
A propeller is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon a working fluid such as water or air. Propellers are used to pump fluid through a pipe or duct, or to create thrust to propel a boat through water or an aircraft through air. The blades are shaped so that their rotational motion through the fluid causes a pressure difference between the two surfaces of the blade by Bernoulli's principle which exerts force on the fluid. Most marine propellers are screw propellers with helical blades rotating on a propeller shaft with an approximately horizontal axis.

The turbojet is an airbreathing jet engine which is typically used in aircraft. It consists of a gas turbine with a propelling nozzle. The gas turbine has an air inlet which includes inlet guide vanes, a compressor, a combustion chamber, and a turbine. The compressed air from the compressor is heated by burning fuel in the combustion chamber and then allowed to expand through the turbine. The turbine exhaust is then expanded in the propelling nozzle where it is accelerated to high speed to provide thrust. Two engineers, Frank Whittle in the United Kingdom and Hans von Ohain in Germany, developed the concept independently into practical engines during the late 1930s.

A magnetohydrodynamic drive or MHD accelerator is a method for propelling vehicles using only electric and magnetic fields with no moving parts, accelerating an electrically conductive propellant with magnetohydrodynamics. The fluid is directed to the rear and as a reaction, the vehicle accelerates forward.
A tugboat or tug is a marine vessel that manoeuvres other vessels by pushing or pulling them, with direct contact or a tow line. These boats typically tug ships in circumstances where they cannot or should not move under their own power, such as in crowded harbors or narrow canals, or cannot move at all, such as barges, disabled ships, log rafts, or oil platforms. Some are ocean-going, and some are icebreakers or salvage tugs. Early models were powered by steam engines, which were later superseded by diesel engines. Many have deluge gun water jets, which help in firefighting, especially in harbours.

A pump-jet, hydrojet, or water jet is a marine system that produces a jet of water for propulsion. The mechanical arrangement may be a ducted propeller, a centrifugal pump, or a mixed flow pump which is a combination of both centrifugal and axial designs. The design also incorporates an intake to provide water to the pump and a nozzle to direct the flow of water out of the pump.

An azimuth thruster is a configuration of marine propellers placed in pods that can be rotated to any horizontal angle (azimuth), making a rudder redundant. These give ships better maneuverability than a fixed propeller and rudder system.

The Voith Schneider Propeller (VSP) is a specialized marine propulsion system (MPS) manufactured by the Voith Group based on a cyclorotor design. It is highly maneuverable, being able to change the direction of its thrust almost instantaneously. It is widely used on tugs and ferries.

A Z-drive is a type of marine propulsion unit. Specifically, it is an azimuth thruster. The pod can rotate 360 degrees allowing for rapid changes in thrust direction and thus vessel direction. This eliminates the need for a conventional rudder.

An impeller or impellor is a driven rotor used to increase the pressure and flow of a fluid. It is the opposite of a turbine, which extracts energy from, and reduces the pressure of, a flowing fluid.

Turbomachinery, in mechanical engineering, describes machines that transfer energy between a rotor and a fluid, including both turbines and compressors. While a turbine transfers energy from a fluid to a rotor, a compressor transfers energy from a rotor to a fluid.

Astern propulsion is a maneuver in which a ship's propelling mechanism is used to develop thrust in a retrograde direction. Astern propulsion does not necessarily imply the ship is moving astern ; astern propulsion is used to slow a ship by applying a force in the direction of the bow of the ship, instead of the stern. The equivalent concept for an airplane is thrust reversal.

The Kitchen rudder is the familiar name for "Kitchen's Patent Reversing Rudders", a combination rudder and directional propulsion delivery system for relatively slow speed displacement boats which was invented in the early 20th century by John G. A. Kitchen of Lancashire, England. It turns the rudder into a directional thruster, and allows the engine to maintain constant revolutions and direction of drive shaft rotation while altering thrust by use of a control which directs thrust forward or aft. Only the rudder pivots; the propeller itself is on a fixed shaft and does not.
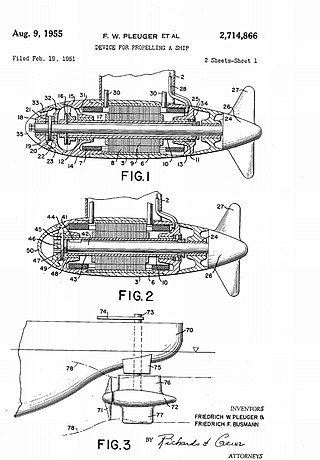
The Pleuger rudder is a power assisted ship's rudder. It creates a flow of water in the direction the rudder points powered by an auxiliary electric motor. This aids maneuverability at low speeds greatly, since it operates on a similar principle to a thruster.

Marine propulsion is the mechanism or system used to generate thrust to move a watercraft through water. While paddles and sails are still used on some smaller boats, most modern ships are propelled by mechanical systems consisting of an electric motor or internal combustion engine driving a propeller, or less frequently, in pump-jets, an impeller. Marine engineering is the discipline concerned with the engineering design process of marine propulsion systems.

A Schilling rudder is a specific type of profiled rudder used on certain boats and ships. The rudder is typically described as 'shaped like a fishtail'.

A ducted propeller, also known as a Kort nozzle, is a marine propeller fitted with a non-rotating nozzle. It is used to improve the efficiency of the propeller and is especially used on heavily loaded propellers or propellers with limited diameter. It was developed first by Luigi Stipa (1931) and later by Ludwig Kort (1934). The Kort nozzle is a shrouded propeller assembly for marine propulsion. The cross-section of the shroud has the form of a foil, and the shroud can offer hydrodynamic advantages over bare propellers, under certain conditions.

The rim-driven thruster, also known as rim-driven propulsor/propeller is a novel type of electric propulsion unit for ships. The concept was proposed by Kort around 1940, but only became commercially practical in the early 21st century due to advances in DC motor controller technology. As of 2017, commercial models of between 500 kW and 3 MW are available from manufacturers such as Rolls-Royce, Schottel, Brunvoll, Voith, Van der Velden, etc.
Schottel is a manufacturer of propulsion and steering systems for ships and offshore applications. The company founder Josef Becker invented the rudderpropeller, a z-drive, in 1950. Today the company develops and manufactures azimuth propulsion, maneuvering and steering systems. In 2014 the subsidiary Schottel Hydro was founded to bundle up the company activities in the hydrokinetic energy segment.

A cyclorotor, cycloidal rotor, cycloidal propeller or cyclogiro, is a fluid propulsion device that converts shaft power into the acceleration of a fluid using a rotating axis perpendicular to the direction of fluid motion. It uses several blades with a spanwise axis parallel to the axis of rotation and perpendicular to the direction of fluid motion. These blades are cyclically pitched twice per revolution to produce force in any direction normal to the axis of rotation. Cyclorotors are used for propulsion, lift, and control on air and water vehicles. An aircraft using cyclorotors as the primary source of lift, propulsion, and control is known as a cyclogyro or cyclocopter. A unique aspect is that it can change the magnitude and direction of thrust without the need of tilting any aircraft structures. The patented application, used on ships with particular actuation mechanisms both mechanical or hydraulic, is named after German company Voith Turbo.

A marine thruster is a device for producing directed hydrodynamic thrust mounted on a marine vehicle, primarily for maneuvering or propulsion. There are a variety of different types of marine thrusters and each of them plays a role in the maritime industry. Marine thrusters come in many different shapes and sizes, for example screw propellers, Voith-Schneider propellers, waterjets, ducted propellers, tunnel bow thrusters, and stern thrusters, azimuth thrusters, rim-driven thrusters, ROV and submersible drive units. A marine thruster consists of a propeller or impeller which may be encased in some kind of tunnel or ducting that directs the flow of water to produce a resultant force intended to obtain movement in the desired direction or resist forces which would cause unwanted movement. The two subcategories of marine thrusters are for propulsion and maneuvering, the maneuvering thruster typically in the form of bow or stern thrusters and propulsion thrusters ranging from Azimuth thrusters to Rim Drive thrusters.




















