Related Research Articles
The Transporter Classification Database is an International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (IUBMB)-approved classification system for membrane transport proteins, including ion channels.
The enzyme (2R)-sulfolactate sulfo-lyase catalyzes the reaction
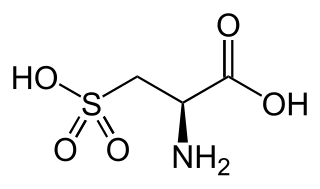
Cysteic acid also known as 3-sulfo-l-alanine is the organic compound with the formula HO3SCH2CH(NH2)CO2H. It is often referred to as cysteate, which near neutral pH takes the form −O3SCH2CH(NH3+)CO2−.

L-2-hydroxycarboxylate dehydrogenase (NAD+) (EC 1.1.1.337, (R)-sulfolactate:NAD+ oxidoreductase, L-sulfolactate dehydrogenase, (R)-sulfolactate dehydrogenase, L-2-hydroxyacid dehydrogenase (NAD+), ComC) is an enzyme with systematic name (2S)-2-hydroxycarboxylate:NAD+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Roseovarius nubinhibens is a species of Gram-negative, rod-shaped, aerobic dimethylsulfoniopropionate-demethylating bacteria. Its type strain is ISMT.
The 4-Toluene Sulfonate Uptake Permease (TSUP) family is also referred to as the TauE/SafE/YfcA/DUF81 Family.
The amino acid-polyamine-organocation (APC) superfamily is the second largest superfamily of secondary carrier proteins currently known, and it contains several Solute carriers. Originally, the APC superfamily consisted of subfamilies under the transporter classification number. This superfamily has since been expanded to include eighteen different families.
The multidrug/oligosaccharidyl-lipid/polysaccharide (MOP) flippase superfamily is a group of integral membrane protein families. The MOP flippase superfamily includes twelve distantly related families, six for which functional data are available:
- One ubiquitous family (MATE) specific for drugs - (TC# 2.A.66.1) The Multi Antimicrobial Extrusion (MATE) Family
- One (PST) specific for polysaccharides and/or their lipid-linked precursors in prokaryotes - (TC# 2.A.66.2) The Polysaccharide Transport (PST) Family
- One (OLF) specific for lipid-linked oligosaccharide precursors of glycoproteins in eukaryotes - (TC# 2.A.66.3) The Oligosaccharidyl-lipid Flippase (OLF) Family
- One (MVF) lipid-peptidoglycan precursor flippase involved in cell wall biosynthesis - (TC# 2.A.66.4) The Mouse Virulence Factor (MVF) Family
- One (AgnG) which includes a single functionally characterized member that extrudes the antibiotic, Agrocin 84 - (TC# 2.A.66.5) The Agrocin 84 Antibiotic Exporter (AgnG) Family
- And finally, one (Ank) that shuttles inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi) - (TC# 2.A.66.9) The Progressive Ankylosis (Ank) Family
The iron/lead transporter (ILT) family is a family of transmembrane proteins within the lysine exporter (LysE) superfamily. The ILT family includes two subfamilies, the iron-transporting (OFeT) family and the lead-transporting (PbrT) family. A representative list of the proteins belonging to these subfamilies of the ILT family can be found in the Transporter Classification Database.
The Nickel/Cobalt Transporter (NicO) Family is a member of the Lysine Exporter (LysE) Superfamily.
The Disulfide bond oxidoreductase D (DsbD) family is a member of the Lysine Exporter (LysE) Superfamily. A representative list of proteins belonging to the DsbD family can be found in the Transporter Classification Base.
Divalent anion:Na+ symporters were found in bacteria, archaea, plant chloroplasts and animals.
The HP1 Holin Family is a member of the Holin Superfamily II. Proteins in this family are typically found to contain two transmembrane segments (TMSs) and range between 70 and 80 amino acyl residues (aas) in length. A representative list of proteins belonging to the HP1 holin family can be found in the Transporter Classification Database.
The Citrate-Mg2+:H+ (CitM) / Citrate-Ca2+:H+ (CitH) Symporter (CitMHS) Family (TC# 2.A.11) is a family of transport proteins belonging to the Ion transporter superfamily. Members of this family are found in Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, archaea and possibly eukaryotes. These proteins all probably arose by an internal gene duplication event. Lensbouer & Doyle (2010) have reviewed these systems, classifying the porters with three superfamilies, according to ion-preference:
The Malonate Uptake (MatC) family is a constituent of the ion transporter (IT) superfamily. It consists of proteins from Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, simple eukaryotes and archaea. The proteins are of about 450 amino acyl residues in length with 12-14 putative transmembrane segments (TMSs). Closest functionally-characterized homologues are in the DASS family. One member of this family is a putative malonate transporter.
The Basic Amino Acid Antiporter (ArcD) family is a constituent of the IT superfamily. This family consists of proteins from Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. The proteins are of about 480 amino acyl residues (aas) in length and have 10-12 putative transmembrane segments (TMSs). Functionally characterized homologues are in the DcuC and ArsB families. Some members of the family probably catalyze arginine/ornithine or citrulline/ornithine antiport.
The NhaE family belongs to the Ion Transporter (IT) Superfamily, which has an end. A representative list of proteins belonging to the NhaE family can be found in the Transporter Classification Database.
The inorganic phosphate transporter (PiT) family is a group of carrier proteins derived from Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes.
The cation:proton antiporter (CPA) superfamily is a superfamily of transport proteins named after one of its constituent members, the monovalent cation:proton antiporter-2 (CPA2).
Bilophila wadsworthia is a Gram-negative, obligately anaerobic, catalase-positive, bile-resistant, and asaccharolytic bacillus. Approximately 75% of B. wadsworthia strains are urease positive. B. wadsworthia is linked to various diseases and is not well known due to frequent misidentification of the bacteria, and the National Center for Biotechnology Information is including it the phylum of Proteobacteria. The two unique characteristics of B. wadsworthia are the utilisation of the sulfated amino acid taurine in the production of hydrogen sulfide and the rapid catalase reaction. This bacterium is susceptible to the β-lactam antibiotics imipenem, cefoxitin, and ticarcillin.
References
- ↑ Rein, Ulrike; Gueta, Ronnie; Denger, Karin; Ruff, Jürgen; Hollemeyer, Klaus; Cook, Alasdair M. (2005-03-01). "Dissimilation of cysteate via 3-sulfolactate sulfo-lyase and a sulfate exporter in Paracoccus pantotrophus NKNCYSA". Microbiology. 151 (Pt 3): 737–747. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27548-0 . ISSN 1350-0872. PMID 15758220.
- ↑ "2.A.98 The Putative Sulfate Exporter (PSE) Family". TCDB. Retrieved 2016-04-08.
As of this edit, this article uses content from "2.A.98 The Putative Sulfate Exporter (PSE) Family" , which is licensed in a way that permits reuse under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, but not under the GFDL. All relevant terms must be followed.