In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula R−C(=O)−NR′R″, where R, R', and R″ represent any group, typically organyl groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is part of the main chain of a protein, and an isopeptide bond when it occurs in a side chain, as in asparagine and glutamine. It can be viewed as a derivative of a carboxylic acid with the hydroxyl group replaced by an amine group ; or, equivalently, an acyl (alkanoyl) group joined to an amine group.
Alkylation is a chemical reaction that entails transfer of an alkyl group. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene. Alkylating agents are reagents for effecting alkylation. Alkyl groups can also be removed in a process known as dealkylation. Alkylating agents are often classified according to their nucleophilic or electrophilic character. In oil refining contexts, alkylation refers to a particular alkylation of isobutane with olefins. For upgrading of petroleum, alkylation produces a premium blending stock for gasoline. In medicine, alkylation of DNA is used in chemotherapy to damage the DNA of cancer cells. Alkylation is accomplished with the class of drugs called alkylating antineoplastic agents.

The aldol reaction is a reaction in organic chemistry that combines two carbonyl compounds to form a new β-hydroxy carbonyl compound. Its simplest form might involve the nucleophilic addition of an enolized ketone to another:

Lithium aluminium hydride, commonly abbreviated to LAH, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Li[AlH4] or LiAlH4. It is a white solid, discovered by Finholt, Bond and Schlesinger in 1947. This compound is used as a reducing agent in organic synthesis, especially for the reduction of esters, carboxylic acids, and amides. The solid is dangerously reactive toward water, releasing gaseous hydrogen (H2). Some related derivatives have been discussed for hydrogen storage.

In organic chemistry, an imine is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond. The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bonds. Imines are common in synthetic and naturally occurring compounds and they participate in many reactions.
In organic chemistry, the Knoevenagel condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction named after German chemist Emil Knoevenagel. It is a modification of the aldol condensation.

Diethyl azodicarboxylate, conventionally abbreviated as DEAD and sometimes as DEADCAT, is an organic compound with the structural formula CH3CH2−O−C(=O)−N=N−C(=O)−O−CH2CH3. Its molecular structure consists of a central azo functional group, RN=NR, flanked by two ethyl ester groups. This orange-red liquid is a valuable reagent but also quite dangerous and explodes upon heating. Therefore, commercial shipment of pure diethyl azodicarboxylate is prohibited in the United States and is carried out either in solution or on polystyrene particles.
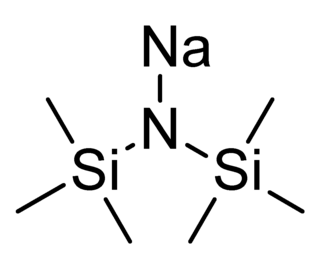
Sodium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide is the organosilicon compound with the formula NaN(Si 3)2. This species, usually called NaHMDS, is a strong base used for deprotonation reactions or base-catalyzed reactions. Its advantages are that it is commercially available as a solid and it is soluble not only in ethers, such as THF or diethyl ether, but also in aromatic solvents, like benzene and toluene by virtue of the lipophilic TMS groups.

The Curtius rearrangement, first defined by Theodor Curtius in 1885, is the thermal decomposition of an acyl azide to an isocyanate with loss of nitrogen gas. The isocyanate then undergoes attack by a variety of nucleophiles such as water, alcohols and amines, to yield a primary amine, carbamate or urea derivative respectively. Several reviews have been published.

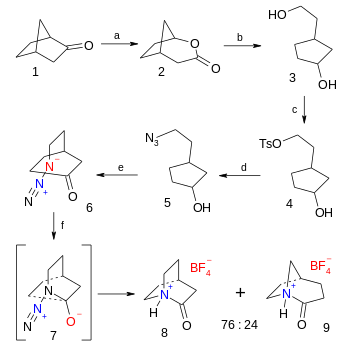
In organic chemistry, an anti-Bredt molecule is a bridged molecule with a double bond at the bridgehead. Bredt's rule is the empirical observation that such molecules only form in large ring systems. For example, two of the following norbornene isomers violate Bredt's rule, and are too unstable to prepare:
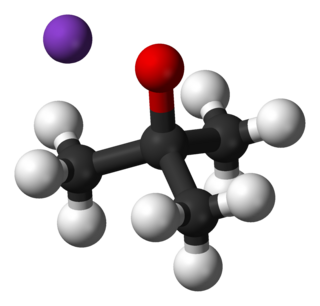
Potassium tert-butoxide (or potassium t-butoxide) is a chemical compound with the formula [(CH3)3COK]n (abbr. KOtBu). This colourless solid is a strong base (pKa of conjugate acid around 17), which is useful in organic synthesis. The compound is often depicted as a salt, and it often behaves as such, but its ionization depends on the solvent.

Indium(III) chloride is the chemical compound with the formula InCl3 which forms a tetrahydrate. This salt is a white, flaky solid with applications in organic synthesis as a Lewis acid. It is also the most available soluble derivative of indium. This is one of three known indium chlorides.
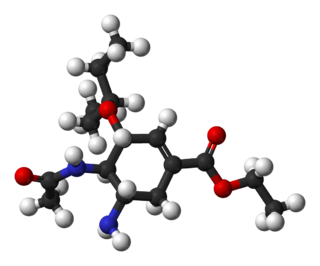
Oseltamivir total synthesis concerns the total synthesis of the antiinfluenza drug oseltamivir marketed by Hoffmann-La Roche under the trade name Tamiflu. Its commercial production starts from the biomolecule shikimic acid harvested from Chinese star anise and from recombinant E. coli. Control of stereochemistry is important: the molecule has three stereocenters and the sought-after isomer is only 1 of 8 stereoisomers.
The total synthesis of quinine, a naturally-occurring antimalarial drug, was developed over a 150-year period. The development of synthetic quinine is considered a milestone in organic chemistry although it has never been produced industrially as a substitute for natural occurring quinine. The subject has also been attended with some controversy: Gilbert Stork published the first stereoselective total synthesis of quinine in 2001, meanwhile shedding doubt on the earlier claim by Robert Burns Woodward and William Doering in 1944, claiming that the final steps required to convert their last synthetic intermediate, quinotoxine, into quinine would not have worked had Woodward and Doering attempted to perform the experiment. A 2001 editorial published in Chemical & Engineering News sided with Stork, but the controversy was eventually laid to rest once and for all when Robert Williams and coworkers successfully repeated Woodward's proposed conversion of quinotoxine to quinine in 2007.
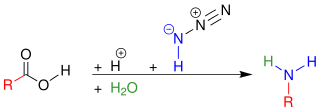
In organic chemistry, the Schmidt reaction is an organic reaction in which an azide reacts with a carbonyl derivative, usually an aldehyde, ketone, or carboxylic acid, under acidic conditions to give an amine or amide, with expulsion of nitrogen. It is named after Karl Friedrich Schmidt (1887–1971), who first reported it in 1924 by successfully converting benzophenone and hydrazoic acid to benzanilide. The intramolecular reaction was not reported until 1991 but has become important in the synthesis of natural products. The reaction is effective with carboxylic acids to give amines (above), and with ketones to give amides (below).

The Mukaiyama taxol total synthesis published by the group of Teruaki Mukaiyama of the Tokyo University of Science between 1997 and 1999 was the 6th successful taxol total synthesis. The total synthesis of Taxol is considered a hallmark in organic synthesis.
The Stieglitz rearrangement is a rearrangement reaction in organic chemistry which is named after the American chemist Julius Stieglitz (1867–1937) and was first investigated by him and Paul Nicholas Leech in 1913. It describes the 1,2-rearrangement of trityl amine derivatives to triaryl imines. It is comparable to a Beckmann rearrangement which also involves a substitution at a nitrogen atom through a carbon to nitrogen shift. As an example, triaryl hydroxylamines can undergo a Stieglitz rearrangement by dehydration and the shift of a phenyl group after activation with phosphorus pentachloride to yield the respective triaryl imine, a Schiff base.

N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethylformamidinium chloride is the simplest representative of quaternary formamidinium cations of the general formula [R2N−CH=NR2]+ with a chloride as a counterion in which all hydrogen atoms of the protonated formamidine [HC(=NH2)NH2]+ are replaced by methyl groups.

Diethyl oxomalonate is the diethyl ester of mesoxalic acid (ketomalonic acid), the simplest oxodicarboxylic acid and thus the first member (n = 0) of a homologous series HOOC–CO–(CH2)n–COOH with the higher homologues oxalacetic acid (n = 1), α-ketoglutaric acid (n = 2) and α-ketoadipic acid (n = 3) (the latter a metabolite of the amino acid lysine). Diethyl oxomalonate reacts because of its highly polarized keto group as electrophile in addition reactions and is a highly active reactant in pericyclic reactions such as the Diels-Alder reactions, cycloadditions or ene reactions. At humid air, mesoxalic acid diethyl ester reacts with water to give diethyl mesoxalate hydrate and the green-yellow oil are spontaneously converted to white crystals.

3-Dimethylaminoacrolein is an organic compound with the formula Me2NC(H)=CHCHO. It is a pale yellow water-soluble liquid. The compound has a number of useful and unusual properties, e.g. it "causes a reversal of the hypnotic effect of morphine in mice" and has a "stimulating effect in humans".