Dieting is the practice of eating food in a regulated way to decrease, maintain, or increase body weight, or to prevent and treat diseases such as diabetes and obesity. As weight loss depends on calorie intake, different kinds of calorie-reduced diets, such as those emphasising particular macronutrients, have been shown to be no more effective than one another. As weight regain is common, diet success is best predicted by long-term adherence. Regardless, the outcome of a diet can vary widely depending on the individual.

In nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.

Nutrition is the biochemical and physiological process by which an organism uses food to support its life. It provides organisms with nutrients, which can be metabolized to create energy and chemical structures. Failure to obtain the required amount of nutrients causes malnutrition. Nutritional science is the study of nutrition, though it typically emphasizes human nutrition.
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excreted by cells to create non-cellular structures such as hair, scales, feathers, or exoskeletons. Some nutrients can be metabolically converted into smaller molecules in the process of releasing energy such as for carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and fermentation products leading to end-products of water and carbon dioxide. All organisms require water. Essential nutrients for animals are the energy sources, some of the amino acids that are combined to create proteins, a subset of fatty acids, vitamins and certain minerals. Plants require more diverse minerals absorbed through roots, plus carbon dioxide and oxygen absorbed through leaves. Fungi live on dead or living organic matter and meet nutrient needs from their host.

Human nutrition deals with the provision of essential nutrients in food that are necessary to support human life and good health. Poor nutrition is a chronic problem often linked to poverty, food security, or a poor understanding of nutritional requirements. Malnutrition and its consequences are large contributors to deaths, physical deformities, and disabilities worldwide. Good nutrition is necessary for children to grow physically and mentally, and for normal human biological development.
Food energy is chemical energy that animals derive from their food to sustain their metabolism, including their muscular activity.

Starvation is a severe deficiency in caloric energy intake, below the level needed to maintain an organism's life. It is the most extreme form of malnutrition. In humans, prolonged starvation can cause permanent organ damage and eventually, death. The term inanition refers to the symptoms and effects of starvation. Starvation by outside forces is a crime according to international criminal law and may also be used as a means of torture or execution.

Low-carbohydrate diets restrict carbohydrate consumption relative to the average diet. Foods high in carbohydrates are limited, and replaced with foods containing a higher percentage of fat and protein, as well as low carbohydrate foods.

Cat food is food specifically formulated and designed for consumption by cats. As obligate carnivores, cats have specific requirements for their dietary nutrients, namely nutrients found only in meat or synthesized, such as taurine and Vitamin A. Certain nutrients, including many vitamins and amino acids, are degraded by the temperatures, pressures and chemical treatments used during manufacture, and hence must be added after manufacture to avoid nutritional deficiency. Cat food is typically sold as dry kibble, or as wet food in cans and pouches.
Calorie restriction is a dietary regimen that reduces the energy intake from foods and beverages without incurring malnutrition. The possible effect of calorie restriction on body weight management, longevity, and aging-associated diseases has been an active area of research.

A healthy diet is a diet that maintains or improves overall health. A healthy diet provides the body with essential nutrition: fluid, macronutrients such as protein, micronutrients such as vitamins, and adequate fibre and food energy.
Specific dynamic action (SDA), also known as thermic effect of food (TEF) or dietary induced thermogenesis (DIT), is the amount of energy expenditure above the basal metabolic rate due to the cost of processing food for use and storage. Heat production by brown adipose tissue which is activated after consumption of a meal is an additional component of dietary induced thermogenesis. The thermic effect of food is one of the components of metabolism along with resting metabolic rate and the exercise component. A commonly used estimate of the thermic effect of food is about 10% of one's caloric intake, though the effect varies substantially for different food components. For example, dietary fat is very easy to process and has very little thermic effect, while protein is hard to process and has a much larger thermic effect.

Sports nutrition is the study and practice of nutrition and diet with regards to improving anyone's athletic performance. Nutrition is an important part of many sports training regimens, being popular in strength sports and endurance sports. Sports nutrition focuses its studies on the type, as well as the quantity of fluids and food taken by an athlete. In addition, it deals with the consumption of nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, supplements and organic substances that include carbohydrates, proteins and fats.

A very-low-calorie diet (VLCD), also known as semistarvation diet and crash diet, is a type of diet with very or extremely low daily food energy consumption. VLCDs are defined as a diet of 800 kilocalories (3,300 kJ) per day or less. Modern medically supervised VLCDs use total meal replacements, with regulated formulations in Europe and Canada which contain the recommended daily requirements for vitamins, minerals, trace elements, fatty acids, protein and electrolyte balance. Carbohydrates may be entirely absent, or substituted for a portion of the protein; this choice has important metabolic effects. Medically supervised VLCDs have specific therapeutic applications for rapid weight loss, such as in morbid obesity or before a bariatric surgery, using formulated, nutritionally complete liquid meals containing 800 kilocalories or less per day for a maximum of 12 weeks.
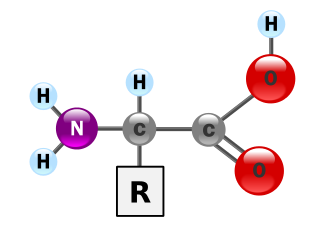
Proteins are essential nutrients for the human body. They are one of the building blocks of body tissue and can also serve as a fuel source. As a fuel, proteins provide as much energy density as carbohydrates: 4 kcal per gram; in contrast, lipids provide 9 kcal per gram. The most important aspect and defining characteristic of protein from a nutritional standpoint is its amino acid composition.

A low-fat diet is one that restricts fat, and often saturated fat and cholesterol as well. Low-fat diets are intended to reduce the occurrence of conditions such as heart disease and obesity. For weight loss, they perform similarly to a low-carbohydrate diet, since macronutrient composition does not determine weight loss success. Fat provides nine calories per gram while carbohydrates and protein each provide four calories per gram. The Institute of Medicine recommends limiting fat intake to 35% of total calories to control saturated fat intake.

The Western pattern diet is a modern dietary pattern that is generally characterized by high intakes of pre-packaged foods, refined grains, red meat, processed meat, high-sugar drinks, candy and sweets, fried foods, industrially produced animal products, butter and other high-fat dairy products, eggs, potatoes, corn, and low intakes of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, pasture-raised animal products, fish, nuts, and seeds.
Dietary Reference Values (DRV) is the name of the nutritional requirements systems used by the United Kingdom Department of Health and the European Union's European Food Safety Authority.

Weight management refers to behaviors, techniques, and physiological processes that contribute to a person's ability to attain and maintain a healthy weight. Most weight management techniques encompass long-term lifestyle strategies that promote healthy eating and daily physical activity. Moreover, weight management involves developing meaningful ways to track weight over time and to identify the ideal body weights for different individuals.
High performance sport dogs are those bred and trained to compete in various athletic events. Events include but are not limited to, agility trials, hunting and racing. These events are physically and metabolically demanding. As a result, canine athletes require specialized nutrition in order to perform at high levels during events and for maintenance and recovery. The main nutritional concern for sport dogs is adequate energy. A well-balanced diet, containing the appropriate amounts of protein, fat, carbohydrate, fiber and micronutrients is essential to meet these energy requirements.














