
Fenrir or Fenrisúlfr, also referred to as Hróðvitnir and Vánagandr, is a monstrous wolf in Norse mythology. In Old Norse texts, Fenrir plays a key role during the events of Ragnarök, where he is foretold to assist in setting the world aflame, resulting in the collapse of humanity and society, and killing the god Odin.

Frigg is a goddess, one of the Æsir, in Germanic mythology. In Norse mythology, the source of most surviving information about her, she is associated with marriage, prophecy, clairvoyance and motherhood, and dwells in the wetland halls of Fensalir. In wider Germanic mythology, she is known in Old High German as Frīja, in Langobardic as Frēa, in Old English as Frīg, in Old Frisian as Frīa, and in Old Saxon as Frī, all ultimately stemming from the Proto-Germanic theonym *Frijjō. Nearly all sources portray her as the wife of the god Odin.

Skíðblaðnir, sometimes anglicized as Skidbladnir or Skithblathnir, is the best of ships in Norse mythology. It is attested in the Poetic Edda, compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources, and in the Prose Edda and Heimskringla, both written in the 13th century by Snorri Sturluson. All sources note that the ship is the finest of ships, and the Poetic Edda and Prose Edda attest that it is owned by the god Freyr, while the euhemerized account in Heimskringla attributes it to the magic of Odin. Both Heimskringla and the Prose Edda attribute to it the ability to be folded up—as cloth may be—into one's pocket when not needed.

In Norse mythology, the Vanir are a group of gods associated with fertility, wisdom, and the ability to see the future. The Vanir are one of two groups of gods and are the namesake of the location Vanaheimr. After the Æsir–Vanir War, the Vanir became a subgroup of the Æsir. Subsequently, members of the Vanir are sometimes also referred to as members of the Æsir.

In Norse mythology, Sif is a golden-haired goddess associated with earth. Sif is attested in the Poetic Edda, compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources, and the Prose Edda, written in the 13th century by Snorri Sturluson, and in the poetry of skalds. In both the Poetic Edda and the Prose Edda, she is known for her golden hair and is married to the thunder god Thor.

Mímir or Mim is a figure in Norse mythology, renowned for his knowledge and wisdom, who is beheaded during the Æsir–Vanir War. Afterward, the god Odin carries around Mímir's head and it recites secret knowledge and counsel to him.

In Norse mythology, Gerðr is a jötunn, goddess, and the wife of the god Freyr. Gerðr is attested in the Poetic Edda, compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources; the Prose Edda and Heimskringla, written in the 13th century by Snorri Sturluson; and in the poetry of skalds. Gerðr is sometimes modernly anglicized as Gerd or Gerth.

Sceafa was an ancient Lombardic king in English legend. According to his story, Sceafa appeared mysteriously as a child, coming out of the sea in an empty skiff. The name also appears in the corrupt forms Seskef, Stefius, Strephius, and Stresaeus. Though the name has historically been modernized Shava, J.R.R. Tolkien used the correctly constructed modern English spelling Sheave.

Old Norse Yngvi, Old High German Ing/Ingwi and Old English Ing are names that relate to a theonym which appears to have been the older name for the god Freyr. Proto-Germanic Ingwaz was the legendary ancestor of the Ingaevones, or more accurately Ingvaeones, and is also the reconstructed name of the Elder Futhark rune ᛜ and Anglo-Saxon rune ᛝ, representing ŋ.

The Ynglings were a dynasty of kings, first in Sweden and later in Norway, primarily attested through the poem Ynglingatal. The dynasty also appears as Scylfings in Beowulf. When Beowulf and Ynglingatal were composed sometime in the eighth to tenth centuries, their respective authors expected their audience to have a great deal of background information about these kings, which is shown in the allusiveness of the references.
Various gods and men appear as sons of Odin in Old Norse and Old English texts.
In Norse mythology, Þrúðvangr is a field where the god Thor resides. The field is attested in the Prose Edda and in Heimskringla, both written by Snorri Sturluson in the 13th century.
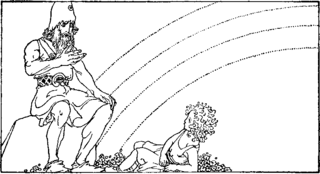
In Norse mythology, Himinbjörg is the home of the god Heimdallr. Himinbjörg is attested in the Poetic Edda, compiled from earlier traditional sources, and the Prose Edda and Heimskringla, both written in the 13th century by Snorri Sturluson. Himinbjörg is associated with Heimdallr in all sources. According to the Poetic Edda, Heimdallr dwells there as watchman for the gods and there drinks fine mead, whereas in the Prose Edda Himinbjörg is detailed as located where the burning rainbow bridge Bifröst meets heaven. Scholars have commented on the differences between the two attestations and linked the name of the mythical location to various place names.
Sæmingr was a king of Norway according to Snorri Sturluson's euhemerized accounts or Hålogaland. He was said to be the son of Odin.

Hár, Jafnhár, and Þriði are three men on thrones who appear in the Prose Edda in the Gylfaginning, one of the oldest and most important sources on Norse mythology. Their names translate as High, Just-as-High, and Third in Old Norse, respectively. In the story, King Gylfi, calling himself Gangleri, engages in a test of wisdom with the three, asking them detailed questions about the Æsir, their deeds, and their future. The three respond until the final segment, in which the three men and the great hall suddenly disappear.

Skáldskaparmál is the second part of the Prose Edda, compiled by Snorri Sturluson. It consists of a dialogue between Ægir, the divine personification of the sea, and Bragi, the god of poetry, in which both stories of the Æsir and discourse on the nature of poetry are intertwined. The work additionally includes tales of human heroes and kings. The overarching mythological setup gradually fades and the work becomes more of an early form of a poetic thesaurus of Old Norse, presumably intended for usage by skalds. Much of the work is focused on poetic phrases and descriptors. The origin of these kennings is given; Bragi delivers a systematic list of kennings for various Æsir, people, places, and things. He then goes on to discuss poetic language in some detail, in particular heiti, essentially poetic synonyms or alternate words. For example, the simple hestr, "horse", might be replaced by jór, "steed".

In Norse mythology, Gefjon is a goddess associated with ploughing, the Danish island of Zealand, the legendary Swedish king Gylfi, the legendary Danish king Skjöldr, foreknowledge, her oxen children, and virginity. Gefjon is attested in the Poetic Edda, compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources; the Prose Edda and Heimskringla, written in the 13th century by Snorri Sturluson; in the works of skalds; and appears as a gloss for various Greco-Roman goddesses in some Old Norse translations of Latin works.
A number of royal genealogies of the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, collectively referred to as the Anglo-Saxon royal genealogies, have been preserved in a manuscript tradition based in the 8th to 10th centuries.
Langfeðgatal is an anonymous, twelfth-century Icelandic genealogy of Scandinavian kings.
These are family trees of the Norse gods showing kin relations among gods and other beings in Nordic mythology. Each family tree gives an example of relations according to principally Eddic material however precise links vary between sources. In addition, some beings are identified by some sources and scholars.













