A jet engine is a type of reaction engine, discharging a fast-moving jet of heated gas that generates thrust by jet propulsion. While this broad definition may include rocket, water jet, and hybrid propulsion, the term jet engine typically refers to an internal combustion air-breathing jet engine such as a turbojet, turbofan, ramjet, pulse jet, or scramjet. In general, jet engines are internal combustion engines.

A steam turbine is a machine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work on a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Charles Parsons in 1884. Fabrication of a modern steam turbine involves advanced metalwork to form high-grade steel alloys into precision parts using technologies that first became available in the 20th century; continued advances in durability and efficiency of steam turbines remains central to the energy economics of the 21st century.

A turbine is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced can be used for generating electrical power when combined with a generator. A turbine is a turbomachine with at least one moving part called a rotor assembly, which is a shaft or drum with blades attached. Moving fluid acts on the blades so that they move and impart rotational energy to the rotor. Early turbine examples are windmills and waterwheels.

The Tesla turbine is a bladeless centripetal flow turbine invented by Nikola Tesla in 1913. It functions as nozzles apply a moving fluid to the edges of a set of discs. The engine uses smooth discs rotating in a chamber to generate rotational movement due to the momentum exchange between the fluid and the discs. The discs are arranged in an orientation similar to a stack of CDs on an axle.

A water turbine is a rotary machine that converts kinetic energy and potential energy of water into mechanical work.

A turbofan or fanjet is a type of airbreathing jet engine that is widely used in aircraft propulsion. The word "turbofan" is a combination of the preceding generation engine technology of the turbojet, and a reference to the additional fan stage added. It consists of a gas turbine engine which achieves mechanical energy from combustion, and a ducted fan that uses the mechanical energy from the gas turbine to force air rearwards. Thus, whereas all the air taken in by a turbojet passes through the combustion chamber and turbines, in a turbofan some of that air bypasses these components. A turbofan thus can be thought of as a turbojet being used to drive a ducted fan, with both of these contributing to the thrust.

The turbojet is an airbreathing jet engine which is typically used in aircraft. It consists of a gas turbine with a propelling nozzle. The gas turbine has an air inlet which includes inlet guide vanes, a compressor, a combustion chamber, and a turbine. The compressed air from the compressor is heated by burning fuel in the combustion chamber and then allowed to expand through the turbine. The turbine exhaust is then expanded in the propelling nozzle where it is accelerated to high speed to provide thrust. Two engineers, Frank Whittle in the United Kingdom and Hans von Ohain in Germany, developed the concept independently into practical engines during the late 1930s.

A de Laval nozzle is a tube which is pinched in the middle, making a carefully balanced, asymmetric hourglass shape. It is used to accelerate a compressible fluid to supersonic speeds in the axial (thrust) direction, by converting the thermal energy of the flow into kinetic energy. De Laval nozzles are widely used in some types of steam turbines and rocket engine nozzles. It also sees use in supersonic jet engines.

The Rolls-Royce RB.80 Conway was the first turbofan jet engine to enter service. Development started at Rolls-Royce in the 1940s, but the design was used only briefly, in the late 1950s and early 1960s, before other turbofan designs replaced it. The Conway engine was used on versions of the Handley Page Victor, Vickers VC10, Boeing 707-420 and Douglas DC-8-40.

Turbomachinery, in mechanical engineering, describes machines that transfer energy between a rotor and a fluid, including both turbines and compressors. While a turbine transfers energy from a fluid to a rotor, a compressor transfers energy from a rotor to a fluid. It is an important application of fluid mechanics.
A jet engine performs by converting fuel into thrust. How well it performs is an indication of what proportion of its fuel goes to waste. It transfers heat from burning fuel to air passing through the engine. In doing so it produces thrust work when propelling a vehicle but a lot of the fuel is wasted and only appears as heat. Propulsion engineers aim to minimize the degradation of fuel energy into unusable thermal energy. Increased emphasis on performance improvements for commercial airliners came in the 1970s from the rising cost of fuel.

A radial turbine is a turbine in which the flow of the working fluid is radial to the shaft. The difference between axial and radial turbines consists in the way the fluid flows through the components. Whereas for an axial turbine the rotor is 'impacted' by the fluid flow, for a radial turbine, the flow is smoothly orientated perpendicular to the rotation axis, and it drives the turbine in the same way water drives a watermill. The result is less mechanical stress which enables a radial turbine to be simpler, more robust, and more efficient when compared to axial turbines. When it comes to high power ranges the radial turbine is no longer competitive and the efficiency becomes similar to that of the axial turbines.

A turbine blade is a radial aerofoil mounted in the rim of a turbine disc and which produces a tangential force which rotates a turbine rotor. Each turbine disc has many blades. As such they are used in gas turbine engines and steam turbines. The blades are responsible for extracting energy from the high temperature, high pressure gas produced by the combustor. The turbine blades are often the limiting component of gas turbines. To survive in this difficult environment, turbine blades often use exotic materials like superalloys and many different methods of cooling that can be categorized as internal and external cooling, and thermal barrier coatings. Blade fatigue is a major source of failure in steam turbines and gas turbines. Fatigue is caused by the stress induced by vibration and resonance within the operating range of machinery. To protect blades from these high dynamic stresses, friction dampers are used.

This article briefly describes the components and systems found in jet engines.

Heinrich Zoelly (1862–1937) was a Mexican-Swiss engineer. He developed steam turbines and turbine-driven locomotives and patented the geothermal heat pump in 1912.
In turbomachinery, degree of reaction or reaction ratio (R) is defined as the ratio of the static pressure rise in the rotating blades of a compressor (or drop in turbine blades) to the static pressure rise in the compressor stage (or drop in a turbine stage). Alternatively it is the ratio of static enthalpy change in the rotor to the static enthalpy change in the stage.
Because they are heat engines, steam turbines are subject to inefficiencies as they convert thermal energy in high-pressure steam to rotational kinetic energy in a shaft.
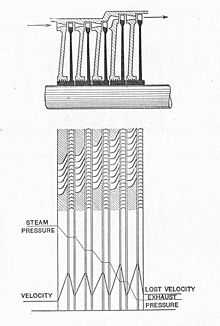
Compounding of steam turbines is a method of extracting steam energy in multiple stages rather than in a single stage in a steam turbine. A compounded steam turbine has multiple stages with more than one set of nozzles and rotors. These are arranged in series, either keyed to the common shaft or fixed to the casing. The result of this arrangement allows either the steam pressure or the jet velocity to be absorbed by the turbine in a number of stages.

A compound engine is an engine that has more than one stage for recovering energy from the same working fluid, with the exhaust from the first stage passing through the second stage, and in some cases then on to another subsequent stage or even stages. Originally invented as a means of making steam engines more efficient, the compounding of engines by use of several stages has also been used on internal combustion engines and continues to have niche markets there.
An axial turbine is a turbine in which the flow of the working fluid is parallel to the shaft, as opposed to radial turbines, where the fluid runs around a shaft, as in a watermill. An axial turbine has a similar construction as an axial compressor, but it operates in the reverse, converting flow of the fluid into rotating mechanical energy.