
A pipeline is a system of pipes for long-distance transportation of a liquid or gas, typically to a market area for consumption. The latest data from 2014 gives a total of slightly less than 2,175,000 miles (3,500,000 km) of pipeline in 120 countries around the world. The United States had 65%, Russia had 8%, and Canada had 3%, thus 76% of all pipeline were in these three countries.

A sanitary sewer is an underground pipe or tunnel system for transporting sewage from houses and commercial buildings to a sewage treatment plant or disposal. Sanitary sewers are a type of gravity sewer and are part of an overall system called a "sewage system" or sewerage. Sanitary sewers serving industrial areas may also carry industrial wastewater. In municipalities served by sanitary sewers, separate storm drains may convey surface runoff directly to surface waters. An advantage of sanitary sewer systems is that they avoid combined sewer overflows. Sanitary sewers are typically much smaller in diameter than combined sewers which also transport urban runoff. Backups of raw sewage can occur if excessive stormwater inflow or groundwater infiltration occurs due to leaking joints, defective pipes etc. in aging infrastructure.

An inspection is, most generally, an organized examination or formal evaluation exercise. In engineering activities inspection involves the measurements, tests, and gauges applied to certain characteristics in regard to an object or activity. The results are usually compared to specified requirements and standards for determining whether the item or activity is in line with these targets, often with a Standard Inspection Procedure in place to ensure consistent checking. Inspections are usually non-destructive.

Within industry, piping is a system of pipes used to convey fluids from one location to another. The engineering discipline of piping design studies the efficient transport of fluid.
Trenchless technology is a type of subsurface construction work that requires few trenches or no continuous trenches. It is a rapidly growing sector of the construction and civil engineering industry. It can be defined as "a family of methods, materials, and equipment capable of being used for the installation of new or replacement or rehabilitation of existing underground infrastructure with minimal disruption to surface traffic, business, and other activities."

In pipeline transportation, pigging is the practice of using pipeline inspection gauges or gadgets, devices generally referred to as pigs or scrapers, to perform various maintenance operations. This is done without stopping the flow of the product in the pipeline.
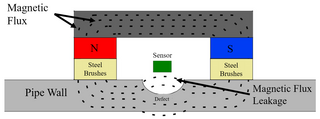
Magnetic flux leakage is a magnetic method of nondestructive testing that is used to detect corrosion and pitting in steel structures, most commonly pipelines and storage tanks. The basic principle is that a powerful magnet is used to magnetize the steel. At areas where there is corrosion or missing metal, the magnetic field "leaks" from the steel. In an MFL tool, a magnetic detector is placed between the poles of the magnet to detect the leakage field. Analysts interpret the chart recording of the leakage field to identify damaged areas and to estimate the depth of metal loss.

Tennessee Gas Pipeline (TGPL) is a set of natural gas pipelines that run from the Texas and Louisiana coast through Arkansas, Mississippi, Alabama, Tennessee, Kentucky, Ohio, and Pennsylvania to deliver natural gas in West Virginia, New Jersey, New York, and New England. The 11,900-mile (19,200 km) long system is operated by the Tennessee Gas Pipeline Company, a subsidiary of Kinder Morgan. It is one of the largest pipeline systems in the United States. Its FERC code is 9. TGP's PHMSA pipeline operator i.d. is 19160.
Dallas Water Utilities (DWU) is the water and wastewater service operated by the City of Dallas, Texas, in the United States. DWU is a non-profit City of Dallas department that provides services to the city and 31 nearby communities, employs approximately 1450 people, and consists of 26 programs. DWU's budget is completely funded through the rates charged for water and wastewater services provided to customers. Rates are based on the cost of providing the services. The department does not receive any tax revenues. Primary authority and rules for the department are listed in Chapter 49 of the Dallas City Code.

A vacuum sewer or pneumatic sewer system is a method of transporting sewage from its source to a sewage treatment plant. It maintains a partial vacuum, with an air pressure below atmospheric pressure inside the pipe network and vacuum station collection vessel. Valves open and reseal automatically when the system is used, so differential pressure can be maintained without expending much energy pumping. A single central vacuum station can collect the wastewater of several thousand individual homes, depending on terrain and the local situation.

The Prudhoe Bay oil spill was an oil spill that was discovered on March 2, 2006 at a pipeline owned by BP Exploration, Alaska (BPXA) in western Prudhoe Bay, Alaska. Initial estimates of the five-day leak said that up to 267,000 US gallons (6,400 bbl) were spilled over 1.9 acres (7,700 m2), making it the largest oil spill on Alaska's north slope to date. Alaska's unified command ratified the volume of crude oil spilled as 212,252 US gallons (5,053.6 bbl) in March 2008. The spill originated from a 0.25-inch (0.64 cm) hole in a 34-inch (86 cm) diameter pipeline. The pipeline was decommissioned and later replaced with a 20-inch (51 cm) diameter pipeline with its own pipeline inspection gauge (pig) launch and recovery sites for easier inspection.

Infrared and thermal testing refer to passive thermographic inspection techniques, a class of nondestructive testing designated by the American Society for Nondestructive Testing (ASNT). Infrared thermography is the science of measuring and mapping surface temperatures.
"Infrared thermography, a nondestructive, remote sensing technique, has proved to be an effective, convenient, and economical method of testing concrete. It can detect internal voids, delaminations, and cracks in concrete structures such as bridge decks, highway pavements, garage floors, parking lot pavements, and building walls. As a testing technique, some of its most important qualities are that (1) it is accurate; (2) it is repeatable; (3) it need not inconvenience the public; and (4) it is economical."
Pipeline leak detection is used to determine if and in some cases where a leak has occurred in systems which contain liquids and gases. Methods of detection include hydrostatic testing, infrared, and laser technology after pipeline erection and leak detection during service.

The Long Lake oil sands upgrader project is an in situ oil extraction project near Anzac, Alberta, 40 km (25 mi) southeast of Fort McMurray in the Athabasca oil sands region of Alberta.
SPX Corporation is a supplier of highly engineered infrastructure equipment and technologies. The company operates within four markets: heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC), detection and measurement, power transmission and generation, and engineered solutions. Examples of SPX’s products include cooling towers and boilers, underground pipe and cable locators, power transformers, and heat exchangers. Brands include Waukesha, Dielectric, Fahrenheat, Radiodetection, and Pearpoint. SPX operates in 17 countries with a sales presence in 100 countries. In 2019, the company earned approximately $1.5 billion in annual revenue. Based in Charlotte, North Carolina, SPX employs over 6,000 employees. Eugene Joseph Lowe is the CEO.
Echologics LLC is a Canadian engineering company based in Toronto that specializes in non-invasive acoustic detection of underground leaks and pipe condition assessment. It has completed projects in North America, Europe, Australia, South Africa, and Singapore that have minimized the loss of millions of gallons of drinking water via leaking infrastructure. Echologics and Mueller Systems are both part of Mueller Water Products' Mueller Technologies reporting segment.
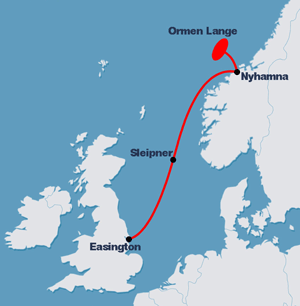
A submarine pipeline is a pipeline that is laid on the seabed or below it inside a trench. In some cases, the pipeline is mostly on-land but in places it crosses water expanses, such as small seas, straits and rivers. Submarine pipelines are used primarily to carry oil or gas, but transportation of water is also important. A distinction is sometimes made between a flowline and a pipeline. The former is an intrafield pipeline, in the sense that it is used to connect subsea wellheads, manifolds and the platform within a particular development field. The latter, sometimes referred to as an export pipeline, is used to bring the resource to shore. Sizeable pipeline construction projects need to take into account many factors, such as the offshore ecology, geohazards and environmental loading – they are often undertaken by multidisciplinary, international teams.
Electro Scan Inc. is a designer and manufacturer of water and sewer machine-intelligent pipeline inspection devices and provider of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) based cloud reporting. The company utilizes electric currents to detect leaks in non-conductive sewer pipes. The company is based in Sacramento, California, with additional offices in London, England and Toronto, Canada.
Water supply and sanitation in the Wellington region involves the provision of the "three waters" – drinking water, stormwater, and wastewater services in the Greater Wellington region.











