The turkey vulture, also known in some North American regions as the turkey buzzard, and in some areas of the Caribbean as the John crow or carrion crow, is the most widespread of the New World vultures. One of three species in the genus Cathartes of the family Cathartidae, the turkey vulture ranges from southern Canada to the southernmost tip of South America. It inhabits a variety of open and semi-open areas, including subtropical forests, shrublands, pastures, and deserts.

Gran Canaria, also Grand Canary Island, is the third largest and second most populous island of the Canary Islands, an archipelago off the Atlantic coast of Northwest Africa which is part of Spain. As of 2019 the island had a population of 851,231 that constitutes approximately 40% of the population of the archipelago. Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, the capital of the island, is the biggest city of the Canary Islands and the ninth of Spain.

La Magdalena Contreras is one of the 16 administrative boroughs of the Federal District of Mexico City. As of the 2010 census, it has a population of 239,086 inhabitants and is the third-least populous of Mexico City's boroughs. It lies at an elevation of 2,365 m (7,759 ft) above sea level. It is named after two historically important communities—La Magdalena Atlitic and Colonia Contreras. The northern end of the borough is urbanized. The rest of Magdalena Contreras, with its mountains and ravines, is designated as a conservation zone. However, urban sprawl has put pressure on these conservation areas. In an effort to preserve the area's forests and natural resources, the borough government has started promoting ecotourism. The largest ecotourism park is Los Dinamos where canyons and ravines are cut by streams and freshwater springs that eventually form the Río Magdalena, Mexico City’s only remaining free-flowing river.

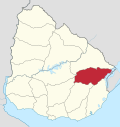
Cerro Largo Department is a department of Uruguay. Its capital is Melo. It is located in the east of the country, bordering Brazil to its northeast with Yaguaron River as the natural border, Treinta y Tres Department to its south, Durazno Department to its west and the departments of Tacuarembó and Rivera to its northwest with Negro River as its natural border with them.
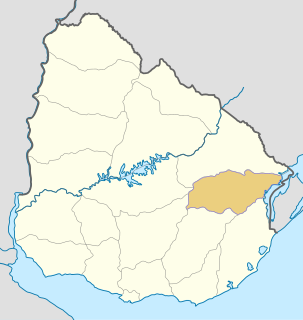
Treinta y Tres is a department of Uruguay. Its capital is Treinta y Tres. It is located in the east of the country, bordering the departments of Cerro Largo to the north, Durazno and Florida to the west, Lavalleja and Rocha to the south, while to its east is the lake Laguna Merín separating it from the southernmost end of Brazil.

The Calchaquí Valley is an area in the northwestern region of Argentina which crosses the provinces of Catamarca, Tucumán, Jujuy and Salta. It is best known for its contrast of colours and its unique geography that ranges from the mountain desert to the subtropical forest.

The lesser yellow-headed vulture also known as the savannah vulture, is a species of bird in the New World vulture family Cathartidae. It was considered to be the same species as the greater yellow-headed vulture until they were split in 1964. It is found in Mexico, Central America, and South America in seasonally wet or flooded lowland grassland, swamps, and heavily degraded former forest. It is a large bird, with a wingspan of 150–165 cm (59–65 in). The body plumage is black, and the head and neck, which are featherless, are pale orange with red or blue areas. It lacks a syrinx, so therefore its vocalizations are limited to grunts or low hisses.

The straight-billed reedhaunter is a South American bird species in the family Furnariidae.

The chestnut seedeater is a species of bird in the family Thraupidae. It is found in Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay.

The dark-throated seedeater is a bird species in the family Thraupidae. It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay.

The saffron-cowled blackbird is a species of bird in the family Icteridae, in the monotypic genus Xanthopsar. It is found in Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay.

Río Pastillo is a river in the municipality of Ponce, Puerto Rico. It is also known as Río Marueño in the area of the municipality where it runs through barrio Marueño. Together with Cañas River, Pastillo forms Matilde River. Pastillo is one of the 14 rivers in the municipality. The river originates at an altitude of 435 feet. Its tributaries are Quebrada Limon and Quebrada del Agua brooks and the river runs for 19 kilometers before feeding into Río Matilde at a height of 15 feet in Barrio Canas Urbano.

Pampa de Achala is the name given to a vast region that lies at the heart of the Sierras de Córdoba located within Sierras Pampeanas, and located in central-northwest of Argentina. It is a rugged area with little vegetation, lying over 1,500 m above sea level, and which has distinctive species, ecology, relief and hydrography. The region is protected by provincial law, and that this region basin is head of the vast majority of streams that run through the Córdoba.

Club de Golf del Uruguay is an Uruguayan sports and social club from the city of Montevideo. Although golf is the main sport of the institution, the club hosts a large variety of sports such as billar, basketball, basque pelota, fencing, football, futsal, karate, rugby union and swimming apart from other social activities.

Pilancones Natural Park is located in San Bartolomé de Tirajana municipality on the island of Gran Canaria, Spain. Its area is 5794.4 ha. It adjoins Roque Nublo country park to the north, and Fataga protected area to the east. The park plays an important role in soil protection and the replenishment of an aquifer, along which there are several ravines running southward which are of geomorphological interest and landscape value. The pine forests on hilltops are a well-preserved habitat with abundant bird life. The park also harbours several varieties of cactus and spurge, and a number of aquatic habitats. The park takes its name from natural pools, formerly known locally as pilancones, which remain after the runoff of water. Throughout the area there are threatened animal and plant species, and features of scientific interest.

El Chico National Park is a protected area in the State of Hidalgo, Mexico. It is one of the oldest protected areas in Mexico, as its foundation dates to 1898 when the then president of the republic, General Porfirio Díaz, by decree, created "Monte Vedado del Mineral del Chico". Since this date, the ancient conifer forests have been protected from the deforestation suffered in other parts of the country. Another decree followed in 1915 and still another by Presidential Agreement on 13 September 1922, which declared Monte Vedado to be cataloged as a forest reservation.

The Guayadeque ravine, in Spanish Barranco de Guayadeque, is a ravine-type valley located on the Spanish municipalities of Ingenio and Agüimes, in the province of Las Palmas on Grand Canary island, off the coast of Morocco.

The Juan Amarillo, Arzobispo, or Salitre River is a river on the Bogotá savanna and a left tributary of the Bogotá River in Colombia. The river originates from various quebradas in the Eastern Hills and flows into the Bogotá River at the largest of the wetlands of Bogotá, Tibabuyes, also called Juan Amarillo Wetland. The total surface area of the Juan Amarillo basin, covering the localities Usaquén, Chapinero, Santa Fe, Suba, Barrios Unidos, Teusaquillo, and Engativá, is 12,892 hectares. Together with the Fucha and Tunjuelo Rivers, the Juan Amarillo River forms part of the left tributaries of the Bogotá River in the Colombian capital.

The Bioma Pampa Quebradas del Norte is a protected ecological area in Uruguay, protected by UNESCO since 2. June 2014..:. This biological reserve consists out of a landscape with native grasses, streams and subtropical rainforests. The biosphere reserve has a surface area of 110.882 hectares, consisting of a mosaic of ecosystems.