Related Research Articles
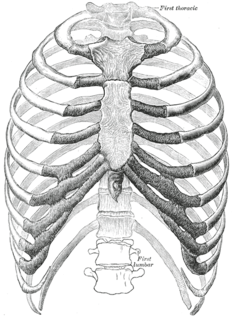
The rib cage, as an enclosure that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum in the thorax of most vertebrates, protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels.

The respiratory system is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies greatly, depending on the size of the organism, the environment in which it lives and its evolutionary history. In land animals the respiratory surface is internalized as linings of the lungs. Gas exchange in the lungs occurs in millions of small air sacs; in mammals and reptiles these are called alveoli, and in birds they are known as atria. These microscopic air sacs have a very rich blood supply, thus bringing the air into close contact with the blood. These air sacs communicate with the external environment via a system of airways, or hollow tubes, of which the largest is the trachea, which branches in the middle of the chest into the two main bronchi. These enter the lungs where they branch into progressively narrower secondary and tertiary bronchi that branch into numerous smaller tubes, the bronchioles. In birds the bronchioles are termed parabronchi. It is the bronchioles, or parabronchi that generally open into the microscopic alveoli in mammals and atria in birds. Air has to be pumped from the environment into the alveoli or atria by the process of breathing which involves the muscles of respiration.
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the creature's body, each of which is in turn composed of multiple segments.
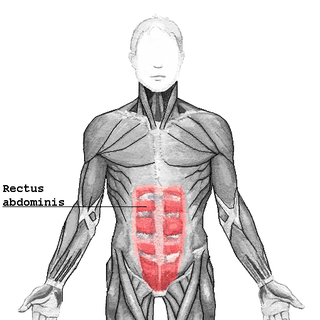
The rectus abdominis muscle, also known as the "abdominal muscle" or simply the "abs", is a paired straight muscle. There are two parallel muscles, separated by a midline band of connective tissue called the linea alba. It extends from the pubic symphysis, pubic crest and pubic tubercle inferiorly, to the xiphoid process and costal cartilages of ribs V to VII superiorly. The proximal attachments are the pubic crest and the pubic symphysis. It attaches distally at the costal cartilages of ribs 5-7 and the xiphoid process of the sternum.
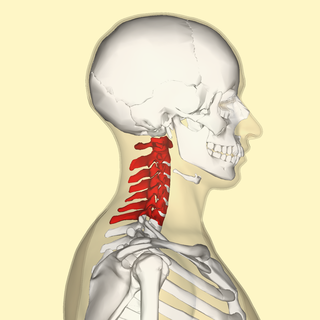
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae lie caudal of cervical vertebrae. In sauropsid species, the cervical vertebrae bear cervical ribs. In lizards and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes. Most mammals have seven cervical vertebrae, with the only three known exceptions being the manatee with six, the two-toed sloth with five or six, and the three-toed sloth with nine.
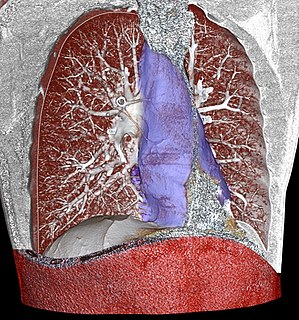
The mediastinum is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is an undelineated region that contains a group of structures within the thorax, namely the heart and its vessels, the esophagus, the trachea, the phrenic and cardiac nerves, the thoracic duct, the thymus and the lymph nodes of the central chest.
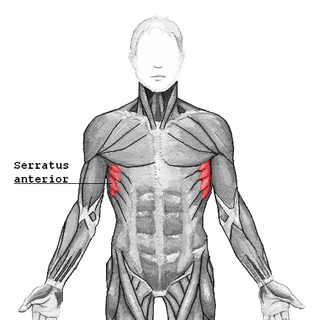
The serratus anterior is a muscle that originates on the surface of the 1st to 8th ribs at the side of the chest and inserts along the entire anterior length of the medial border of the scapula. The serratus anterior acts to pull the scapula forward around the thorax. The muscle is named from Latin: serrare = to saw, referring to the shape, anterior = on the front side of the body.

The transversus thoracis muscle, also known as triangularis sterni, lies internal to the thoracic cage, anteriorly. It is usually a thin plane of muscular and tendinous fibers, however on athletic individuals it can be a thick 'slab of meat', situated upon the inner surface of the front wall of the chest. It is in the same layer as the subcostal muscles and the innermost intercostal muscles.

The thoracic outlet is the lower opening of the thoracic cavity whose edges are the lowest ribs. It is closed by the diaphragm, which separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity. The thoracic outlet is much larger than the thoracic inlet.

The external intercostal muscles, or external intercostals are eleven in number on both sides.

The abdominal external oblique muscle is the largest and outermost of the three flat abdominal muscles of the lateral anterior abdomen.

A respiratory examination, or lung examination, is performed as part of a physical examination, in response to respiratory symptoms such as shortness of breath, cough, or chest pain, and is often carried out with a cardiac examination.

The shoulder girdle or pectoral girdle is the set of bones in the appendicular skeleton which connects to the arm on each side. In humans it consists of the clavicle and scapula; in those species with three bones in the shoulder, it consists of the clavicle, scapula, and coracoid. Some mammalian species have only the scapula.

The sacrococcygeal symphysis is an amphiarthrodial joint, formed between the oval surface at the apex of the sacrum, and the base of the coccyx.
In common parlance, the core of the body is broadly considered to be the torso. Functional movements are highly dependent on this part of the body, and lack of core muscular development can result in a predisposition to injury. The major muscles of the core reside in the area of the belly and the mid and lower back, and peripherally include the hips, the shoulders and the neck.
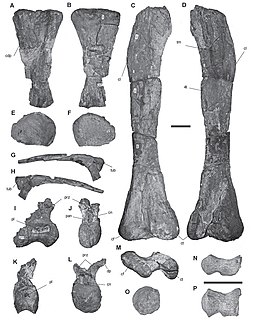
Atacamatitan is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaurs that lived in South America during the Late Cretaceous period.

The pelvis is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs, together with its embedded skeleton.

Anatomical terminology is a form of scientific terminology used by anatomists, zoologists, and health professionals such as doctors.

The spinal column, characteristic of each vertebrate species, is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae, each constituting a characteristic irregular bone whose complex structure is composed primarily of bone, and secondarily of hyaline cartilage. They show variation in the proportion contributed by these two tissue types; such variations correlate on one hand with the cerebral/caudal rank, and on the other with phylogenetic differences among the vertebrate taxa.
Bucket-handle is a movement of ribs that results in change in transverse diameter of the thorax.
References
- 1 2 3 "Chapter 20: The thoracic wall and mediastinum". www.dartmouth.edu. Archived from the original on 2005-02-26.
- ↑ Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, Wayne; Tibbitts, Adam W.M. Mitchell; illustrations by Richard; Richardson, Paul (2005). Gray's anatomy for students. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 978-0-8089-2306-0.
- ↑ "Figure 20-7". www.dartmouth.edu. Archived from the original on 2006-12-08.