In organic chemistry, amines (, UK also ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group (these may respectively be called alkylamines and arylamines; amines in which both types of substituent are attached to one nitrogen atom may be called alkylarylamines). Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline; see Category:Amines for a list of amines. Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as chloramine (NClH2); see Category:Inorganic amines.

Allotropy or allotropism is the property of some chemical elements to exist in two or more different forms, in the same physical state, known as allotropes of the elements. Allotropes are different structural modifications of an element; the atoms of the element are bonded together in a different manner. For example, the allotropes of carbon include diamond, graphite, graphene, and fullerenes. The term allotropy is used for elements only, not for compounds. The more general term, used for any crystalline material, is polymorphism. Allotropy refers only to different forms of an element within the same phase ; differences in these states alone would not constitute examples of allotropy.
Chemistry is the scientific discipline involved with elements and compounds composed of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during a reaction with other substances.
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and plus (+) and minus (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulas can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than are chemical names and structural formulas.
Inorganic chemistry deals with the synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers all chemical compounds except the myriad organic compounds, which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, as there is much overlap in the subdiscipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry, including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medications, fuels, and agriculture.

Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkaline, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and tin, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide, cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term "metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are representative members of this class. The field of organometallic chemistry combines aspects of traditional inorganic and organic chemistry.
In chemistry, the term transition metal has three possible meanings:

In chemistry, a zwitterion, formerly called a dipolar ion, is a molecule with two or more functional groups, of which at least one has a positive and one has a negative electrical charge and the net charge of the entire molecule is zero. Because they contain at least one positive and one negative charge, zwitterions are also sometimes called inner salts. The charges on the different functional groups balance each other out, and the molecule as a whole is electrically neutral. The pH where this happens is known as the isoelectric point.
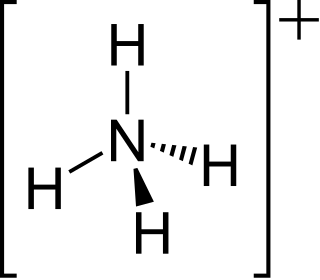
The ammonium cation is a positively charged polyatomic ion with the chemical formula NH+
4. It is formed by the protonation of ammonia (NH3). Ammonium is also a general name for positively charged or protonated substituted amines and quaternary ammonium cations (NR+
4), where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups (indicated by R).

In materials chemistry, a binary phase is a chemical compound containing two different elements. Some binary phases compounds are molecular, e.g. carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). More typically binary phase refers to extended solids. Famous examples are the two polymorphs of zinc sulfide.
A carbon–carbon bond is a covalent bond between two carbon atoms. The most common form is the single bond: a bond composed of two electrons, one from each of the two atoms. The carbon–carbon single bond is a sigma bond and is formed between one hybridized orbital from each of the carbon atoms. In ethane, the orbitals are sp3-hybridized orbitals, but single bonds formed between carbon atoms with other hybridizations do occur. In fact, the carbon atoms in the single bond need not be of the same hybridization. Carbon atoms can also form double bonds in compounds called alkenes or triple bonds in compounds called alkynes. A double bond is formed with an sp2-hybridized orbital and a p-orbital that is not involved in the hybridization. A triple bond is formed with an sp-hybridized orbital and two p-orbitals from each atom. The use of the p-orbitals forms a pi bond.

An intermetallic is a type of metallic alloy that forms a solid-state compound exhibiting defined stoichiometry and ordered crystal structure.

Quaternary ammonium cations, also known as quats, are positively charged polyatomic ions of the structure NR+
4, R being an alkyl group or an aryl group. Unlike the ammonium ion and the primary, secondary, or tertiary ammonium cations, the quaternary ammonium cations are permanently charged, independent of the pH of their solution. Quaternary ammonium salts or quaternary ammonium compounds are salts of quaternary ammonium cations.
In chemistry, an arsenide is a compound of arsenic with a less electronegative element or elements. Many metals form binary compounds containing arsenic, and these are called arsenides. They exist with many stoichiometries, and in this respect arsenides are similar to phosphides.

A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. A chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., without breaking chemical bonds. Chemical substances can be simple substances, chemical compounds, or alloys. Chemical elements may or may not be included in the definition, depending on expert viewpoint.

In chemistry, a quaternary compound is or has a cation consisting of a central positively charged atom with four substituents, especially organic groups, discounting hydrogen atoms.

Actinide chemistry is one of the main branches of nuclear chemistry that investigates the processes and molecular systems of the actinides. The actinides derive their name from the group 3 element actinium. The informal chemical symbol An is used in general discussions of actinide chemistry to refer to any actinide. All but one of the actinides are f-block elements, corresponding to the filling of the 5f electron shell; lawrencium, a d-block element, is also generally considered an actinide. In comparison with the lanthanides, also mostly f-block elements, the actinides show much more variable valence. The actinide series encompasses the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through lawrencium.

In materials chemistry, a ternary phase is chemical compound containing three different elements. Some ternary phases compounds are molecular, e.g. chloroform (HCCl3). More typically ternary phases refer to extended solids. Famous example are the perovskites.












