Related Research Articles
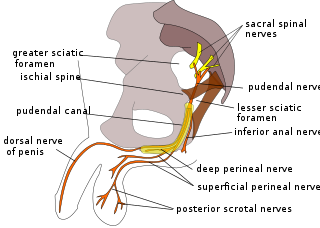
The pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the perineum. It carries sensation from the external genitalia of both sexes and the skin around the anus and perineum, as well as the motor supply to various pelvic muscles, including the male or female external urethral sphincter and the external anal sphincter. If damaged, most commonly by childbirth, lesions may cause sensory loss or fecal incontinence. The nerve may be temporarily blocked as part of an anaesthetic procedure.

Fecal incontinence (FI), or in some forms encopresis, is a lack of control over defecation, leading to involuntary loss of bowel contents, both liquid stool elements and mucus, or solid feces. When this loss includes flatus (gas), it is referred to as anal incontinence. FI is a sign or a symptom, not a diagnosis. Incontinence can result from different causes and might occur with either constipation or diarrhea. Continence is maintained by several interrelated factors, including the anal sampling mechanism, and incontinence usually results from deficiency of multiple mechanisms. The most common causes are thought to be immediate or delayed damage from childbirth, complications from prior anorectal surgery, altered bowel habits, and receptive anal sex. An estimated 2.2% of community dwelling adults are affected. However, reported prevalence figures vary. A prevalence of 8.39% among non-institutionalized U.S adults between 2005 and 2010 has been reported, and among institutionalized elders figures come close to 50%.
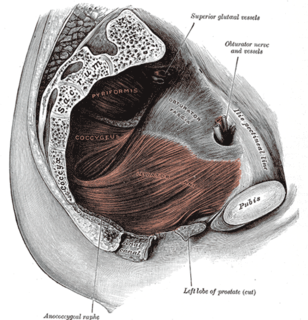
The levator ani is a broad, thin muscle group, situated on either side of the pelvis. It is formed from three muscle components: the pubococcygeus, the iliococcygeus, and the puborectalis.

The spermatic cord is the cord-like structure in males formed by the vas deferens and surrounding tissue that runs from the deep inguinal ring down to each testicle. Its serosal covering, the tunica vaginalis, is an extension of the peritoneum that passes through the transversalis fascia. Each testicle develops in the lower thoracic and upper lumbar region and migrates into the scrotum during its descent it carries along with it vas deferens, its vessels, nerves etc. There is one on each side.
Pudendal nerve entrapment (PNE), also known as Alcock canal syndrome, is an uncommon source of chronic pain in which the pudendal nerve is entrapped or compressed in Alcock's canal. There are several different types of PNE based on the site of entrapment anatomically. Pain is positional and is worsened by sitting. Other symptoms include genital numbness, fecal incontinence and urinary incontinence.

The mesentery is an organ that attaches the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall in humans and is formed by the double fold of peritoneum. It helps in storing fat and allowing blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves to supply the intestines, among other functions.

A rectal prolapse occurs when walls of the rectum have prolapsed to such a degree that they protrude out of the anus and are visible outside the body. However, most researchers agree that there are 3 to 5 different types of rectal prolapse, depending on whether the prolapsed section is visible externally, and whether the full or only partial thickness of the rectal wall is involved.

The pelvic floor or pelvic diaphragm is composed of muscle fibers of the levator ani, the coccygeus muscle, and associated connective tissue which span the area underneath the pelvis. The pelvic diaphragm is a muscular partition formed by the levatores ani and coccygei, with which may be included the parietal pelvic fascia on their upper and lower aspects. The pelvic floor separates the pelvic cavity above from the perineal region below. Both males and females have a pelvic floor. To accommodate the birth canal, a female's pelvic cavity is larger than a male's.
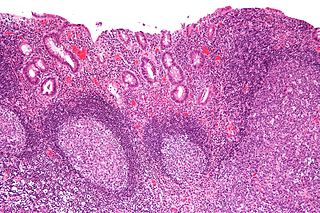
Diversion colitis is an inflammation of the colon which can occur as a complication of ileostomy or colostomy, where symptoms may occur between one month and three years following surgery. It also occurs frequently in a neovagina created by colovaginoplasty, with varying delay after the original procedure. Despite the presence of a variable degree of inflammation the most suggestive histological feature remains the prominent lymphoid aggregates.

An imperforate anus or anorectal malformations (ARMs) are birth defects in which the rectum is malformed. ARMs are a spectrum of different congenital anomalies which vary from fairly minor lesions to complex anomalies. The cause of ARMs is unknown; the genetic basis of these anomalies is very complex because of their anatomical variability. In 8% of patients, genetic factors are clearly associated with ARMs. Anorectal malformation in Currarino syndrome represents the only association for which the gene HLXB9 has been identified.

Anal fistula is a chronic abnormal communication between the epithelialised surface of the anal canal and usually the perianal skin. An anal fistula can be described as a narrow tunnel with its internal opening in the anal canal and its external opening in the skin near the anus. Anal fistulae commonly occur in people with a history of anal abscesses. They can form when anal abscesses do not heal properly.

Perineal hernia is a hernia involving the perineum. The hernia may contain fluid, fat, any part of the intestine, the rectum, or the bladder. It is known to occur in humans, dogs, and other mammals, and often appears as a sudden swelling to one side of the anus.
Total mesorectal excision (TME) is a standard surgical technique for treatment of rectal cancer, first described in 1982 by Professor Bill Heald at the UK's Basingstoke District Hospital. It is a precise dissection of the mesorectal envelope comprising rectum containing the tumour together with all the surrounding fatty tissue and the sheet of tissue that contains lymph nodes and blood vessels. Dissection is along the avascular alveolar plane between the presacral and mesorectal fascia, described as holy plane. Dissection along this plane facilitates a straightforward dissection and preserves the sacral vessels and hypogastric nerves and is a sphincter-sparing resection and decreases permanent stoma rates. It is possible to rejoin the two ends of the colon; however, most patients require a temporary ileostomy pouch to bypass the colon, allowing it to heal with less risk of infection, perforation or leakage.

Anorectal abscess is an abscess adjacent to the anus. Most cases of perianal abscesses are sporadic, though there are certain situations which elevate the risk for developing the disease, such as diabetes mellitus, Crohn's disease, chronic corticosteroid treatment and others. It arises as a complication of paraproctitis. Ischiorectal, inter- and intrasphincteric abscesses have been described.

Defecography is a type of medical radiological imaging in which the mechanics of a patient's defecation are visualized in real time using a fluoroscope. The anatomy and function of the anorectum and pelvic floor can be dynamically studied at various stages during defecation.

The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the gut in others. The adult human rectum is about 12 centimetres (4.7 in) long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction at the level of the third sacral vertebra or the sacral promontory depending upon what definition is used. Its diameter is similar to that of the sigmoid colon at its commencement, but it is dilated near its termination, forming the rectal ampulla. It terminates at the level of the anorectal ring or the dentate line, again depending upon which definition is used. In humans, the rectum is followed by the anal canal which is about 4 centimetres (1.6 in) long, before the gastrointestinal tract terminates at the anal verge. The word rectum comes from the Latin rectumintestinum, meaning straight intestine.
Transanal hemorrhoidal dearterialization (THD) is a minimally invasive surgical procedure for the treatment of internal hemorrhoids.

Friedrich Stelzner was a German academic surgeon, scientist and educator with specialization in gastrointestinal surgery. He served consecutively as Professor and Chairman of three university departments and was inducted as President of the German Society for Surgery in 1985. Stelzner contributed more than 80 books and book chapters to the literature and authored over 450 publications and presentations. Throughout his scientific career, Stelzner investigated questions of functional anatomy and its impact on surgical operative methods.
Anismus or dyssynergic defecation is the failure of normal relaxation of pelvic floor muscles during attempted defecation. It can occur in both children and adults, and in both men and women. It can be caused by physical defects or it can occur for other reasons or unknown reasons. Anismus that has a behavioral cause could be viewed as having similarities with parcopresis, or psychogenic fecal retention.

The vaginal support structures are those muscles, bones, ligaments, tendons, membranes and fascia, of the pelvic floor that maintain the position of the vagina within the pelvic cavity and allow the normal functioning of the vagina and other reproductive structures in the female. Defects or injuries to these support structures in the pelvic floor leads to pelvic organ prolapse. Anatomical and congenital variations of vaginal support structures can predispose a woman to further dysfunction and prolapse later in life. The urethra is part of the anterior wall of the vagina and damage to the support structures there can lead to incontinence and urinary retention.
References
- ↑ Longo, Walter; Northover, John (2003-07-17). Reoperative Colon and Rectal Surgery. pp. 36–37. ISBN 978-1-84184-183-0.
- ↑ García-Armengol, J.; García-Botello, S.; Martinez-Soriano, F.; Roig, J. V.; Lledó, S. (2008). "Review of the anatomic concepts in relation to the retrorectal space and endopelvic fascia: Waldeyer's fascia and the rectosacral fascia". Colorectal Disease. 10 (3): 298–302. doi:10.1111/j.1463-1318.2007.01472.x. PMID 18257849. S2CID 25385980.
- ↑ Santoro, Giulio Aniello; Falco, Giuseppe Di (2006-03-13). Benign Anorectal Diseases: Diagnosis with Endoanal and Endorectal Ultrasound and New Treatment Options. pp. 71–72. ISBN 978-88-470-0336-1.
- ↑ Heald, R. J. (2018). "The 'Holy Plane' of Rectal Surgery". Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine. 81 (9): 503–508. doi: 10.1177/014107688808100904 . PMC 1291757 . PMID 3184105.
- ↑ García-Armengol, J.; García-Botello, S.; Martinez-Soriano, F.; Roig, J. V.; Lledó, S. (March 2008). "Review of the anatomic concepts in relation to the retrorectal space and endopelvic fascia: Waldeyer's fascia and the rectosacral fascia". Colorectal Disease. 10 (3): 298–302. doi:10.1111/j.1463-1318.2007.01472.x. ISSN 1463-1318. PMID 18257849. S2CID 25385980.
- ↑ Jin, Zhi-ming; Peng, Jia-Yuan; Zhu, Qing-Chao; Yin, Lu (2011-10-11). "Waldeyer's fascia: anatomical location and relationship to neighboring fasciae in retrorectal space". Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy. 33 (10): 851–854. doi:10.1007/s00276-011-0887-6. ISSN 0930-1038. PMID 21986989. S2CID 4959248.
- ↑ MacFarlane, J.K.; Ryall, R.D.H.; Heald, R.J. (1993). "Mesorectal excision for rectal cancer". The Lancet. 341 (8843): 457–460. doi:10.1016/0140-6736(93)90207-w. PMID 8094488. S2CID 29476773.
- ↑ De Calan, L.; Gayet, B.; Bourlier, P.; Perniceni, T. (2004). "Cancer du rectum : Anatomie chirurgicale, préparation à l'intervention, installation du patient". Emc - Chirurgie. 1 (3): 275–292. doi:10.1016/j.emcchi.2004.03.002.