
Pseudomonas is a genus of Gram-negative, Gammaproteobacteria, belonging to the family Pseudomonadaceae and containing 191 validly described species. The members of the genus demonstrate a great deal of metabolic diversity and consequently are able to colonize a wide range of niches. Their ease of culture in vitro and availability of an increasing number of Pseudomonas strain genome sequences has made the genus an excellent focus for scientific research; the best studied species include P. aeruginosa in its role as an opportunistic human pathogen, the plant pathogen P. syringae, the soil bacterium P. putida, and the plant growth-promoting P. fluorescens, P. lini, P. migulae and P. graminis

Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a common encapsulated, Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, P. aeruginosa is a multidrug resistant pathogen recognized for its ubiquity, its intrinsically advanced antibiotic resistance mechanisms, and its association with serious illnesses – hospital-acquired infections such as ventilator-associated pneumonia and various sepsis syndromes.
Pseudomonas citronellolis is a Gram-negative, bacillus bacterium that is used to study the mechanisms of pyruvate carboxylase. It was first isolated from forest soil, under pine trees, in northern Virginia, United States.

The PrrF RNAs are small non-coding RNAs involved in iron homeostasis and are encoded by all Pseudomonas species. The PrrF RNAs are analogs of the RyhB RNA, which is encoded by enteric bacteria. Expression of the PrrF RNAs is repressed by the ferric uptake regulator (Fur) when cells are grown in iron-replete conditions. Under iron limitation, the PrrF RNAs are expressed and act to negatively regulate several genes encoding iron-containing proteins, including SodB and succinate dehydrogenase. As such, PrrF regulation "spares" iron when this nutrient becomes scarce.
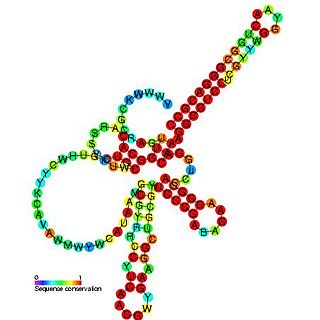
Pseudomonas sRNA P11 is a ncRNA that was predicted using bioinformatic tools in the genome of the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its expression verified by northern blot analysis. P11 is located between a putative threonine protein kinase and putative nitrate reductase and is conserved in several Pseudomonas species. P11 has a predicted Rho independent terminator at the 3′ end but the function of P11 is unknown.
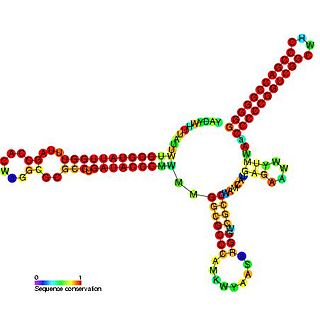
Pseudomonas sRNA P15 is a ncRNA that was predicted using bioinformatic tools in the genome of the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its expression verified by northern blot analysis.
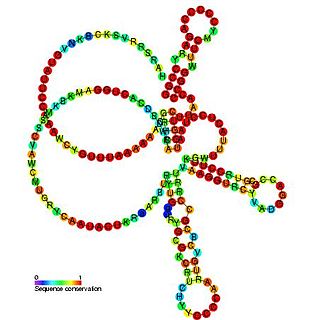
Pseudomonas sRNA P16 is a ncRNA that was predicted using bioinformatic tools in the genome of the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its expression verified by northern blot analysis. P16 sRNA appears to be conserved across several Pseudomonas species and is consistently located downstream of a predicted TatD deoxyribonuclease gene. P16 has a predicted Rho independent terminator at the 3′ end but the function of P16 is unknown.
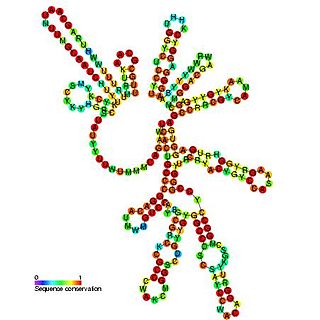
Pseudomonas sRNA P24 is a ncRNA that was predicted using bioinformatic tools in the genome of the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its expression verified by northern blot analysis.
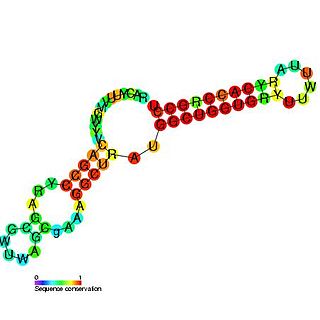
Pseudomonas sRNA P26 is a ncRNA that was predicted using bioinformatic tools in the genome of the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its expression verified by northern blot analysis. P26 is conserved across many Gammaproteobacteria species and appears to be consistently located between the DNA directed RNA polymerase and 50S ribosomal protein L7/L12 genes.

Pseudomonas sRNA P9 is a ncRNA that was predicted using bioinformatic tools in the genome of the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its expression verified by northern blot analysis.
Pseudomonas sRNA are non-coding RNAs (ncRNA) that were predicted by the bioinformatic program SRNApredict2. This program identifies putative sRNAs by searching for co-localization of genetic features commonly associated with sRNA-encoding genes and the expression of the predicted sRNAs was subsequently confirmed by Northern blot analysis. These sRNAs have been shown to be conserved across several pseudomonas species but their function is yet to be determined. Using Tet-Trap genetic approach RNAT genes post-transcriptionally regulated by temperature upshift were identified: ptxS and PA5194.

The gabT RNA motif is the name of a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics whose function is unknown. The gabT motif has been detected exclusively in bacteria within the genus Pseudomonas, and is found only upstream of gabT genes, and downstream to gabD genes.

The gyrA RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics. The RNAs are present in multiple species of bacteria within the order Pseudomonadales. This order contains the genus Pseudomonas, which includes the opportunistic human pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas syringae, a plant pathogen.

The Pseudomon-1 RNA motif is a conserved RNA identified by bioinformatics. It is used by most species whose genomes have been sequenced and that are classified within the genus Pseudomonas, and is also present in Azotobacter vinelandii, a closely related species. It is presumed to function as a non-coding RNA. Pseudomon-1 RNAs consistently have a downstream rho-independent transcription terminator.
The Pseudomon-groES RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified in certain bacteria using bioinformatics. It is found in most species within the family Pseudomonadaceae, and is consistently located in the 5' untranslated regions of operons that contain groES genes. RNA transcripts of the groES genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa where shown experimentally to be initiated at one of two start sites, from promoters called "P1" and "P2". The Pseudomon-groES RNA is in the 5' UTR of transcripts initiated from the P1 site, but is truncated in P2 transcripts. groES genes are involved in the cellular response to heat shock, but it is not thought that the Pseudomonas-groES RNA motif is involved in heat shock regulation. However, it is thought that the motif might regulate groES genes in response to other stimuli.

Mycobacterium tuberculosis contains at least nine small RNA families in its genome. The small RNA (sRNA) families were identified through RNomics – the direct analysis of RNA molecules isolated from cultures of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The sRNAs were characterised through RACE mapping and Northern blot experiments. Secondary structures of the sRNAs were predicted using Mfold.
Phikmvlikevirus is a genus of viruses that infect bacteria. There are currently four species in this genus including the type species Pseudomonas phage phiKMV. Bacteriophage phiKMV and its relatives are known to be highly virulent phages, producing large clear plaques on a susceptible host. The only reported exception is phage LKA1, which yields small plaques surrounded by a halo. While all other P. aeruginosa-specific phikmvlikeviruses use the Type IV pili as primary receptor, LKA1 particles attach to the bacterial lipopolysaccharide layer.
PhrS is a bacterial small RNA found in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. It was first identified in a RNAomics screen and has since been found to act as a link between oxygen availability and quorum sensing.
CRISPR-Cas design tools are computer software platforms and bioinformatics tools used to facilitate the design of guide RNAs (gRNAs) for use with the CRISPR/Cas gene editing system.

The ivy-DE RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. ivy-DE motifs are found in the genus Pseudomonas.














