedition, 1907–09 and named by Ernest Shackleton for the Dominion of New Zealand, which generously aided the expedition.
The Prince Olav Mountains is a mountain group in the Queen Maud Mountains in Antarctica stretching from Shackleton Glacier to Liv Glacier at the head of the Ross Ice Shelf.

Ferrar Glacier is a glacier in Antarctica. It is about 35 nautical miles long, flowing from the plateau of Victoria Land west of the Royal Society Range to New Harbour in McMurdo Sound. The glacier makes a right (east) turn northeast of Knobhead, where it where it is apposed, i.e., joined in Siamese-twin fashion, to Taylor Glacier. From there, it continues east along the south side of Kukri Hills to New Harbor.

The Prince Charles Mountains are a major group of mountains in Mac. Robertson Land in Antarctica, including the Athos Range, the Porthos Range, and the Aramis Range. The highest peak is Mount Menzies, with a height of 3,228 m (10,591 ft). Other prominent peaks are Mount Izabelle and Mount Stinear. These mountains, together with other scattered peaks, form an arc about 420 km (260 mi) long, extending from the vicinity of Mount Starlight in the north to Goodspeed Nunataks in the south.

Queen Mary Land or the Queen Mary Coast is the portion of the coast of Antarctica lying between Cape Filchner, in 91° 54' E, and Cape Hordern, at 100° 30' E. It is claimed by Australia as part of the Australian Antarctic Territory.
Avalanche Rocks is a vertical rock outcrop rising to 185 metres (600 ft), midway between Delay Point and Jones Rocks on the west side of Melba Peninsula, Antarctica. It was discovered in September 1912 by the Australasian Antarctic Expedition under Douglas Mawson, and so named because of the occurrence of a tremendous avalanche while members of the expedition were encamped nearby.
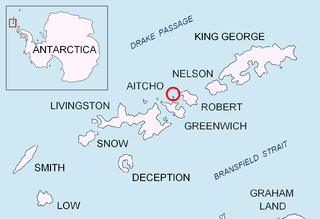
Okol Rocks is a group of rocks in the north of Aitcho Islands group on the west side of English Strait in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The principal feature in the group is Lambert Island (62°22′16″S59°45′49″W).

Posadowsky Glacier is a glacier about 9 nautical miles long, flowing north to Posadowsky Bay immediately east of Gaussberg. Posadowsky Bay is an open embayment, located just east of the West Ice Shelf and fronting on the Davis Sea in Kaiser Wilhelm II Land. Kaiser Wilhelm II Land is the part of East Antarctica lying between Cape Penck, at 87°43'E, and Cape Filchner, at 91°54'E, and is claimed by Australia as part of the Australian Antarctic Territory. Other notable geographic features in this area include Drygalski Island, located 45 mi NNE of Cape Filchner in the Davis Sea, and Mirny Station, a Russian scientific research station.
On the continent of Antarctica, the Aramis Range is the third range south in the Prince Charles Mountains, situated 11 miles southeast of the Porthos Range and extending for about 30 miles in a southwest–northeast direction. It was first visited in January 1957 by Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions (ANARE) southern party led by W.G. Bewsher, who named it for a character in Alexandre Dumas' novel The Three Musketeers, the most popular book read on the southern journey.
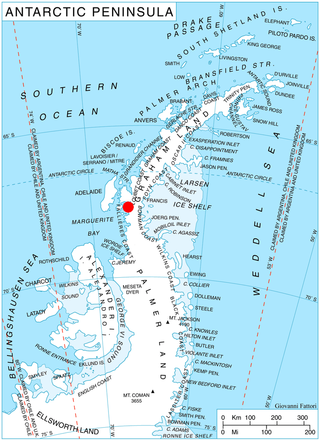
Bader Glacier is a small glacier draining the west slopes of Rudozem Heights and flowing to Bourgeois Fjord just south of Thomson Head on German Peninsula, Fallières Coast on the west side of Graham Land, Antarctica.
The Baldwin Rocks are a group of rock outcrops about 5 nautical miles (10 km) northwest of Watson Bluff on the north side of David Island. They were charted by the Australasian Antarctic Expedition, 1911–14, under Mawson, and named by him for Joseph M. Baldwin of the Melbourne Observatory.

Priboy Rocks is the group of rocks off the east coast of Robert Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica, extending 1.65 km (1.03 mi) in east–west direction and 1.2 km (0.75 mi) in north–south direction.
Patience Rocks is a group of rocks lying 1.5 nautical miles (2.8 km) northwest of Avian Island, close off the south end of Adelaide Island. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) for Leading Engineer Mechanic Donald Patience, a member of the Royal Navy Hydrographic Survey Unit which charted this area in 1963.
The Fortress Rocks are a cluster of low rock summits 0.5 nautical miles (1 km) north of the summit of Observation Hill on Hut Point Peninsula, Ross Island. The descriptive name was given by members of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13, under Robert Falcon Scott.

The Morozumi Range is a spectacular mountain range of unusual scenic beauty in the Usarp Mountains of North Victoria Land, Antarctica. It extends northwest–southeast for 25 miles (40 km), with its northern elevations overlooking the convergence of Gressitt Glacier and Rennick Glacier.
The Morrison Rocks are a group of rocks which outcrop along the southern slope of Mount Frakes, in the Crary Mountains of Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica. They were mapped by the United States Geological Survey from ground surveys and U.S. Navy aerial photographs, 1959–66, and were named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Paul W. Morrison, U.S. Navy, a hospital corpsman at South Pole Station in 1974.
Northern Tibet volcanic field is a volcanic field in China.
References
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "Possession Rocks". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Possession Rocks". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.