
In the United States today, the organized environmental movement is represented by a wide range of organizations sometimes called non-governmental organizations or NGOs. These organizations exist on local, national, and international scales. Environmental NGOs vary widely in political views and in the amount they seek to influence the environmental policy of the United States and other governments. The environmental movement today consists of both large national groups and also many smaller local groups with local concerns. Some resemble the old U.S. conservation movement - whose modern expression is The Nature Conservancy, Audubon Society and National Geographic Society - American organizations with a worldwide influence.

Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions that release nuclear energy to generate heat, which most frequently is then used in steam turbines to produce electricity in a nuclear power plant. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced by nuclear fission of uranium and plutonium. Nuclear decay processes are used in niche applications such as radioisotope thermoelectric generators. Generating electricity from fusion power remains at the focus of international research. This article mostly deals with nuclear fission power for electricity generation.

Radioactive waste is a type of hazardous waste that contains radioactive material. Radioactive waste is a by-product of various nuclear technology processes. Industries generating radioactive waste include nuclear medicine, nuclear research, nuclear power, manufacturing, construction, coal and rare-earth mining, and nuclear weapons reprocessing. Radioactive waste is regulated by government agencies in order to protect human health and the environment.

The Hanford Site is a decommissioned nuclear production complex operated by the United States federal government on the Columbia River in Benton County in the U.S. state of Washington. The site has been known by many names, including Hanford Project, Hanford Works, Hanford Engineer Works and Hanford Nuclear Reservation.

The Gulf of Saint Lawrence is the outlet of the North American Great Lakes via the Saint Lawrence River into the Atlantic Ocean. The gulf is a semi-enclosed sea, covering an area of about 226,000 square kilometres (87,000 sq mi) and containing about 34,500 cubic kilometres (8,300 cu mi) of water, which results in an average depth of 152 metres (499 ft).

The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, groups together all islands lying to the north of the Canadian continental mainland excluding Greenland.

The Yucca Mountain Nuclear Waste Repository, as designated by the Nuclear Waste Policy Act amendments of 1987, is a proposed deep geological repository storage facility within Yucca Mountain for spent nuclear fuel and other high-level radioactive waste in the United States. The site is on federal land adjacent to the Nevada Test Site in Nye County, Nevada, about 80 mi (130 km) northwest of the Las Vegas Valley.
Nuclear reprocessing is the chemical separation of fission products and unused uranium from spent nuclear fuel. Originally, reprocessing was used solely to extract plutonium for producing nuclear weapons. With commercialization of nuclear power, the reprocessed plutonium was recycled back into MOX nuclear fuel for thermal reactors. The reprocessed uranium, also known as the spent fuel material, can in principle also be re-used as fuel, but that is only economical when uranium supply is low and prices are high. A breeder reactor is not restricted to using recycled plutonium and uranium. It can employ all the actinides, closing the nuclear fuel cycle and potentially multiplying the energy extracted from natural uranium by about 60 times.

Low-level waste (LLW) is nuclear waste that does not fit into the categorical definitions for intermediate-level waste (ILW), high-level waste (HLW), spent nuclear fuel (SNF), transuranic waste (TRU), or certain byproduct materials known as 11e(2) wastes, such as uranium mill tailings. In essence, it is a definition by exclusion, and LLW is that category of radioactive wastes that do not fit into the other categories. If LLW is mixed with hazardous wastes, then it has a special status as mixed low-level waste (MLLW) and must satisfy treatment, storage, and disposal regulations both as LLW and as hazardous waste. While the bulk of LLW is not highly radioactive, the definition of LLW does not include references to its activity, and some LLW may be quite radioactive, as in the case of radioactive sources used in industry and medicine.

Amchitka is a volcanic, tectonically unstable island in the Rat Islands group of the Aleutian Islands in southwest Alaska. It is part of the Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Refuge. The island, with a land area of roughly 116 square miles (300 km2), is about 42 miles (68 km) long and 1 to 4 miles wide. The area has a maritime climate, with many storms, and mostly overcast skies.

The Thames Estuary is where the River Thames meets the waters of the North Sea, in the south-east of Great Britain.

A deep geological repository is a way of storing toxic or radioactive waste within a stable geologic environment. It entails a combination of waste form, waste package, engineered seals and geology that is suited to provide a high level of long-term isolation and containment without future maintenance. A number of mercury, cyanide and arsenic waste repositories are operating worldwide including Canada and Germany.
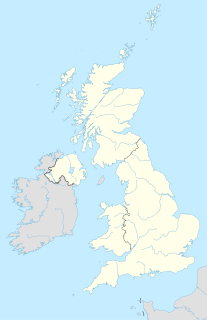
Nuclear power in the United Kingdom generates 20% of the country's electricity, as of 2020. The UK has 15 operational nuclear reactors at seven locations, as well as nuclear reprocessing plants at Sellafield and the Tails Management Facility (TMF) operated by Urenco in Capenhurst.

Nuclear safety is defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) as "The achievement of proper operating conditions, prevention of accidents or mitigation of accident consequences, resulting in protection of workers, the public and the environment from undue radiation hazards". The IAEA defines nuclear security as "The prevention and detection of and response to, theft, sabotage, unauthorized access, illegal transfer or other malicious acts involving nuclear material, other radioactive substances or their associated facilities".
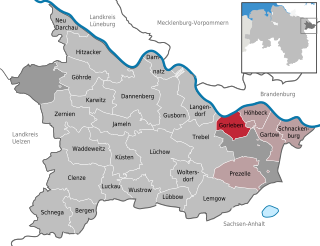
Gorleben is a small municipality (Gemeinde) in the Gartow region of the Lüchow-Dannenberg district in the far north-east of Lower Saxony, Germany, a region also known as the Wendland.

Nuclear safety in the United States is governed by federal regulations issued by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC). The NRC regulates all nuclear plants and materials in the United States except for nuclear plants and materials controlled by the U.S. government, as well those powering naval vessels.

Nuclear power in Taiwan accounts for 5,028 MWe of capacity by means of 3 active plants and 6 reactors, which makes up around 8.1% of its national energy consumption, and 19% of its electricity generation as of 2015. The technology chosen for the reactors has been General Electric BWR technology for 2 plants and Westinghouse PWR technology for the Maanshan Nuclear Power Plant. Construction of the Lungmen Nuclear Power Plant using the ABWR design has encountered public opposition and a host of delays, and in April 2014 the government decided to suspend construction.

The environmental impact of nuclear power results from the nuclear fuel cycle, operation, and the effects of nuclear accidents.

High-level radioactive waste management concerns how radioactive materials created during production of nuclear power and nuclear weapons are dealt with. Radioactive waste contains a mixture of short-lived and long-lived nuclides, as well as non-radioactive nuclides. There was reportedly some 47,000 tonnes of high-level nuclear waste stored in the United States 2002.

The nuclear energy policy of the United States developed within two main periods, from 1954–1992 and 2005–2010. The first period saw the ongoing building of nuclear power plants, the enactment of numerous pieces of legislation such as the Energy Reorganization Act of 1974, and the implementation of countless policies which have guided the Nuclear Regulatory Commission and the Department of Energy in the regulation and growth of nuclear energy companies. This includes, but is not limited to, regulations of nuclear facilities, waste storage, decommissioning of weapons-grade materials, uranium mining, and funding for nuclear companies, along with an increase in power plant building. Both legislation and bureaucratic regulations of nuclear energy in the United States have been shaped by scientific research, private industries' wishes, and public opinion, which has shifted over time and as a result of different nuclear disasters.


















