
Urology, also known as genitourinary surgery, is the branch of medicine that focuses on surgical and medical diseases of the urinary system and the reproductive organs. Organs under the domain of urology include the kidneys, adrenal glands, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra, and the male reproductive organs.
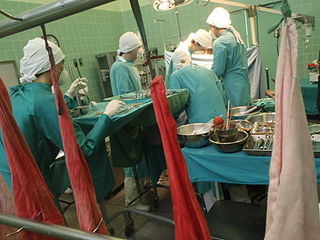
Organ transplantation is a medical procedure in which an organ is removed from one body and placed in the body of a recipient, to replace a damaged or missing organ. The donor and recipient may be at the same location, or organs may be transported from a donor site to another location. Organs and/or tissues that are transplanted within the same person's body are called autografts. Transplants that are recently performed between two subjects of the same species are called allografts. Allografts can either be from a living or cadaveric source.

A urethral stricture is a narrowing of the urethra, the tube connected to the bladder that allows urination. The narrowing reduces the flow of urine and makes it more difficult or even painful to empty the bladder.
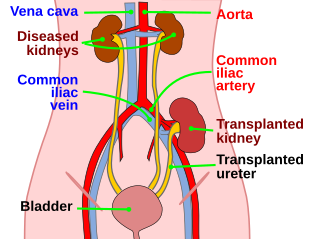
Kidney transplant or renal transplant is the organ transplant of a kidney into a patient with end-stage kidney disease (ESRD). Kidney transplant is typically classified as deceased-donor or living-donor transplantation depending on the source of the donor organ. Living-donor kidney transplants are further characterized as genetically related (living-related) or non-related (living-unrelated) transplants, depending on whether a biological relationship exists between the donor and recipient. The first successful kidney transplant was performed in 1954 by a team including Joseph Murray, the recipient's surgeon, and Hartwell Harrison, surgeon for the donor. Murray was awarded a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1990 for this and other work. In 2018, an estimated 95,479 kidney transplants were performed worldwide, 36% of which came from living donors.

Mahendra Bhandari is an Indian surgeon who has made substantial contributions to the specialty of urology, medical training, hospital administration, robotic surgery and medical ethics. For his efforts, he was awarded the Padma Shri by the government of India in 2000. Bhandari is currently Senior Bio-scientist and Director of Robotic Surgery Research & Education at the Vattikuti Urology Institute (VUI) in Detroit, MI. He was the Symposium coordinator of the International Robotic Urology Symposium. He also has been the CEO of the Vattikuti Foundation since 2010.

Mani Menon, born 9 July 1948 in Trichur, India, is an American surgeon whose work has helped to lay the foundation for modern Robotic Cancer Surgery. He is the founding director and the Raj and Padma Vattikuti Distinguished Chair of the Vattikuti Urology Institute at the Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit, MI, where he established the first cancer-oriented robotics program in the world. Menon is widely regarded for his role in the development of robotic surgery techniques for the treatment of patients with prostate, kidney, and bladder cancers, as well as for the development of robotic kidney transplantation.
R.V.S. Yadav was born on 27 July 1937 in Nauliharnathpur, Uttar Pradesh, India. He was awarded the MBBS in 1961 and the MS (Surgery) in 1964 respectively from the King George's Medical College, Lucknow University, Lucknow. He received the FICS in 1974 from the International College of Surgeons and the FACS in 1977 from the American College of Surgeons.

Dr. Michael A. Palese, is an American urologist specializing in robotic, laparoscopic and endoscopic surgery, with a special emphasis on robotic surgeries relating to kidney cancer and kidney stone disease.
Mahesh Desai is an Indian urologist who treats various kidney and urological diseases in India. He performs renal transplants in Gujarat, India.

Sunil Shroff is the managing trustee of a non-government and non-profit organisation called MOHAN Foundation and is well known for his work in the field of deceased donation transplantation in India. He has worked towards improving the deceased organ donation rate in India.

Prokar Dasgupta is an Indian-born British surgeon and academic who is professor of surgery at the surgical academy at King's Health Partners, London, UK. Since 2002, he has been consultant urologist to Guy's Hospital, and in 2009 became the first professor of robotic surgery and urology at King's, and subsequently the chairman of the King's College-Vattikuti Institute of Robotic Surgery.
Sarbeswar Sahariah is an Indian nephrologist and organ transplant specialist, known for his expertise in renal and pancreatic transplantation. He was honoured by the Government of India, in 2014, by bestowing on him the Padma Shri, the fourth highest civilian award, for his contributions to the field of medicine. Sahariah is credited with more than 3000 renal transplantations, which many consider, has made him the most prolific kidney transplant surgeon in the country.
André van der Merwe is a South African urologist. He is currently head of urology at the University of Stellenbosch and an associate professor at Tygerberg Hospital. He is best known for conducting the world's first successful penis transplant in 2014. He also performed the first laparoscopic kidney removal in South Africa.
Kidney paired donation (KPD), or paired exchange, is an approach to living donor kidney transplantation where patients with incompatible donors swap kidneys to receive a compatible kidney. KPD is used in situations where a potential donor is incompatible. Because better donor HLA and age matching are correlated with lower lifetime mortality and longer lasting kidney transplants, many compatible pairs are also participating in swaps to find better matched kidneys. In the United States, the National Kidney Registry organizes the majority of U.S. KPD transplants, including the largest swaps. The first large swap was a 60 participant chain in 2012 that appeared on the front page of the New York Times and the second, even larger swap, included 70 participants and was completed in 2014. Other KPD programs in the U.S. include the UNOS program, which was launched in 2010 and completed its 100th KPD transplant in 2014, and the Alliance for Paired Donation.

Benjamin James Challacombe is a British consultant urological surgeon at Guy's & St Thomas' Hospitals, and at King’s College London, who specialises in the treatment of kidney and prostatic disease using robotic surgery. In 2005, he was part of the team that published the results of a randomised controlled trial of human versus telerobotics in the field of urology and renal transplant, one of the first of its kind.
Inderbir Singh Gill is a professor of urology and robotic surgeon who is one of the pioneers of minimally invasive surgery. He currently resides in Los Angeles, California. In 2017, he led the team that performed Mumbai’s first robotic kidney transplantation.

The Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences (KIMS) is an Indian hospital chain based in Telangana. It was founded by Dr. Bhaskar Rao Bollineni in 2000 in the city of Nellore. Currently, the KIMS Group operates 12 hospitals across the states of Andhra Pradesh, Telangana and Maharashtra. The KIMS Hospital Group is certified by NABH and NABL. It is listed on BSE and the NSE.
Organ transplantation in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu is regulated by India's Transplantation of Human Organs Act, 1994 and is facilitated by the Transplant Authority of Tamil Nadu (TRANSTAN) of the Government of Tamil Nadu and several NGOs. Tamil Nadu ranks first in India in deceased organ donation rate at 1.8 per million population, which is seven times higher than the national average.
Organ donation in India is regulated by the Transplantation of Human Organs and Tissues Act, 1994. The law allows both deceased and living donors to donate their organs. It also identifies brain death as a form of death. The National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (NOTTO) functions as the apex body for activities relating to procurement, allotment and distribution of organs in the country.
Mukut Minz is an Indian doctor. In 2017, he was awarded the Padma Shri by the Indian Government for his contribution in medicine.











