
Pope Clement VII was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 19 November 1523 to his death on 25 September 1534. Deemed "the most unfortunate of the popes", Clement VII's reign was marked by a rapid succession of political, military, and religious struggles—many long in the making—which had far-reaching consequences for Christianity and world politics.

Orvieto is a city and comune in the Province of Terni, southwestern Umbria, Italy, situated on the flat summit of a large butte of volcanic tuff. The city rises dramatically above the almost-vertical faces of tuff cliffs that are completed by defensive walls built of the same stone, called tufa.

The Sack of Rome, then part of the Papal States, followed the capture of the city on 6 May 1527 by the mutinous troops of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor during the War of the League of Cognac. Despite not being ordered to storm the city, with Charles V intending to only use the threat of military action to make Pope Clement VII come to his terms, a largely unpaid Imperial army formed by 14,000 Germans, many of Lutheran faith, 6,000 Spaniards and some Italian contingents, occupied the scarcely defended Rome and began looting, slaying and holding citizens for ransom in excess without any restraint. Clement VII took refuge in Castel Sant'Angelo after the Swiss Guard were annihilated in a delaying rearguard action, where he remained until a ransom was paid to the pillagers. Benvenuto Cellini, eyewitness to the events, described the sack in his works. It was not until February, 1528 that the spread of a plague and the approach of the League forces under Odet de Foix forced the army to withdraw towards Naples from the city. Rome's population had dropped from 55,000 to 10,000 due to the atrocities, famine, an outbreak of plague and fleeing the city. The subsequent loss of the League army during the Siege of Naples secured victory in the war of League of Cognac for Charles V. The Emperor denied responsibility in the sack and was eventually absolved by Clement VII for the event. On the other hand, the Sack of Rome further exacerbated religious hatred and antagonism between Catholics and Lutherans.

Villa Madama is a Renaissance-style rural palace (villa) located on Via di Villa Madama #250 in Rome, Italy. Located west of the city center and a few miles north of the Vatican, and just south of the Foro Olimpico Stadium. Even though incomplete, this villa with its loggia and segmented columned garden court and its casino with an open center and terraced gardens, was initially planned by Raphael, and highly influential for subsequent architects of the High Renaissance.

Giuliano da Sangallo was an Italian sculptor, architect and military engineer active during the Italian Renaissance. He is known primarily for being the favored architect of Lorenzo de' Medici, his patron. In this role, Giuliano designed a villa for Lorenzo as well as a monastery for Augustinians and a church where a miracle was said to have taken place. Additionally, Giuliano was commissioned to build multiple structures for Pope Julius II and Pope Leo X. Leon Battista Alberti and Filippo Brunelleschi heavily influenced Sangallo and in turn, he influenced other important Renaissance figures such as Raphael, Leonardo da Vinci, his brother Antonio da Sangallo the Elder, and his sons, Antonio da Sangallo the Younger and Francesco da Sangallo.

Antonio da Sangallo the Elder was an Italian Renaissance architect who specialized in the design of fortifications.

Antonio da Sangallo the Younger, also known as Antonio da San Gallo, was an Italian architect active during the Renaissance, mainly in Rome and the Papal States.
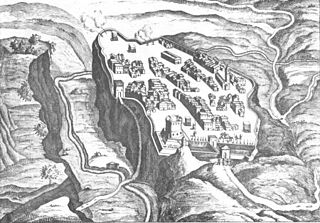
Castro was an ancient city on the west side of Lake Bolsena in the present-day comune of Ischia di Castro, northern Lazio, Italy. It was destroyed at the conclusion of the Wars of Castro in the 17th century.

Juan Bautista de Toledo was a Spanish architect. He was educated in Italy, in the Italian High Renaissance. As many Italian renaissance architects, he had experience in both architecture and military and civil public works. Born, either in Toledo or in Madrid around 1515. He died on 19 May 1567 in Madrid, and was buried in Madrid in the choir of the primitive “Convento de Santo Tomás, Iglesia de la Santa Cruz”.

The Minor Basilica of St. Lawrence in Damaso or simply San Lorenzo in Damaso is a parish and titular church in central Rome, Italy that is dedicated to St. Lawrence, deacon and martyr. It is incorporated into the Palazzo della Cancelleria, which enjoys the extraterritoriality of the Holy See.

Scala Regia is a flight of steps in the Vatican City and is part of the formal entrance to the Vatican. It was designed by Gian Lorenzo Bernini.

Cesare Nebbia (c.1536–c.1614) was an Italian painter from Orvieto who painted in a Mannerist style.

Lorenzo Lotti, also known as Lorenzetto, (1490–1541), born Lorenzo di Lodovico di Guglielmo, was an Italian Renaissance sculptor and architect in the circle of Raphael.

The Diocese of Orvieto-Todi is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church in central Italy. It was created in 1986 when the historical Diocese of Orvieto was united to the Diocese of Todi. The Diocese of Orvieto-Todi is immediately exempt to the Holy See and not part of any ecclesiastical province.

Orvieto, Umbria, Italy, was the refuge of five popes during the 13th century: Urban IV (1261–1264), Gregory X (1271–1276), Martin IV (1281–1285), Nicholas IV (1288–1292) and Boniface VIII (1294–1303). During this time, the popes took up residence in the Papal Palace of Orvieto, which was adjacent to the Orvieto Cathedral and expanded onto the bishop's residence. None of these popes died in Orvieto, and thus no papal elections took place in there, nor are there any papal tombs.

Bramante Staircase is the name given to two staircases in the Vatican Museums in the Vatican City State: the original stair, built in 1505, and a modern equivalent from 1932.

Porta Santo Spirito is one of the gates of the Leonine walls in Rome (Italy). It rises on the back side of the Hospital of the same name, in Via dei Penitenzieri, close to the crossing with Piazza della Rovere.

Giovanni Mangone was an Italian artist active almost exclusively in Rome during the Renaissance. Mangone's skills were manifold: he worked as sculptor, architect, stonecutter and building estimator. Moreover, he was a keen antiquarian and among the founders of the Academy dei Virtuosi al Pantheon. As military engineer, he was renowned among his contemporaries.

The Palazzo del Governatore di Borgo, also called Palazzo delle Prigioni di Borgo, Palazzo del Soldano, or Palazzo dal Pozzo, was a Renaissance palace in Rome, important for artistic and historical reasons. Designed by Antonio da Sangallo the Younger, it was demolished in 1936 for the opening of Via della Conciliazione.

Palazzo Sacchetti is a palazzo in Rome, important for historical and artistic reasons.






















