
Yukon is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It is the third-least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 45,148 as of 2023. However, Whitehorse, the territorial capital, is the largest settlement in any of the three territories.

The Yukon River is a major watercourse of northwestern North America. From its source in British Columbia, Canada, it flows through Canada's territory of Yukon. The lower half of the river continues westward through the U.S. state of Alaska. The river is 3,190 kilometres (1,980 mi) long and empties into the Bering Sea at the Yukon–Kuskokwim Delta. The average flow is 6,400–7,000 m3/s (230,000–250,000 cu ft/s). The total drainage area is 833,000 km2 (321,500 sq mi), of which 323,800 km2 (125,000 sq mi) lies in Canada. The total area is more than 25% larger than Texas or Alberta.

Tutchone is an Athabaskan language spoken by the Northern and Southern Tutchone First Nations in central and southern regions of Yukon Territory, Canada. Tutchone belongs to the Northern Athabaskan linguistic subfamily and has two primary varieties, Southern and Northern. Although they are sometimes considered separate languages, Northern and Southern Tutchone speakers are generally able to understand each other in conversation, albeit with moderate difficulty.

The Chinook salmon is the largest and most valuable species of Pacific salmon. Its common name is derived from the Chinookan peoples. Other vernacular names for the species include king salmon, Quinnat salmon, Tsumen, spring salmon, chrome hog, Blackmouth, and Tyee salmon. The scientific species name is based on the Russian common name chavycha (чавыча).

The Taku River is a river running from British Columbia, Canada, to the northwestern coast of North America, at Juneau, Alaska. The river basin spreads across 27,500 square kilometres (10,600 sq mi). The Taku is a very productive salmon river and its drainage basin is primarily wilderness.

Carmacks is a village in Yukon, Canada, on the Yukon River along the Klondike Highway, and at the west end of the Robert Campbell Highway from Watson Lake. The population is 588, an increase from the Census of 2016. It is the home of the Little Salmon/Carmacks First Nation, a Northern Tutchone-speaking people.

Schwatka Lake is a reservoir created by the damming of the Yukon River in Whitehorse, Yukon, completed in 1958. The dam provides electrical power generation and is operated by the Yukon Energy Corporation. The White Horse Rapids, which gave the city its name, are now under the lake. The lake was named after Frederick Schwatka, a US Army Lieutenant who was first to explore the total length of the Yukon River.

The Klondike River is a tributary of the Yukon River in Canada that gave its name to the Klondike Gold Rush and the Klondike region of the Yukon Territory. The Klondike River rises in the Ogilvie Mountains and flows into the Yukon River at Dawson City.

Atlin Lake is the largest natural lake in the province of British Columbia, Canada. The northern tip of the lake is in Yukon, as is Little Atlin Lake. However, most of the lake lies within the Atlin District of British Columbia. Atlin Lake is generally considered to be the source of the Yukon River although it is drained via the short Atlin River into Tagish Lake. Atlin Lake was named by the Tlingit First Nation people of the region.
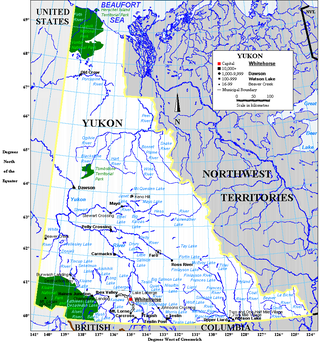
Yukon is in the northwestern corner of Canada and is bordered by Alaska and the Northwest Territories. The sparsely populated territory abounds with natural scenery, snowmelt lakes and perennial white-capped mountains, including many of Canada's highest mountains. The territory's climate is Arctic in territory north of Old Crow, subarctic in the region, between Whitehorse and Old Crow, and humid continental climate south of Whitehorse and in areas close to the British Columbia border. Most of the territory is boreal forest with tundra being the main vegetation zone only in the extreme north and at high elevations.
The Little Salmon/Carmacks First Nation is a First Nation in the central Yukon Territory in Canada. Its original population centre was Little Salmon, Yukon, but most of its citizens live in Carmacks, Yukon. The language originally spoken by the Little Salmon/Carmacks First Nation people was Northern Tutchone. They call themselves Tagé Cho Hudän.
The Kaska or Kaska Dena are a First Nations people of the Athabaskan-speaking ethnolinguistic group living mainly in northern British Columbia and the southeastern Yukon in Canada. The Kaska language, originally spoken by the Kaska, is an Athabaskan language.

The Northern Tutchone are a First Nations people of the Athabaskan-speaking ethnolinguistic group living mainly in the central Yukon in Canada.

Tsútswecw Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada, located northeast of Kamloops and northwest of Salmon Arm. It stretches along the banks of the Adams River, between the south end of Adams Lake and the western portion of Shuswap Lake.

Teslin Lake is a large lake spanning the border between British Columbia and Yukon, Canada. It is one of a group of large lakes in the region of far northwestern BC, east of the upper Alaska Panhandle, which are the southern extremity of the basin of the Yukon River, and which are known in Yukon as "the Southern Lakes". The lake is fed and drained primarily by the Teslin River, south and north, but is also fed from the east by the Jennings River and the Swift River, and from the west by the Hayes River.
The Taku River Tlingit First Nation are the band government of the Inland Tlingit in far northern British Columbia, Canada and also in Yukon. They comprise two ḵwaan (tribes) of the Tlingit people, who are otherwise coastal, the Áa Tlein Ḵwáan of the Atlin Lake area and the Deisleen Ḵwáan of Teslin Lake, whose main focus is the Teslin Tlingit Council in Teslin, Yukon. Their band offices are in Atlin, British Columbia.

The Indigenous peoples of Yukon are ethnic groups who, prior to European contact, occupied the former countries now collectively known as Yukon. While most First Nations in the Canadian territory are a part of the wider Dene Nation, there are Tlingit and Métis nations that blend into the wider spectrum of indigeneity across Canada. Traditionally hunter-gatherers, indigenous peoples and their associated nations retain close connections to the land, the rivers and the seasons of their respective countries or homelands. Their histories are recorded and passed down the generations through oral traditions. European contact and invasion brought many changes to the native cultures of Yukon including land loss and non-traditional governance and education. However, indigenous people in Yukon continue to foster their connections with the land in seasonal wage labour such as fishing and trapping. Today, indigenous groups aim to maintain and develop indigenous languages, traditional or culturally-appropriate forms of education, cultures, spiritualities and indigenous rights.














