
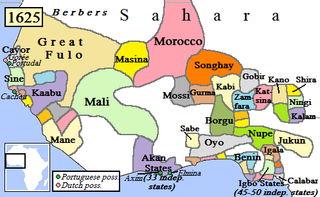
The Kingdom of Dahomey was a West African kingdom located within present-day Benin that existed from approximately 1600 until 1904. Dahomey developed on the Abomey Plateau amongst the Fon people in the early 17th century and became a regional power in the 18th century by conquering key cities on the Atlantic coast.

Vodun is a religion practiced by the Aja, Ewe, and Fon peoples of Benin, Togo, Ghana, and Nigeria.
The Akan are a meta-ethnicity living primarily in the countries of present-day Ghana and Ivory Coast in West Africa. The Akan language are a group of dialects within the Central Tano branch of the Potou–Tano subfamily of the Niger–Congo family. Subgroups of the Akan people include: the Agona, Akuapem, Akwamu, Akyem, Ashanti, Bono, Fante, Kwahu, Wassa, and Ahanta. The Akan subgroups all have cultural attributes in common; most notably the tracing of matrilineal descent, inheritance of property, and succession to high political office.

The Bono, also called the Brong and the Abron, are an Akan people of West Africa. Bonos are normally tagged Akan piesie or Akandifo of which Akan is a derivative name. Bono is the genesis and cradle of Akans. Bono is one of the largest ethnic group of Akan and are matrilineal people. Bono people speak the Bono Twi of Akan language. Twi language, thus the dialect of Bono is a derivative of a Bono King Nana Twi. In the late fifteenth century, the Bono people founded the Gyaaman kingdom as extension of Bono state in what is now Ghana and Côte d'Ivoire.

Efunroye Tinubu, born Ẹfúnpọ̀róyè Ọ̀ṣuntinúbú, was a powerful Yoruba female aristocrat, merchant, and slave trader in pre-colonial and colonial Nigeria. She was a politically and economically influential figure in Lagos during the reigns of Oba (monarchs) Adele, Dosunmu, Oluwole, and Akitoye, helping the latter two Oba gain political power. She was married to Oba Adele of Lagos, and she used his connections to establish a successful trade network with European merchants in slaves, tobacco, salt, cotton, palm oil, coconut oil, and firearms. She allegedly owned over 360 personal slaves.

Oba Esigie was an Oba (king) of Benin who ruled the ancient Benin Kingdom, now Benin City, Edo State, Nigeria.

Idia was the mother of Esigie, the Oba of Benin who ruled from 1504 to 1550. She played a significant role in the rise and reign of her son, being described as a great warrior who fought relentlessly before and during her son's reign as the oba (king) of the Edo people. Queen Idia was instrumental in securing the title of oba for Esigie following the death of his father Oba Ozolua. To that end, she raised an army to fight off his brother Arhuaran, who was subsequently defeated in battle. Esigie thus became the 17th Oba of Benin.

The Legends of Africa reflect a wide-ranging series of kings, queens, chiefs and other leaders from across the African continent including Mali, Benin, Ghana, Nigeria, Congo, Ethiopia, Eritrea and South Africa.
Oba means ″ruler″ in the Yoruba and Bini languages of West Africa. Kings in Yorubaland, a region which is in the modern republics of Benin, Nigeria and Togo, make use of it as a pre-nominal honorific. Examples of Yoruba bearers include Oba Ogunwusi of Ile-Ife, Oba Aladelusi of Akure, and Oba Akiolu of Lagos. An example of a Bini bearer is Oba Ewuare II of Benin.

The Asante Empire was an Akan state that lasted between 1701 to 1901, in what is now modern-day Ghana. It expanded from the Ashanti Region to include the Northern Region, Brong-Ahafo Region, Central Region, Eastern Region and Western Region of present-day Ghana as well as some parts of Ivory Coast and Togo. Due to the empire's military prowess, wealth, architecture, sophisticated hierarchy and culture, the Ashanti Empire has been extensively studied and has more historic records written by European, primarily British authors than any other indigenous culture of Sub-Saharan Africa.

In many parts of West Africa, there is an old chieftaincy tradition, and the Akan people have developed their own hierarchy, which exists alongside the democratic structure of the country. The Akan word for the ruler or one of his various courtiers is "Nana". In colonial times, Europeans translated it as "chief", but that is not an exact equivalent. Other sources speak of "kings", which is also not entirely correct, especially in the case of the said courtiers. The term "chief" has become common even among modern Ghanaians, though it would be more correct to use the expression "Nana" without translation wherever possible.
The Kingdom of Benin was a kingdom in what is now in southwestern Nigeria. It has no historical relation to the modern republic of Benin, which was historically known as Dahomey from the 17th century until 1975. The Kingdom of Benin's capital was Edo, now known as Benin City in Edo state, Nigeria. The Benin Kingdom was "one of the oldest and most developed states in the coastal hinterland of West Africa". It was formed out of the previous Edo Kingdom of Igodomigodo around the 11th century AD, and lasted until it was annexed by the British Empire in 1897. The Kingdom drew a significant source of its income from the slave trade.
Nigerian traditional rulers often derive their titles from the rulers of independent states or communities that existed before the formation of modern Nigeria. Although they do not have formal political power, in many cases they continue to command respect from their people and have considerable influence.
The Ondo Kingdom is a traditional state that traces its origins back for over 500 years, with its capital in Ode Ondo. Ondo Kingdom was established by Princess Pupupu, one the twins of Alafin Oluaso. Her mother was Queen Olu who later died at Ile oluji. The princess gave birth to twins in the era where twins were considered an abomination. They called them Ese Omo. One of the twins died at Epe near Ondo. There were wars in the town between 1865 to 1885 when people in the kingdom fled to Oke Opa. Three Osemawes were installed and died there. Before then the kingdom was ruled by the son of Pupupu called Airo. Airo went to Benin under the pupilage of his uncle Oba Eiseghie 1516 to train in the art of governance.
Hwanjile was a high priest and kpojito of the African Kingdom of Dahomey, in what is now Benin.

The Benin ivory mask is a miniature sculptural portrait in ivory of Idia, the first Iyoba of the 16th century Benin Empire, taking the form of a traditional African mask. The masks were looted by the British from the palace of the Oba of Benin in the Benin Expedition of 1897.
Unuamen also spelt Unuame is an ancient village community by Ovia river in Ovia North-East Local Government Area of Edo State, Nigeria. Unuame is about 15 kilometres (9 mi) from Benin City and 20 kilometres (12 mi) from Benin Airport. Unuame is one of the ancestral homes of Oba Esigie's maternal grandfather and home town to some group of Binis. The people of Unuame have remained loyal to the monarch since the establishment of the ancient Kingdom of Benin. Being a part of the Kingdom of Benin, Unuame is at the heart of the tropical rainforest in the southern part of Nigeria, way to the west of the delta of the Niger River and inland from the coast.
Nana Amba Eyiaba I, known non-formally as Eunice Amba Amoah, is a Ghanaian queen mother from the Effutu Municipal District of Central Region, Ghana. She is the former Director of Education for Central Region. From 2004 to 2010, Eyiaba was appointed by President John Kufuor to serve as a member of the national Electoral Commission of Ghana, co-organizing and supervising the parliamentary and presidential elections of 2004 and 2008.

The Iyoba of Benin is an important female titleholder in the chieftaincy system of the Kingdom of Benin, a Nigerian traditional state. She is otherwise known in English as the Queen Mother.

Mama Ametor Hoebuadzu II is the Paramount Queen of the Alavanyo Traditional Area in the Volta region of Ghana.














