The PrrF RNAs are small non-coding RNAs involved in iron homeostasis and are encoded by all Pseudomonas species. The PrrF RNAs are analogs of the RyhB RNA, which is encoded by enteric bacteria. Expression of the PrrF RNAs is repressed by the ferric uptake regulator (Fur) when cells are grown in iron-replete conditions. Under iron limitation, the PrrF RNAs are expressed and act to negatively regulate several genes encoding iron-containing proteins, including SodB and succinate dehydrogenase. As such, PrrF regulation "spares" iron when this nutrient becomes scarce.
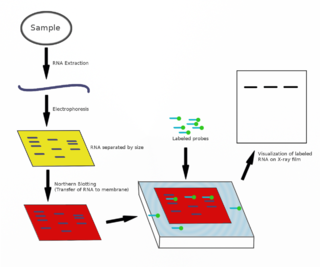
Pseudomonas sRNA P16 is a ncRNA that was predicted using bioinformatic tools in the genome of the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its expression verified by northern blot analysis. P16 sRNA appears to be conserved across several Pseudomonas species and is consistently located downstream of a predicted TatD deoxyribonuclease gene. P16 has a predicted Rho independent terminator at the 3'end but the function of P16 is unknown.
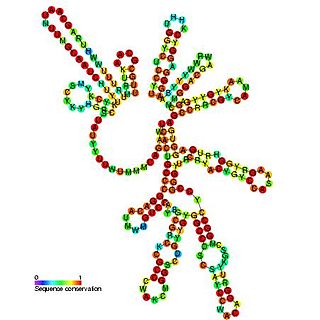
Pseudomonas sRNA P24 is a ncRNA that was predicted using bioinformatic tools in the genome of the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its expression verified by northern blot analysis.
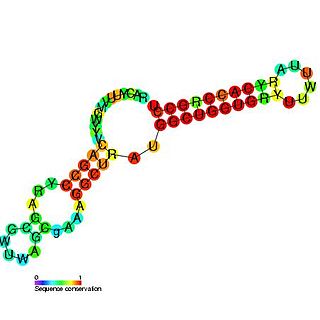
Pseudomonas sRNA P26 is a ncRNA that was predicted using bioinformatic tools in the genome of the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its expression verified by northern blot analysis. P26 is conserved across many Gammaproteobacteria species and appears to be consistently located between the DNA directed RNA polymerase and 50S ribosomal protein L7/L12 genes.

The gabT RNA motif is the name of a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics whose function is unknown. The gabT motif has been detected exclusively in bacteria within the genus Pseudomonas, and is found only upstream of gabT genes, and downstream to gabD genes.

The gyrA RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics. The RNAs are present in multiple species of bacteria within the order Pseudomonadales. This order contains the genus Pseudomonas, which includes the opportunistic human pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas syringae, a plant pathogen.

The livK RNA motif describes a conserved RNA structured that was discovered using bioinformatics. The livK motif is detected only in the species Pseudomonas syringae. It is found in the potential 5' untranslated regions of livK genes and downstream livM and livH genes, as well as the 5' UTRs of amidase genes. The liv genes are predicted to be transporters of branched-chain amino acids, i.e., leucine, isoleucine or valine. The specific reaction catalyzed the amidase genes is not predicted.

The Pseudomon-1 RNA motif is a conserved RNA identified by bioinformatics. It is used by most species whose genomes have been sequenced and that are classified within the genus Pseudomonas, and is also present in Azotobacter vinelandii, a closely related species. It is presumed to function as a non-coding RNA. Pseudomon-1 RNAs consistently have a downstream rho-independent transcription terminator.
The Pseudomon-groES RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified in certain bacteria using bioinformatics. It is found in most species within the family Pseudomonadaceae, and is consistently located in the 5' untranslated regions of operons that contain groES genes. RNA transcripts of the groES genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa where shown experimentally to be initiated at one of two start sites, from promoters called "P1" and "P2". The Pseudomon-groES RNA is in the 5' UTR of transcripts initiated from the P1 site, but is truncated in P2 transcripts. groES genes are involved in the cellular response to heat shock, but it is not thought that the Pseudomonas-groES RNA motif is involved in heat shock regulation. However, it is thought that the motif might regulate groES genes in response to other stimuli.
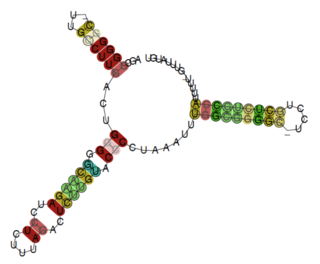
The Pseudomonas rpsL leader is a putative attenuator RNA element identified by bioinformatics searches within bacteria of the Pseudomonadaceae phylum. It is located upstream of the operon encoding ribosomal proteins S12 and S7, and presents a Rho-independent terminator at the 3' end. This RNA is presumed to operate as a non-coding ribosomal protein leader potentially interacting with the S12 or S7 proteins, which are encoded by the operon. The motif might be related to other rpsL leaders, such as the Rickettsia rpsL leader.
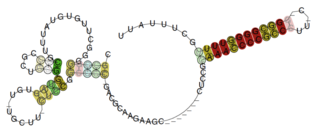
The Pseudomonas rnk leader is a putative attenuator element identified by bioinformatics within bacteria of the γ-proteobacterial Pseudomonas genus. It is located upstream of the rnk gene, encoding a nucleoside diphosphate kinase regulator, and presents a Rho-independent terminator at the 3' end. This RNA is presumed to operate as a non-coding leader, which regulatory mechanism remains to be elucidated. The motif might be related to other rnk-and greA-leaders, such the Enterobacteria rnk leader and Enterobacteria greA leader.
PhrS is a bacterial small RNA found in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. It was first identified in a RNAomics screen and has since been found to act as a link between oxygen availability and quorum sensing.
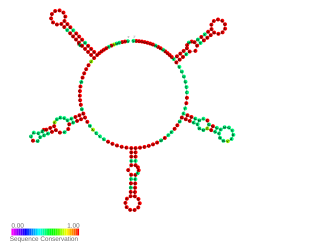
NrsZ is a bacterial small RNA found in the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Its transcription is induced during nitrogen limitation by the NtrB/C two-component system together with the alternative sigma factor RpoN. NrsZ by activating rhlA positively regulates the production of rhamnolipid surfactants needed for swarming motility.
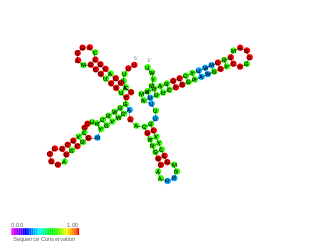
RsmW is a part of the Rsm/Csr family of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) discovered in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. It specifically binds to RsmA protein in vitro, restores biofilm production and partially complements the loss of RsmY and RsmZ in rsmY/rsmZ double mutant in regards to their contribution to swarming. Compared to RsmY and RsmZ its production is induced in high temperatures and rsmW is not transcriptionally activated by GacA.
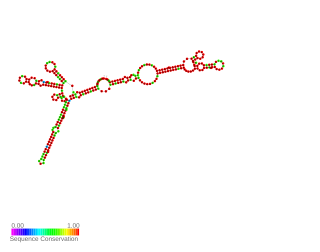
AsponA is a small asRNA transcribed antisense to the penicillin-binding protein 1A gene called ponA. It was identified by RNAseq and the expression was validated by 5' and 3' RACE experiments in Pseudomanas aeruginosa. AsponA expression was up or down regulated under different antibiotic stress. Due to it s location it may be able to prevent the transcription or translation of the opposite gene. Study by Wurtzel et al. and Ferrara et al. also detected its expression.

The ivy-DE RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. ivy-DE motifs are found in the genus Pseudomonas.