Paul Joseph Goebbels was a German Nazi politician and philologist who was the Gauleiter of Berlin, chief propagandist for the Nazi Party, and then Reich Minister of Propaganda from 1933 to 1945. He was one of Adolf Hitler's closest and most devoted followers, known for his skills in public speaking and his deeply virulent antisemitism which was evident in his publicly voiced views. He advocated progressively harsher discrimination, including the extermination of the Jews in the Holocaust.

The Weimar Republic, officially known as the German Reich, was a historical period of Germany from 9 November 1918 to 23 March 1933, during which it was a constitutional republic for the first time in history; hence it is also referred to, and unofficially proclaimed itself, as the German Republic. The period's informal name is derived from the city of Weimar, which hosted the constituent assembly that established its government. In English, the republic was usually simply called "Germany", with "Weimar Republic" not commonly used until the 1930s. The Weimar Republic had a semi-presidential system.

Wilhelm Frick was a convicted war criminal and prominent German politician of the Nazi Party (NSDAP) who served as Minister of the Interior in Adolf Hitler's cabinet from 1933 to 1943 and as the last governor of the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia.

Reichswehr was the official name of the German armed forces during the Weimar Republic and the first years of the Third Reich. After Germany was defeated in World War I, the Imperial German Army was dissolved in order to be reshaped into a peacetime army. From it a provisional Reichswehr was formed in March 1919. Under the terms of the Treaty of Versailles, the rebuilt German Army was subject to severe limitations in size, structure and armament. The official formation of the Reichswehr took place on 1 January 1921 after the limitations had been met. The German armed forces kept the name Reichswehr until Adolf Hitler's 1935 proclamation of the "restoration of military sovereignty", at which point it became part of the new Wehrmacht.

Alfred Ernst Christian Alexander Hugenberg was an influential German businessman and politician. An important figure in nationalist politics in Germany during the first three decades of the twentieth century, Hugenberg became the country's leading media proprietor during the 1920s. As leader of the German National People's Party, he played a part in helping Adolf Hitler become chancellor of Germany and served in his first cabinet in 1933, hoping to control Hitler and use him as his tool. The plan failed, and by the end of 1933 Hugenberg had been pushed to the sidelines. Although he continued to serve as a guest member of the Reichstag until 1945, he wielded no political influence. Following World War II, he was interned by the British in 1946 and classified as "exonerated" in 1951 after undergoing denazification.

Kurt Ferdinand Friedrich Hermann von Schleicher was a German military officer and the penultimate chancellor of Germany during the Weimar Republic. A rival for power with Adolf Hitler, Schleicher was murdered by Hitler's Schutzstaffel during the Night of the Long Knives in 1934.

The president of Germany was the head of state under the Weimar Constitution, which was officially in force from 1919 to 1945, encompassing the periods of the Weimar Republic and Nazi Germany.
The early timeline of Nazism begins with its origins and continues until Hitler's rise to power.

The Hitler cabinet was the government of Nazi Germany between 30 January 1933 and 30 April 1945 upon the appointment of Adolf Hitler as Chancellor of Germany by President Paul von Hindenburg. It was contrived by the national conservative politician Franz von Papen, who reserved the office of the Vice-Chancellor for himself. Originally, Hitler's first cabinet was called the Reich Cabinet of National Salvation, which was a coalition of the Nazi Party (NSDAP) and the national conservative German National People's Party (DNVP). The Hitler cabinet lasted until his suicide during the defeat of Nazi Germany. Hitler's cabinet was succeeded by the short-lived Goebbels cabinet, with Karl Dönitz appointed by Hitler as the new Reichspräsident.

Presidential elections were held in Germany on 13 March 1932, with a runoff on 10 April. Independent incumbent Paul von Hindenburg won a second seven-year term against Adolf Hitler of the Nazi Party (NSDAP). Communist Party (KPD) leader Ernst Thälmann also ran and received more than ten percent of the vote in the runoff. Theodor Duesterberg, the deputy leader of the World War I veterans' organization Der Stahlhelm, ran in the first round but dropped out of the runoff. This was the second and final direct election to the office of President of the Reich, Germany's head of state under the Weimar Republic.

Prince August Wilhelm Heinrich Günther Viktor of Prussia, nicknamed "Auwi", was the fourth son of German Emperor Wilhelm II by his first wife, Augusta Victoria of Schleswig-Holstein. A vocal supporter of Nazism and of Adolf Hitler, he joined the Nazi party in 1930 and rose to the rank of SA-Obergruppenführer.

Federal elections were held in Germany on 5 March 1933, after the Nazi seizure of power on 30 January and just six days after the Reichstag fire. The election saw Nazi stormtroopers unleash a widespread campaign of violence against the Communist Party (KPD), left-wingers, trade unionists, the Social Democratic Party and the Centre Party. They were the last multi-party elections in a united Germany until 1990.

The Harzburg Front was a short-lived radical right-wing, anti-democratic political alliance in Weimar Germany, formed in 1931 as an attempt to present a unified opposition to the government of Chancellor Heinrich Brüning. It was a coalition of the national conservative German National People's Party (DNVP) under millionaire press-baron Alfred Hugenberg with Adolf Hitler's National Socialist German Workers' Party (NSDAP), the leadership of Der Stahlhelm paramilitary veterans' association, the Agricultural League and the Pan-German League organizations.

Adolf Hitler's rise to power began in the newly established Weimar Republic in September 1919 when Hitler joined the Deutsche Arbeiterpartei. He rose to a place of prominence in the early years of the party. Being one of its most popular speakers, he was made the party leader after he threatened to otherwise leave.

The government of Nazi Germany was a totalitarian dictatorship governed by Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party according to the Führerprinzip. Nazi Germany was established in January 1933 with the appointment of Adolf Hitler as Chancellor of Germany, followed by suspension of basic rights with the Reichstag Fire Decree and the Enabling Act which gave Hitler's regime the power to pass and enforce laws without the involvement of the Reichstag or German president, and de facto ended with Germany's surrender in World War II on 8 May 1945 and de jure ended with the Berlin Declaration on 5 June 1945.

The Secret Meeting of 20 February 1933 was a secret meeting held by Adolf Hitler and 25 industrialists at the official residence of the President of the Reichstag Hermann Göring in Berlin. Its purpose was to raise funds for the election campaign of the Nazi Party.

Events in the year 1933 in Germany.
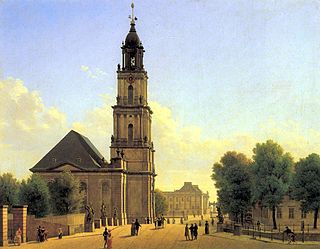
The Garrison Church was a Protestant church in the historic centre of Potsdam. Built by order of King Frederick William I of Prussia according to plans by Philipp Gerlach from 1730 to 1735, it was considered as a major work of Prussian Baroque architecture. With a height of almost 90 metres, it was Potsdam's tallest building and shaped its cityscape. In addition, the Garrison Church was part of the city's famous "Three Churches View" together with the St. Nicholas Church and the Holy Spirit Church. After it was damaged during the British bombing in World War II, the East German authorities demolished the church in 1968. After the German reunification, the Garrison Church is currently being rebuilt as a centre for remembrance and reconciliation. The first section opened in 2024, containing a Coventry chapel, an exhibition about the history of the place and a viewing platform at a height of 57 meters.
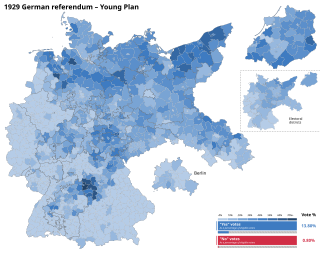
A referendum on the Young Plan was held in Germany on 22 December 1929. It was an attempt to use popular legislation to annul the Young Plan agreement between the German government and the World War I opponents of the German Reich regarding the amount and conditions of reparations payments. The referendum was the result of the initiative "Against the Enslavement of the German People " launched in 1929 by right-wing parties and organizations. It called for an overall revision of the Treaty of Versailles and stipulated that government officials who accepted new reparation obligations would be committing treason.

Beginning in 1925, some members of higher levels of the German nobility joined the Nazi Party, registered by their title, date of birth, NSDAP Party registration number, and date of joining the Nazi Party, from the registration of their first prince (Ernst) into NSDAP in 1928, until the end of World War II in 1945.