
Sher Shah Suri, often referred to as Sultan Adil, was the founder of the Sur Empire in India. He was the regent and later sole ruler of Bihar from 1529—1540 until he defeated the Mughal Empire in 1540, founding the Sur Empire, and establishing his rule in Delhi, crowning himself as Emperor. After his accidental death in 1545 CE, his son Islam Shah became his successor. The influence of his innovations and reforms extended far beyond his brief reign. In his reign, he remained undefeated in battle, being renowned as one of the most skillful Afghan generals ever produced.

Shah Alam II, also known by his birth name Ali Gohar, or Ali Gauhar, was the seventeenth Mughal emperor and the son of Alamgir II. Shah Alam II became the emperor of a crumbling Mughal Empire. His power was so depleted during his reign that it led to a saying in the Persian language, Sultanat-e-Shah Alam, Az Dilli ta Palam, meaning, 'The empire of Shah Alam is from Delhi to Palam', Palam being a suburb of Delhi.

Mirza Azim-ush-Shan was the second son of Mughal emperor Shah Alam I, by his second wife, Amrita Bai, Princess of Kishangarh. He was the great grandson of Emperor Shah Jahan and the grandson of Emperor Aurangzeb, during whose reign he was the last subahdar (viceroy) of Bengal Subah, Bihar Subah and Orissa Subah from 1697 to his death in 1712.

The Kamboj, also Kamboh, is a caste and cultivating community of India and Pakistan that originated from the central Punjab region.

The Battle of Buxar was fought between 22 and 23 October 1764, between the forces of the British East India Company, under the command of Major Hector Munro, and the combined armies of Balwant Singh, Maharaja of the Banaras State; Mir Qasim, Nawab of Bengal; Shuja-ud-Daula, Nawab of Awadh; and Shah Alam II, Emperor of the Mughal Empire.
Muslim Rajputs or Musalman Rajpoots are the descendants of Rajputs in the northern regions of the Indian subcontinent who generally are followers of Islam. Reportedly, they converted from Hinduism to Islam from the medieval period onwards, creating various dynasties and states while retaining Hindu surnames such as Chauhan. Today, Muslim Rajputs can be found mostly in present-day Northern India and Pakistan. They are further divided into different clans.

Bihari Muslims are adherents of Islam who identify linguistically, culturally, and genealogically as Biharis. They are geographically native to the region comprising the Bihar state of India, although there are significantly large communities of Bihari Muslims living elsewhere in the subcontinent due to the Partition of British India in 1947, which prompted the community to migrate en masse from Bihar to the dominion of Pakistan.
The region have been inhabited since the Stone Age. Copper tools from the Chalcolithic period have been discovered. This area entered the Iron Age during the mid-2nd millennium BCE.

Gidhaur is a small town in the Jamui District of Bihar. In the early-modern period, it was the centre of the Gidhaur chieftaincy.

Shahrullah Kamboh, better known as Shahbaz Khan Kamboh, was one of the leading generals of Mughal emperor Akbar. He participated in some of the most difficult expeditions of Akbar and annexed numerous territories to the empire. The Mughal officials boasted that he conquered countries ten times the size of Deccan. He was too orthodox a Sunni Muslim for Akbar's taste, but not only was he tolerated but also was greatly valued. He was named "Mang Khan" by the people of Lahore meaning "ask the Khan and it will be done" In Punjabi due to his legendary generosity. The very first 'guzar' in Lahore Fort was named Guzar Shahbaz Khan known locally as Guzar Mang Khan.

Ujjainiya is a clan of Rajputs found in Bihar and Purvanchal. They are originally an off-shoot of Paramara dynasty of Malwa. The Ujjainiya dynasty historically ruled over the parts of Bhojpuri region during the medieval era. They were mainly rulers and aristocrats holding major power of the region.
The Nagvanshis of Chotanagpur, also known as the Khokhra chieftaincy, was an Indian dynasty which ruled the parts of Chota Nagpur plateau region during much of ancient, medieval and modern period. Phani Mukut Rai is considered the first king of dynasty claim to be son of Pundrika Naga, a mythical Naga. Lal Chintamani Sharan Nath Shahdeo (1931–2014) was last ruling king of the dynasty, until the estate was merged to the Republic of India.
The Kol uprising, Kol rebellion, also known in British records as the Kol mutiny was a revolt of the tribal Kol people of Chhota Nagpur that took place between 1831 and 1832. It was due to economic exploitation brought on by the systems of land tenure and administration that had been introduced by the East India Company. Tribal people of Chotanagpur including Mundas, Oraons, Hos and Bhumijs were called Kols. They initially plundered and killed Sikh and Muslims thikedars (contractors) who collected taxes by different means. Later they also started to plunder and kill Hindus of nearby villages and burn their houses. The insurgency was suppressed by killing of the leaders, their followers and arrest of many leaders by Thomas Wilkinson.
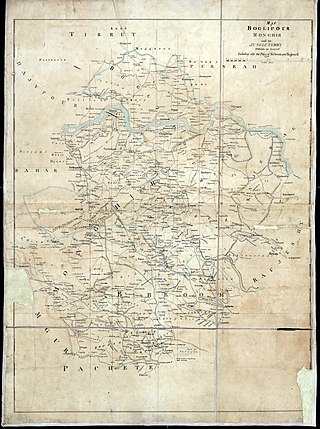
Kharagpur Raj was a prominent chieftaincy, founded in the early 16th century in Bihar situated mainly in modern-day Munger district. They were notable for being one of the few chieftaincies in Bihar to convert to Islam and many of the rulers became firm allies of the Mughal authorities. At its peak, the Kharagpur Raj encompassed parts of the modern-day districts of Munger, Bhagalpur, Jamui, Lakhisarai, Godda and Deoghar. Due to its size, the Privy Council compared it with the Kingdom of Sardinia.
The Chero dynasty or Chyavana dynasty was a polity that ruled the northern regions of the Indian subcontinent, corresponding to the present-day Indian states of Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and Jharkhand, after the fall of the Pala Empire; their rule lasted from the 12th century CE to the middle of the 15th century.
Madhu Karn Shah also known as Madhu Singh was a Nagvanshi king in the 16th century. His capital was at Khukhragarh.

The Gidhaur Chieftaincy was a principality which controlled parts of South Bihar for much of the medieval period in India. The chieftaincy was named after the town of Gidhaur in Jamui district but its territory extended into the wider region.

Bhojpur Kadim is a historic village in Dumraon block of Buxar district, Bihar, India. As of 2011, its population was 18,243, in 3,024 households. Together with the neighboring Bhojpur Jadid, it lends its name to the surrounding Bhojpuri region.
Raja Gajpati Ujjainia, also known as Raja Gajpati Sahi was a ruler of Bhojpur belonging to the Ujjainiya dynasty.
Raja Sangram Singh was ruler of Kharagpur Raj in the 16th century. He was a contemporary of Akbar. Sangram Singh initially was allegiance to Akbar, but during the reign of Jahangir, he declared himself independence and was killed during battle with Mughal forces due to assassination. After his death, his son Toral Mal converting to Islam, changed his name to Roz Afzun, became loyal of Mughal and deployed as king of Kharagpur by Jahangir.












