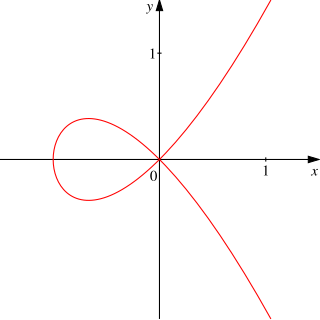Algebraic geometry is a branch of mathematics which uses abstract algebraic techniques, mainly from commutative algebra, to solve geometrical problems. Classically, it studies zeros of multivariate polynomials; the modern approach generalizes this in a few different aspects.
In commutative algebra, the prime spectrum of a commutative ring R is the set of all prime ideals of R, and is usually denoted by ; in algebraic geometry it is simultaneously a topological space equipped with the sheaf of rings .
In mathematics, Hilbert's Nullstellensatz is a theorem that establishes a fundamental relationship between geometry and algebra. This relationship is the basis of algebraic geometry. It relates algebraic sets to ideals in polynomial rings over algebraically closed fields. This relationship was discovered by David Hilbert, who proved the Nullstellensatz in his second major paper on invariant theory in 1893.
In mathematics, complex geometry is the study of geometric structures and constructions arising out of, or described by, the complex numbers. In particular, complex geometry is concerned with the study of spaces such as complex manifolds and complex algebraic varieties, functions of several complex variables, and holomorphic constructions such as holomorphic vector bundles and coherent sheaves. Application of transcendental methods to algebraic geometry falls in this category, together with more geometric aspects of complex analysis.

In algebraic geometry and commutative algebra, the Zariski topology is a topology defined on geometric objects called varieties. It is very different from topologies that are commonly used in real or complex analysis; in particular, it is not Hausdorff. This topology was introduced primarily by Oscar Zariski and later generalized for making the set of prime ideals of a commutative ring a topological space.

In mathematics, the concept of a projective space originated from the visual effect of perspective, where parallel lines seem to meet at infinity. A projective space may thus be viewed as the extension of a Euclidean space, or, more generally, an affine space with points at infinity, in such a way that there is one point at infinity of each direction of parallel lines.

Commutative algebra, first known as ideal theory, is the branch of algebra that studies commutative rings, their ideals, and modules over such rings. Both algebraic geometry and algebraic number theory build on commutative algebra. Prominent examples of commutative rings include polynomial rings; rings of algebraic integers, including the ordinary integers ; and p-adic integers.
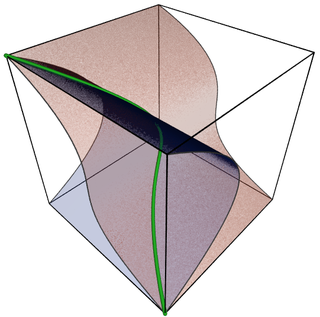
Algebraic varieties are the central objects of study in algebraic geometry, a sub-field of mathematics. Classically, an algebraic variety is defined as the set of solutions of a system of polynomial equations over the real or complex numbers. Modern definitions generalize this concept in several different ways, while attempting to preserve the geometric intuition behind the original definition.
In mathematics and specifically in algebraic geometry, the dimension of an algebraic variety may be defined in various equivalent ways.
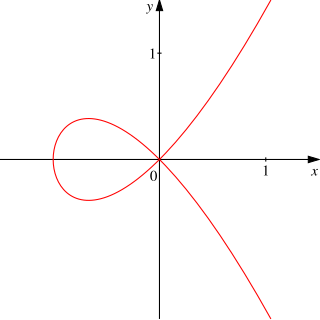
In algebraic geometry, an affine algebraic set is the set of the common zeros over an algebraically closed field k of some family of polynomials in the polynomial ring An affine variety or affine algebraic variety, is an affine algebraic set such that the ideal generated by the defining polynomials is prime.
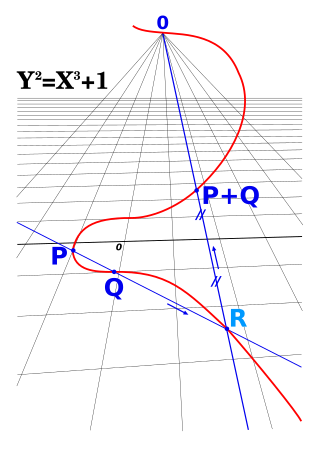
In algebraic geometry, a projective variety is an algebraic variety that is a closed subvariety of a projective space. That is, it is the zero-locus in of some finite family of homogeneous polynomials that generate a prime ideal, the defining ideal of the variety.
In mathematics, specifically algebraic geometry, a scheme is a structure that enlarges the notion of algebraic variety in several ways, such as taking account of multiplicities and allowing "varieties" defined over any commutative ring.
In mathematics, especially in algebraic geometry and the theory of complex manifolds, coherent sheaves are a class of sheaves closely linked to the geometric properties of the underlying space. The definition of coherent sheaves is made with reference to a sheaf of rings that codifies this geometric information.
In mathematics, algebraic spaces form a generalization of the schemes of algebraic geometry, introduced by Michael Artin for use in deformation theory. Intuitively, schemes are given by gluing together affine schemes using the Zariski topology, while algebraic spaces are given by gluing together affine schemes using the finer étale topology. Alternatively one can think of schemes as being locally isomorphic to affine schemes in the Zariski topology, while algebraic spaces are locally isomorphic to affine schemes in the étale topology.
Affine geometry, broadly speaking, is the study of the geometrical properties of lines, planes, and their higher dimensional analogs, in which a notion of "parallel" is retained, but no metrical notions of distance or angle are. Affine spaces differ from linear spaces in that they do not have a distinguished choice of origin. So, in the words of Marcel Berger, "An affine space is nothing more than a vector space whose origin we try to forget about, by adding translations to the linear maps." Accordingly, a complex affine space, that is an affine space over the complex numbers, is like a complex vector space, but without a distinguished point to serve as the origin.
In algebraic geometry, a morphism between algebraic varieties is a function between the varieties that is given locally by polynomials. It is also called a regular map. A morphism from an algebraic variety to the affine line is also called a regular function. A regular map whose inverse is also regular is called biregular, and the biregular maps are the isomorphisms of algebraic varieties. Because regular and biregular are very restrictive conditions – there are no non-constant regular functions on projective varieties – the concepts of rational and birational maps are widely used as well; they are partial functions that are defined locally by rational fractions instead of polynomials.
In algebraic geometry, a Zariski–Riemann space or Zariski space of a subring k of a field K is a locally ringed space whose points are valuation rings containing k and contained in K. They generalize the Riemann surface of a complex curve.
The concept of a Projective space plays a central role in algebraic geometry. This article aims to define the notion in terms of abstract algebraic geometry and to describe some basic uses of projective spaces.
In algebraic geometry, a smooth scheme over a field is a scheme which is well approximated by affine space near any point. Smoothness is one way of making precise the notion of a scheme with no singular points. A special case is the notion of a smooth variety over a field. Smooth schemes play the role in algebraic geometry of manifolds in topology.
This is a glossary of algebraic geometry.