A quantum computer is a computer that exploits quantum mechanical phenomena. On small scales, physical matter exhibits properties of both particles and waves, and quantum computing leverages this behavior using specialized hardware. Classical physics cannot explain the operation of these quantum devices, and a scalable quantum computer could perform some calculations exponentially faster than any modern "classical" computer. In particular, a large-scale quantum computer could break widely used encryption schemes and aid physicists in performing physical simulations; however, the current state of the art is largely experimental and impractical, with several obstacles to useful applications.

Quantum entanglement is the phenomenon of a group of particles being generated, interacting, or sharing spatial proximity in such a way that the quantum state of each particle of the group cannot be described independently of the state of the others, including when the particles are separated by a large distance. The topic of quantum entanglement is at the heart of the disparity between classical and quantum physics: entanglement is a primary feature of quantum mechanics not present in classical mechanics.

A nature reserve is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, funga, or features of geological or other special interest, which is reserved and managed for purposes of conservation and to provide special opportunities for study or research. They may be designated by government institutions in some countries, or by private landowners, such as charities and research institutions. Nature reserves fall into different IUCN categories depending on the level of protection afforded by local laws. Normally it is more strictly protected than a nature park. Various jurisdictions may use other terminology, such as ecological protection area or private protected area in legislation and in official titles of the reserves.

Dame Barbara Mary Quant was a British fashion designer and icon. She became an instrumental figure in the 1960s London-based Mod and youth fashion movements, and played a prominent role in London's Swinging Sixties culture. She was one of the designers who took credit for the miniskirt and hotpants. Ernestine Carter wrote: "It is given to a fortunate few to be born at the right time, in the right place, with the right talents. In recent fashion there are three: Chanel, Dior, and Mary Quant."
Financial engineering is a multidisciplinary field involving financial theory, methods of engineering, tools of mathematics and the practice of programming. It has also been defined as the application of technical methods, especially from mathematical finance and computational finance, in the practice of finance.
In quantum computing, a quantum algorithm is an algorithm that runs on a realistic model of quantum computation, the most commonly used model being the quantum circuit model of computation. A classical algorithm is a finite sequence of instructions, or a step-by-step procedure for solving a problem, where each step or instruction can be performed on a classical computer. Similarly, a quantum algorithm is a step-by-step procedure, where each of the steps can be performed on a quantum computer. Although all classical algorithms can also be performed on a quantum computer, the term quantum algorithm is generally reserved for algorithms that seem inherently quantum, or use some essential feature of quantum computation such as quantum superposition or quantum entanglement.
In quantum mechanics, the measurement problem is the problem of definite outcomes: quantum systems have superpositions but quantum measurements only give one definite result.
A Bell test, also known as Bell inequality test or Bell experiment, is a real-world physics experiment designed to test the theory of quantum mechanics in relation to Albert Einstein's concept of local realism. Named for John Stewart Bell, the experiments test whether or not the real world satisfies local realism, which requires the presence of some additional local variables to explain the behavior of particles like photons and electrons. The test empirically evaluates the implications of Bell's theorem. As of 2015, all Bell tests have found that the hypothesis of local hidden variables is inconsistent with the way that physical systems behave.
Quantum Darwinism is a theory meant to explain the emergence of the classical world from the quantum world as due to a process of Darwinian natural selection induced by the environment interacting with the quantum system; where the many possible quantum states are selected against in favor of a stable pointer state. It was proposed in 2003 by Wojciech Zurek and a group of collaborators including Ollivier, Poulin, Paz and Blume-Kohout. The development of the theory is due to the integration of a number of Zurek's research topics pursued over the course of 25 years, including pointer states, einselection and decoherence.

Churchstanton is a village and civil parish in Somerset, England, situated within the Blackdown Hills Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, on the River Otter 5 miles (8.0 km) south of Taunton.
In quantum information and quantum computing, a cluster state is a type of highly entangled state of multiple qubits. Cluster states are generated in lattices of qubits with Ising type interactions. A cluster C is a connected subset of a d-dimensional lattice, and a cluster state is a pure state of the qubits located on C. They are different from other types of entangled states such as GHZ states or W states in that it is more difficult to eliminate quantum entanglement in the case of cluster states. Another way of thinking of cluster states is as a particular instance of graph states, where the underlying graph is a connected subset of a d-dimensional lattice. Cluster states are especially useful in the context of the one-way quantum computer. For a comprehensible introduction to the topic see.
Quantitative analysis is the use of mathematical and statistical methods in finance and investment management. Those working in the field are quantitative analysts (quants). Quants tend to specialize in specific areas which may include derivative structuring or pricing, risk management, investment management and other related finance occupations. The occupation is similar to those in industrial mathematics in other industries. The process usually consists of searching vast databases for patterns, such as correlations among liquid assets or price-movement patterns.

In physics and the philosophy of physics, quantum Bayesianism is a collection of related approaches to the interpretation of quantum mechanics, the most prominent of which is QBism. QBism is an interpretation that takes an agent's actions and experiences as the central concerns of the theory. QBism deals with common questions in the interpretation of quantum theory about the nature of wavefunction superposition, quantum measurement, and entanglement. According to QBism, many, but not all, aspects of the quantum formalism are subjective in nature. For example, in this interpretation, a quantum state is not an element of reality—instead, it represents the degrees of belief an agent has about the possible outcomes of measurements. For this reason, some philosophers of science have deemed QBism a form of anti-realism. The originators of the interpretation disagree with this characterization, proposing instead that the theory more properly aligns with a kind of realism they call "participatory realism", wherein reality consists of more than can be captured by any putative third-person account of it.
In quantum computing, quantum supremacy or quantum advantage is the goal of demonstrating that a programmable quantum computer can solve a problem that no classical computer can solve in any feasible amount of time, irrespective of the usefulness of the problem. The term was coined by John Preskill in 2012, but the concept dates to Yuri Manin's 1980 and Richard Feynman's 1981 proposals of quantum computing.
Continuous-variable (CV) quantum information is the area of quantum information science that makes use of physical observables, like the strength of an electromagnetic field, whose numerical values belong to continuous intervals. One primary application is quantum computing. In a sense, continuous-variable quantum computation is "analog", while quantum computation using qubits is "digital." In more technical terms, the former makes use of Hilbert spaces that are infinite-dimensional, while the Hilbert spaces for systems comprising collections of qubits are finite-dimensional. One motivation for studying continuous-variable quantum computation is to understand what resources are necessary to make quantum computers more powerful than classical ones.
The Eastin–Knill theorem is a no-go theorem that states: "No quantum error correcting code can have a continuous symmetry which acts transversely on physical qubits". In other words, no quantum error correcting code can transversely implement a universal gate set, where a transversal logical gate is one that can be implemented on a logical qubit by the independent action of separate physical gates on corresponding physical qubits.
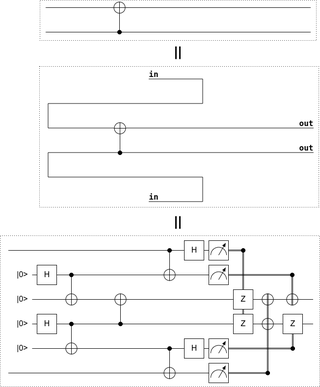
Quantum gate teleportation is a quantum circuit construction where a gate is applied to target qubits by first applying the gate to an entangled state and then teleporting the target qubits through that entangled state.
Cross-entropy benchmarking is a quantum benchmarking protocol which can be used to demonstrate quantum supremacy. In XEB, a random quantum circuit is executed on a quantum computer multiple times in order to collect a set of samples in the form of bitstrings . The bitstrings are then used to calculate the cross-entropy benchmark fidelity via a classical computer, given by
This glossary of quantum computing is a list of definitions of terms and concepts used in quantum computing, its sub-disciplines, and related fields.








