
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist, and political ethicist who employed nonviolent resistance to lead the successful campaign for India's independence from British rule. He inspired movements for civil rights and freedom across the world. The honorific Mahātmā, first applied to him in South Africa in 1914, is now used throughout the world.
Mahātmā is an honorific used in India.

Nathuram Vinayak Godse was the assassin of Mahatma Gandhi. He was a Hindu nationalist from Maharashtra who shot Gandhi in the chest three times at point blank range at a multi-faith prayer meeting in Birla House in New Delhi on 30 January 1948.

Kasturba Mohandas Gandhi was an Indian political activist who was involved in the Indian independence movement during British India. She was married to Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, commonly known as Mahatma Gandhi. National Safe Motherhood Day is observed in India annually on April 11, coinciding with Kasturba's birthday.

Harilal Mohandas Gandhi was the eldest son of Mahatma Gandhi and Kasturba Gandhi. He had three younger brothers: Manilal Gandhi, Ramdas Gandhi and Devdas Gandhi.

Devdas Mohandas Gandhi was the fourth and youngest son of Mahatma Gandhi. He was born in the Colony of Natal and came to India with his parents as a grown man. He became active in his father's movement, spending many terms in jail. He also became a prominent journalist, serving as editor of Hindustan Times. He was also the first pracharak of the Dakshina Bharat Hindi Prachar Sabha (DBHPS), established by Mohandas Gandhi in Tamil Nadu in 1918. The purpose of the Sabha was to propagate Hindi in southern India.

Kaba Gandhi No Delo is a house and a museum in Rajkot, Gujarat, India. It was Indian independence leader Mahatma Gandhi's primary family home from 1881 to 1915. It is built in the traditional Saurashtrian architectural style and houses a permanent pictorial exhibition called Gandhi Smriti.

Madeleine Slade, also known as Mirabehn or Meera Behn, was a British supporter of the Indian Independence Movement who in the 1920s left her home in England to live and work with Mahatma Gandhi. She devoted her life to human development and the advancement of Gandhi's principles.

Thillaiyadi Valliammai was a South African Tamil girl who worked with Mahatma Gandhi in her early years when she developed her nonviolent methods in South Africa fighting its apartheid regime.

Mahatma Gandhi was assassinated on 30 January 1948 at age 78 in the compound of The Birla House, a large mansion in central New Delhi. His assassin was Nathuram Godse, from Pune, Maharashtra, a Hindutva activist, with a history of association with the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS), a right-wing Hindu paramilitary organization and of membership of the Hindu Mahasabha.

Ramachandra "Ram" Guha is an Indian historian, environmentalist, writer and public intellectual whose research interests include social, political, contemporary, environmental and cricket history, and the field of economics. He is an important authority on the history of modern India.
Gandhian economics is a school of economic thought based on the spiritual and socio-economic principles expounded by Indian leader Mahatma Gandhi. It is largely characterised by rejection of the concept of the human being as a rational actor always seeking to maximize material self-interest that underlies classical economic thinking. Where Western economic systems were based on what he called the "multiplication of wants," Gandhi felt that this was both unsustainable and devastating to the human spirit. His model, by contrast, aimed at the fulfillment of needs – including the need for meaning and community. As a school of economics the resulting model contained elements of protectionism, nationalism, adherence to the principles and objectives of nonviolence and a rejection of class war in favor of socio-economic harmony. Gandhi's economic ideas also aim to promote spiritual development and harmony with a rejection of materialism. The term "Gandhian economics" was coined by J. C. Kumarappa, a close supporter of Gandhi.

Karamchand Uttamchand Gandhi was a court official in Porbandar. He served as Diwan of Porbandar and Rajkot and was the father of Mahatma Gandhi.
Dinanath Gopal Tendulkar (1909–1972) was an Indian writer and documentary film maker. He is most well known as the author of an eight-volume biography of Mahatma Gandhi, titled Mahatma: Life of Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi. He was also a close associate of Vithalbhai Jhaveri and collaborated for the documentary film, Mahatma: Life of Gandhi, 1869–1948. He died on Monday, June 12, 1972.

Sarla Behn was an English Gandhian social activist whose work in the Kumaon region of India helped create awareness about the environmental destruction in the Himalayan forests of the state. She played a key role in the evolution of the Chipko Movement and influenced a number of Gandhian environmentalists in India including Chandi Prasad Bhatt, Bimala behn and Sunderlal Bahuguna. Along with Mirabehn, she is known as one of Mahatma Gandhi's two English daughters. The two women's work in Garhwal and Kumaon, respectively, played a key role in bringing focus on issues of environmental degradation and conservation in independent India.
Asha Devi Aryanayakam (1901–1972) was an Indian freedom fighter, educationist and gandhian. She was closely connected with Sevagram of Mahatma Gandhi and the Bhoodan movement of Vinoba Bhave.
Herbert Fischer (1914–2006) was a German diplomat, indologist and the ambassador of the erstwhile German Democratic Republic to India from 1972 to 1976. Fischer was born on 10 April 1914 in Herrnhut, in East Germany to a craftsman. He migrated to western Europe in 1933, where he completed his studies. Fischer moved to India in 1936, which gave him the opportunity to get acquainted with Mahatma Gandhi. After Indian independence in 1947, he returned to the German Democratic Republic, where he joined the Ministry of Foreign Affairs in 1956. He served as the Chief of the East German Trade Mission in the late 1960s, before becoming the East German ambassador to India in 1972. He was the author of many Indological books, including Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, a biography of the Indian leader. He was a recipient of the Patriotic Order of Merit III Class. In 2003, the Government of India awarded him the Padma Bhushan, their third highest civilian honour, for his contributions to public affairs.
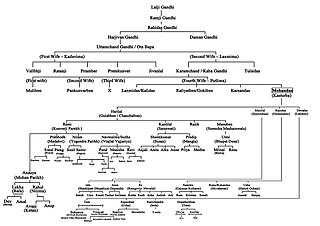
The Gandhi family is the family of Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, commonly known as Mahatma Gandhi; Mahatma meaning "high souled" or "venerable" in Sanskrit; the particular term 'Mahatma' was accorded Mohandas Gandhi for the first time while he was still in South Africa, and not commonly heard as titular for any other civil figure even of similarly rarefied stature or living or posthumous presence.

Mohandas is an Indian biographical film about the childhood of Mahatma Gandhi. It is written and directed by nine-time National Film Award winner P. Sheshadri and was made in three languages simultaneously, English, Hindi and Kannada.














