
A quasar is an extremely luminous active galactic nucleus (AGN). It is sometimes known as a quasi-stellar object, abbreviated QSO. The emission from an AGN is powered by a supermassive black hole with a mass ranging from millions to tens of billions of solar masses, surrounded by a gaseous accretion disc. Gas in the disc falling towards the black hole heats up and releases energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation. The radiant energy of quasars is enormous; the most powerful quasars have luminosities thousands of times greater than that of a galaxy such as the Milky Way. Quasars are usually categorized as a subclass of the more general category of AGN. The redshifts of quasars are of cosmological origin.

In physics, a redshift is an increase in the wavelength, and corresponding decrease in the frequency and photon energy, of electromagnetic radiation. The opposite change, a decrease in wavelength and increase in frequency and energy, is known as a blueshift, or negative redshift. The terms derive from the colours red and blue which form the extremes of the visible light spectrum. The main causes of electromagnetic redshift in astronomy and cosmology are the relative motions of radiation sources, which give rise to the relativistic Doppler effect, and gravitational potentials, which gravitationally redshift escaping radiation. All sufficiently distant light sources show cosmological redshift corresponding to recession speeds proportional to their distances from Earth, a fact known as Hubble's law that implies the universe is expanding.

The observable universe is a ball-shaped region of the universe comprising all matter that can be observed from Earth or its space-based telescopes and exploratory probes at the present time; the electromagnetic radiation from these objects has had time to reach the Solar System and Earth since the beginning of the cosmological expansion. Initially, it was estimated that there may be 2 trillion galaxies in the observable universe. That number was reduced in 2021 to only several hundred billion based on data from New Horizons. Assuming the universe is isotropic, the distance to the edge of the observable universe is roughly the same in every direction. That is, the observable universe is a spherical region centered on the observer. Every location in the universe has its own observable universe, which may or may not overlap with the one centered on Earth.

Abell 2218 is a large cluster of galaxies over 2 billion light-years away in the constellation Draco.
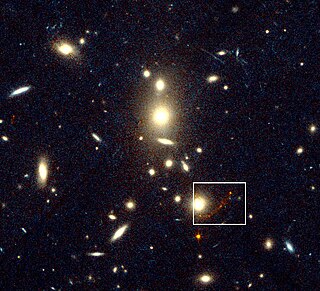
CL 1358+62 is a galaxy cluster located at z=0.33 redshift. Behind the cluster, lensed into a red arc is an infant galaxy that was the farthest object in the observable universe for a few months. It had a record redshift of z=4.92 and was discovered on July 31, 1997 by M. Franx and G. Illingsworth. It is located approximately 26 billion light years from Earth. Its redshift was measured by the Keck Telescope shortly after its discovery. Along with G1, another galaxy also lensed, was found to be at z=4.92. The pair of galaxies were the first things other than quasars to have the title of most distant object found, since the 1960s. The pair of galaxies remained the most distant objects known until the discovery of RD1 at z=5.34, the first object to exceed redshift 5.

UDFy-38135539 is the Hubble Ultra Deep Field (UDF) identifier for a galaxy which was calculated as of October 2010 to have a light travel time of 13.1 billion years with a present proper distance of around 30 billion light-years.

ULAS J1120+0641 was the most distant known quasar when discovered in 2011, surpassed in 2017 by ULAS J1342+0928. ULAS J1120+0641 was the first quasar discovered beyond a redshift of z = 7. Its discovery was reported in June 2011.

MACS0647-JD is a galaxy with a redshift of about z = 10.7, equivalent to a light travel distance of 13.26 billion light-years. If the distance estimate is correct, it formed about 427 million years after the Big Bang.

z8_GND_5296 is a dwarf galaxy discovered in October 2013 which has the highest redshift that has been confirmed through the Lyman-alpha emission line of hydrogen, placing it among the oldest and most distant known galaxies at approximately 13.1 billion light-years (4.0 Gpc) from Earth. It is "seen as it was at a time just 700 million years after the Big Bang [...] when the universe was only about 5 percent of its current age of 13.8 billion years". The galaxy is at a redshift of 7.51, and it is a neighbour to what was announced then as the second-most distant galaxy with a redshift of 7.2. The galaxy in its observable timeframe was producing stars at a phenomenal rate, equivalent in mass to about 330 Suns per year.

The XDCPJ0044.0-2033 (Gioello) galaxy cluster at redshift z=1.579 was discovered in the archive of the XMM-Newton mission, as part of the XMM-Newton Distant Cluster Project (XDCP) and first published by Santos et al. 2011. Gioiello is the most distant massive galaxy cluster that has been found and studied today. This massive galaxy cluster contains 400 trillion times the mass of the Sun and is located 9.6 billion light years away from Earth. The name Gioiello, meaning "jewel" in Italian, was given to this massive galaxy cluster because an image of the cluster contains many beautiful pink, purple, and red sparkling colors from the hot X-ray–emitting gas and other star-forming galaxies within the cluster.

EGSY8p7 (EGSY-2008532660) is a distant galaxy in the constellation of Boötes, with a spectroscopic redshift of z = 8.68, a light travel distance of 13.2 billion light-years from Earth. Therefore, at an age of 13.2 billion years, it is observed as it existed 570 million years after the Big Bang, which occurred 13.8 billion years ago, using the W. M. Keck Observatory. In July 2015, EGSY8p7 was announced as the oldest and most-distant known object, surpassing the previous record holder, EGS-zs8-1, which was determined in May 2015 as the oldest and most distant object. In March 2016, Pascal Oesch, one of the discoverers of EGSY8p7, announced the discovery of GN-z11, an older and more distant galaxy.

GN-z11 is a high-redshift galaxy found in the constellation Ursa Major. It is among the farthest known galaxies from Earth ever discovered. The 2015 discovery was published in a 2016 paper headed by Pascal Oesch and Gabriel Brammer. Up until the discovery of JADES-GS-z13-0 in 2022 by the James Webb Space Telescope, GN-z11 was the oldest and most distant known galaxy yet identified in the observable universe, having a spectroscopic redshift of z = 10.957, which corresponds to a proper distance of approximately 32 billion light-years. Data published in 2024 established that the galaxy contains the most distant, and therefore earliest, black hole known in the universe.
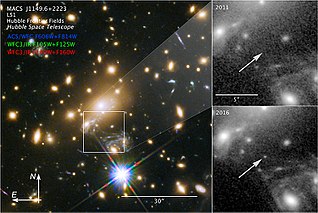
MACS J1149 Lensed Star 1, also known as Icarus, is a blue supergiant star observed through a gravitational lens. It is the seventh most distant individual star to have been detected so far, at approximately 14 billion light-years from Earth. Light from the star was emitted 4.4 billion years after the Big Bang. According to co-discoverer Patrick Kelly, the star is at least a hundred times more distant than the next-farthest non-supernova star observed, SDSS J1229+1122, and is the first magnified individual star seen.

HD1 is a proposed high-redshift galaxy, which is considered to be one of the earliest and most distant known galaxies yet identified in the observable universe. The galaxy, with an estimated redshift of approximately z = 13.27, is seen as it was about 324 million years after the Big Bang, which was 13.787 billion years ago. It has a light-travel distance of 13.463 billion light-years from Earth, and, due to the expansion of the universe, a present proper distance of 33.288 billion light-years.

JADES-GS-z13-0 is a high-redshift Lyman-break galaxy discovered by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) during NIRCam imaging for the JWST Advanced Deep Extragalactic Survey (JADES) on 29 September 2022. Spectroscopic observations by JWST's NIRSpec instrument in October 2022 confirmed the galaxy's redshift of z = 13.2 to a high accuracy, establishing it as the oldest and most distant spectroscopically-confirmed galaxy known as of 2023, with a light-travel distance of 13.4 billion years. Due to the expansion of the universe, its present proper distance is 33.6 billion light-years.
F200DB-045 is a candidate high-redshift galaxy, with an estimated redshift of approximately z = 20.4, corresponding to 168 million years after the Big Bang. If confirmed, it would be one of the earliest and most distant known galaxies observed.














