Related Research Articles

Athanasius I of Alexandria, also called Athanasius the Great, Athanasius the Confessor, or, among Coptic Christians, Athanasius the Apostolic, was a Christian theologian and the 20th pope of Alexandria. His intermittent episcopacy spanned 45 years, of which over 17 encompassed five exiles, when he was replaced on the order of four different Roman emperors. Athanasius was a Church Father, the chief proponent of Trinitarianism against Arianism, and a noted Egyptian Christian leader of the fourth century.

Anthony the Great was a Christian monk from Egypt, revered since his death as a saint. He is distinguished from other saints named Anthony, such as Anthony of Padua, by various epithets: Anthony of Egypt, Anthony the Abbot, Anthony of the Desert, Anthony the Anchorite, Anthony the Hermit, and Anthony of Thebes. For his importance among the Desert Fathers and to all later Christian monasticism, he is also known as the Father of All Monks. His feast day is celebrated on 17 January among the Eastern Orthodox and Catholic churches and on Tobi 22 in the Coptic calendar.
Eusebius of Caesarea, also known as Eusebius Pamphilius, was a Greek Syro-Palestinian historian of Christianity, exegete, and Christian polemicist. In about AD 314 he became the bishop of Caesarea Maritima in the Roman province of Syria Palaestina.

Basil of Caesarea, also called Saint Basil the Great, was an early Roman Christian prelate who served as Bishop of Caesarea in Cappadocia from 370 until his death in 378. He was an influential theologian who supported the Nicene Creed and opposed the heresies of the early Christian church, fighting against both Arianism and the followers of Apollinaris of Laodicea.

The Armenian Rite is a liturgical rite used by both the Armenian Apostolic and the Armenian Catholic churches. Isaac of Armenia, the Catholicos of All Armenians, initiated a series of reforms with help from Mesrop Mashtots in the 5th century that distinguished Armenia from its Greek and Syriac counterparts. These reforms included a retranslation of the Bible and a revised liturgy. During the Crusades and afterwards, missionary activity by the Latin Church influenced liturgical norms and induced some Armenians to join the Catholic Church. The modern Armenian Rite features elements and interpolations from the Byzantine Rite and Latin liturgical rites, with the celebration of the Eucharist emulating the Liturgy of Saint Basil.

Basilian monks are Greek Catholic monks who follow the rule of Basil the Great, bishop of Caesarea (330–379). The term 'Basilian' is typically used only in the Catholic Church to distinguish Greek Catholic monks from other forms of monastic life in the Catholic Church. In the Eastern Orthodox Church, as all monks follow the Rule of Saint Basil, they do not distinguish themselves as 'Basilian'.
The Patrologia Graeca is an edited collection of writings by the Church Fathers and various secular writers, in the Greek language. It consists of 161 volumes produced in 1857–1866 by J.P. Migne's Imprimerie Catholique, Paris.
Hypostasis, from the Greek ὑπόστασις (hypóstasis), is the underlying, fundamental state or substance that supports all of reality. It is not the same as the concept of a substance. In Neoplatonism, the hypostasis of the soul, the intellect (nous) and "the one" was addressed by Plotinus. In Christian theology, the Holy Trinity consists of three hypostases: that of the Father, that of the Son, and that of the Holy Spirit.

Seeing Islam As Others Saw It: A Survey and Evaluation of Christian, Jewish and Zoroastrian Writings on Early Islam from the Studies in Late Antiquity and Early Islam series is a book by scholar of the Middle East Robert G. Hoyland.
The Liturgy of Saint Basil or, more formally, the Divine Liturgy of Saint Basil the Great, is a term for several Eastern Christian celebrations of the Divine Liturgy (Eucharist), or at least several anaphoras, which are named after Basil of Caesarea. Two of these liturgies are in common use today: the one used in the Byzantine Rite ten times a year, and the one ordinarily used by the Coptic Church.
Athanasius II Baldoyo, also known as Athanasius of Balad, and Athanasius of Nisibis, was the Patriarch of Antioch and head of the Syriac Orthodox Church from 684 until his death in 687.

De Viris Illustribus is a collection of short biographies of 135 authors, written in Latin, by the 4th-century Latin Church Father Jerome. He completed this work at Bethlehem in 392–393 AD. The work consists of a prologue plus 135 chapters, each consisting of a brief biography. Jerome himself is the subject of the final chapter. A Greek version of the book, possibly by the same Sophronius who is the subject of Chapter 134, also survives. Many biographies take as their subject figures important in Christian Church history and pay especial attention to their careers as writers. It "was written as an apologetic work to prove that the Church had produced learned men." The book was dedicated to Flavius Lucius Dexter, who served as high chamberlain to Theodosius I and as praetorian prefect to Honorius. Dexter was the son of Saint Pacianus, who is eulogized in the work.

The Order of Saint Basil the Great, also known as the Basilian Order of Saint Josaphat, is a Greek Catholic monastic order of pontifical right that works actively among Ukrainian Catholics and other Greek-Catholic churches in central and Eastern Europe. The order received approbation on August 20, 1631, and is based at the Monastery of the Holy Trinity, Vilnius.

Coptic literature is the body of writings in the Coptic language of Egypt, the last stage of the indigenous Egyptian language. It is written in the Coptic alphabet. The study of the Coptic language and literature is called Coptology.
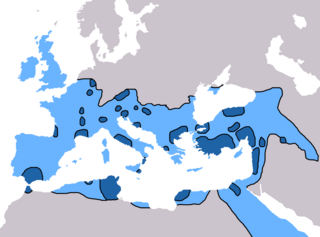
Christianity in the 4th century was dominated in its early stage by Constantine the Great and the First Council of Nicaea of 325, which was the beginning of the period of the First seven Ecumenical Councils (325–787), and in its late stage by the Edict of Thessalonica of 380, which made Nicene Christianity the state church of the Roman Empire.

Kyprian Zochovskyj (1635—1693) was the "Metropolitan of Kiev, Galicia and all Ruthenia" in the Ruthenian Uniate Church — a sui juris Eastern Catholic Church in full communion with the Holy See. He reigned from 1674 until his death in 1693.
Athanasius I Gammolo was the Patriarch of Antioch and head of the Syriac Orthodox Church from 594/595 or 603 until his death in 631. He is commemorated as a saint by the Syriac Orthodox Church in the Martyrology of Rabban Sliba, and his feast day is 3 January.

Admonitio ad filium spiritualem is an anonymous Latin "manual of spiritual edification" written around the year 500. During the Middle Ages, it was believed to be a translation by Rufinus of Aquileia of a Greek original by Basil of Caesarea. It is now thought to be an original Latin composition, most likely by Porcarius of Lérins. Its author is still known conventionally as Pseudo-Basil.

Serapion of Nitria, Serapion of Thmuis, also spelled Sarapion, or Serapion the Scholastic was an early Christian monk and bishop of Thmuis in Lower Egypt, born in the 4th century. He is notable for fighting alongside Athanasius of Alexandria against Arianism.
The Historia monachorum in Aegypto, also called the Lives of the Desert Fathers, is a combination travelogue and hagiography from the late 4th century AD. It recounts the travels of a band of seven Palestinian monks on a pilgrimage through Egypt between September 394 and January 395. They travelled from south to north, stopping in monasteries and meeting hermits and holy men. The Historia is in essence a collection of stories about these men and their miracles.
References
Bibliography
- Fedwick, Paul Jonathan, ed. (1981). Basil of Caesarea, Christian, Humanist, Ascetic: A Sixteen-Hundredth Anniversary Symposium. Pontifical Institute of Mediaeval Studies.