Related Research Articles

RDX (abbreviation of "Research Department eXplosive") or hexogen, among other names, is an organic compound with the formula (O2N2CH2)3. It is a white solid without smell or taste, widely used as an explosive. Chemically, it is classified as a nitroamine alongside HMX, which is a more energetic explosive than TNT. It was used widely in World War II and remains common in military applications.

Dynamite is an explosive made of nitroglycerin, sorbents, and stabilizers. It was invented by the Swedish chemist and engineer Alfred Nobel in Geesthacht, Northern Germany, and patented in 1867. It rapidly gained wide-scale use as a more robust alternative to black powder.

An explosive is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An explosive charge is a measured quantity of explosive material, which may either be composed solely of one ingredient or be a mixture containing at least two substances.
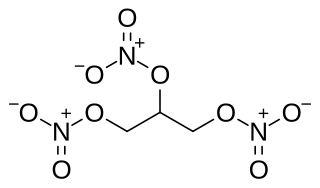
Nitroglycerin (NG), also known as trinitroglycerin (TNG), nitro, glyceryl trinitrate (GTN), or 1,2,3-trinitroxypropane, is a dense, colorless, oily, explosive liquid most commonly produced by nitrating glycerol with white fuming nitric acid under conditions appropriate to the formation of the nitric acid ester. Chemically, the substance is an organic nitrate compound rather than a nitro compound, but the traditional name is retained. Invented in 1847 by Ascanio Sobrero, nitroglycerin has been used ever since as an active ingredient in the manufacture of explosives, namely dynamite, and as such it is employed in the construction, demolition, and mining industries. Since the 1880s, it has been used by militaries as an active ingredient and gelatinizer for nitrocellulose in some solid propellants such as cordite and ballistite. It is a major component in double-based smokeless propellants used by reloaders. Combined with nitrocellulose, hundreds of powder combinations are used by rifle, pistol, and shotgun reloaders.

Trinitrotoluene, more commonly known as TNT, more specifically 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene, and by its preferred IUPAC name 2-methyl-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H2(NO2)3CH3. TNT is occasionally used as a reagent in chemical synthesis, but it is best known as an explosive material with convenient handling properties. The explosive yield of TNT is considered to be the standard comparative convention of bombs and asteroid impacts. In chemistry, TNT is used to generate charge transfer salts.

Cordite is a family of smokeless propellants developed and produced in the United Kingdom since 1889 to replace black powder as a military propellant. Like modern gunpowder, cordite is classified as a low explosive because of its slow burning rates and consequently low brisance. These produce a subsonic deflagration wave rather than the supersonic detonation wave produced by brisants, or high explosives. The hot gases produced by burning gunpowder or cordite generate sufficient pressure to propel a bullet or shell to its target, but not so quickly as to routinely destroy the barrel of the gun.

Royal Ordnance Factory (ROF) Bridgwater was a factory between the villages of Puriton and Woolavington in the Sedgemoor district of Somerset, UK that produced high explosives for munitions. It was slightly above sea level, between the 5 and 10 metre contour lines on Ordnance Survey maps. BAE Systems closed it when decommissioning was completed in July 2008.

Amatol is a highly explosive material made from a mixture of TNT and ammonium nitrate. The British name originates from the words ammonium and toluene. Similar mixtures were known as Schneiderite in France. Amatol was used extensively during World War I and World War II, typically as an explosive in military weapons such as aircraft bombs, shells, depth charges, and naval mines. It was eventually replaced with alternative explosives such as Composition B, Torpex, and Tritonal.

A shell, in a military context, is a projectile whose payload contains an explosive, incendiary, or other chemical filling. Originally it was called a bombshell, but "shell" has come to be unambiguous in a military context. Modern usage sometimes includes large solid kinetic projectiles, which are more properly termed shot. Solid shot may contain a pyrotechnic compound if a tracer or spotting charge is used.
An Explosive ROF was a UK Government-owned Royal Ordnance Factory (ROF), which specialised in manufacturing explosives during and after World War II. Note: In World War I, the name used in the UK for Government-owned explosives factories was National Explosives Factory; and the Cordite factory at Gretna was known as HM Factory, Gretna.
Royal Ordnance Factories (ROFs) was the collective name of the UK government's munitions factories during and after the Second World War. Until privatisation, in 1987, they were the responsibility of the Ministry of Supply, and later the Ministry of Defence.
A filling factory was a manufacturing plant that specialised in filling various munitions, such as bombs, shells, cartridges, pyrotechnics, and screening smokes. In the United Kingdom, during both world wars of the 20th century, the majority of the employees were women.

The Royal Ordnance Factory was a WW2 Ministry of Supply Explosive Factory. It is sited adjacent to the village of Bishopton in Renfrewshire, Scotland. The factory was built to manufacture the propellant cordite for the British Army and the Royal Air Force. It also later produced cordite for the Royal Navy. The Ministry of Works were responsible for the site. It was the biggest munitions factory the MOD had, with up to 20,000 workers.
The Royal Ordnance Factory (ROF) Ranskill was a United Kingdom Ministry of Supply, World War II, Explosive ROF. It was built to manufacture cordite and the site was located adjacent to what is now known as the East Coast Main Line railway at Ranskill, Nottinghamshire, just north of the town of Retford.
Minol is a military explosive developed by the Admiralty early in the Second World War to augment supplies of trinitrotoluene (TNT) and RDX, which were in short supply. The aluminium component in Minol significantly prolongs the explosive pulse, making it ideal for use in underwater naval weapons where munitions with a longer explosive pulse are more destructive than those with high brisance. Minol cannot be used in weapons fired from gun barrels because there is a risk of detonation when subjected to over 250 gs of acceleration. Typically, four Minol formulas were used. All percentages shown are by weight:

The Royal Gunpowder Mills are a former industrial site in Waltham Abbey, England. It was one of three Royal Gunpowder Mills in the United Kingdom. Waltham Abbey is the only site to have survived virtually intact.

Diethylene glycol dinitrate (DEGDN) is an explosive nitrated alcohol ester with the formula C4H8N2O7. While chemically similar to numerous other high explosives, pure diethylene glycol dinitrate is difficult to ignite or detonate. Ignition typically requires localized heating to the decomposition point unless the DEGDN is first atomized.

Methylammonium nitrate is an explosive chemical with the molecular formula CH6N2O3, alternately CH3NH3+NO3−. It is the salt formed by the neutralization of methylamine with nitric acid. This substance is also known as methylamine nitrate and monomethylamine nitrate, not to be confused with methyl nitramine or monomethyl nitramine.

The 1924 Nixon Nitration Works disaster was an explosion and fire that claimed many lives and destroyed several square miles of New Jersey factories. It began on March 1, 1924, about 11:15 a.m., when an explosion destroyed a building in Nixon, New Jersey used for processing ammonium nitrate. The explosion touched off fires in surrounding buildings in the Nixon Nitration Works that contained other highly flammable materials. The disaster killed twenty people, destroyed forty buildings, and demolished the "tiny industrial town of Nixon, New Jersey."

Apache Nitrogen Products began in 1920 as an American manufacturer of nitroglycerin-based explosives (dynamite) for the mining industry and other regional users of dynamite. It occupies a historic location in Cochise County, Arizona, and is one of the county's largest employers. The company changed its name to Apache Nitrogen Products in 1990.
References
- Reader, W.J. (1970). Imperial Chemical Industries. A History. Volume One. The Forerunners 1870 - 1926. London: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-215937-2.
- Hay, Ian (1948). R.O.F: The Story of the Royal Ordnance Factories 1939 - 1948. London: His Majesty's Stationery Office.