
Haile Selassie I was Emperor of Ethiopia from 1930 to 1974. He rose to power as Regent Plenipotentiary of Ethiopia (Enderase) for Empress Zewditu from 1916 until 1930. Haile Selassie is widely considered a defining figure in modern Ethiopian history, and the major figure of Rastafari, a religious movement in Jamaica that emerged shortly after he became emperor in the 1930s. Before he rose to power he defeated Ras Gugsa Welle Bitul of Begemder at the Battle of Anchem in 1928. He was a member of the Solomonic dynasty, which claims to trace its lineage to Emperor Menelik I, a legendary figure believed by the claimants to be the son of King Solomon and the Queen of Sheba, who they name as Makeda.

Addis Ababa is the capital and largest city of Ethiopia. In the 2007 census, the city's population was estimated to be 2,739,551 inhabitants. Addis Ababa is a highly developed and important cultural, artistic, financial and administrative centre of Ethiopia.

Mengistu Haile Mariam is an Ethiopian former politician and former army officer who was the head of state of Ethiopia from 1977 to 1991 and General Secretary of the Workers' Party of Ethiopia from 1984 to 1991. He was the chairman of the Derg, the socialist military junta that governed Ethiopia, from 1977 to 1987, and the president of the People's Democratic Republic of Ethiopia (PDRE) from 1987 to 1991.

Addis Ababa University (AAU) is a national university located in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. It is the oldest university in Ethiopia. AAU has thirteen campuses. Twelve of these are situated in Addis Ababa, and one is located in Bishoftu, about 45 kilometres (28 mi) away. AAU has several associated research institutions including the Institute of Ethiopian Studies. The Ministry of Education admits qualified students to AAU based on their score on the Ethiopian University Entrance Examination (EUEE).

Dire Dawa is a city in eastern Ethiopia near the Oromia and Somali Region border and one of two chartered cities in Ethiopia. Dire Dawa alongside present-day Sitti Zone were a part of the Dire Dawa autonomous region stipulated in the 1987 Ethiopian Constitution until 1993 when it was split by the federal government into a separately administered chartered city.

Nekemte, also spelled as Neqemte, is a market city and separate woreda in western Ethiopia. Located in the East Welega Zone of the Oromia Region, Nekemte has a latitude and longitude of 9°5′N36°33′E and an elevation of 2,088 meters.
The Ethiopian Democratic Union or EDU, also known as Teranafit, was one of the political parties that formed in opposition to the Derg regime of Ethiopia. It merged with the Ethiopian Democratic Party to form the Ethiopian Democratic Unity Party.

The Ethiopian Evangelical Church Mekane Yesus is a Lutheran denomination in Ethiopia. It is the largest member church of the Lutheran World Federation. It is a Lutheran denomination with some Pentecostal influence and one Presbyterian-leaning synod, with a large Pietistic following.

The mass media in Ethiopia consist of radio, television and the Internet, which remain under the control of the Ethiopian government, as well as private newspapers and magazines. Ten radio broadcast stations, eight AM and two shortwave, are licensed to operate in Ethiopia. The major radio broadcasting stations include Radio Fana a private station, Radio Voice of One Free Ethiopia, and the Voice of the Revolution of Tigray. The only terrestrial (broadcast) television networks are government owned and include EBC and other regional stations. In keeping with government policy, radio broadcasts occur in a variety of languages including Amharic, Afaan Oromo, Tigrigna, and more. There are also many video sharing websites which are a popular way of getting information as well as entertainment in Ethiopia.

The Ethiopian Civil War was a civil war in Ethiopia and present-day Eritrea, fought between the Ethiopian military junta known as the Derg and Ethiopian-Eritrean anti-government rebels from 12 September 1974 to 28 May 1991.

The history of Addis Ababa, capital of Ethiopia, formally begins with the founding of the city in the 19th century by Ethiopian Emperor Menelik II and his wife Empress Taytu Betul. In its first years the city was more like a military encampment than a town. The central focus was the emperor’s palace, which was surrounded by the dwellings of his troops and of his innumerable retainers. In the 1920s, Addis Ababa experienced a significant economic upturn, marked by a surge in the number of middle-class-owned buildings, including stone houses furnished with imported European furniture. The middle class also introduced newly manufactured automobiles and expanded banking institutions. Urbanization and modernization persisted during the Italian occupation, guided by a masterplan aimed at transforming Addis Ababa into a more "colonial" city, a trajectory that continued beyond the occupation. Subsequent master plans, formulated from the 1940s onward with the input of European consultants, focused on the development of monuments, civic structures, satellite cities, and the inner city.

The 1960 Ethiopian coup d'etat attempt was perpetrated against Emperor Haile Selassie on 13 December 1960. The Council of the Revolution, four conspirators led by brothers Germame Neway and Brigadier General Mengistu Neway, commander of the Kebur Zabagna, sought to overthrow the Emperor during a state visit to Brazil in order to install a progressive government. The coup leaders declared the beginning of a new government under the rule of Haile Selassie's eldest son, Crown Prince Asfaw Wossen, that would address the numerous economic and social problems Ethiopia faced. The Council gained control of most of the capital city, Addis Ababa, and took several ministers and other important people hostage. After its initial success, the majority of the military and populace quickly aligned against the coup, and by 17 December loyalists had regained control of Addis Ababa. At least 300 people were killed during the coup, including most of the conspirators.
The following is a historical events of Addis Ababa, the capital of Ethiopia, including its formation prior to 20th century by chronology.
Radio Voice of Revolutionary Ethiopia was the former Radio Voice of the Gospel in Addis Abeba.

Hachalu Hundessa was an Ethiopian singer, songwriter, and civil rights activist. Hachalu played a significant role in the 2014–2016 Oromo protests that led to Abiy Ahmed taking charge of the Oromo Democratic Party and Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front, and subsequently becoming prime minister of Ethiopia in 2018.
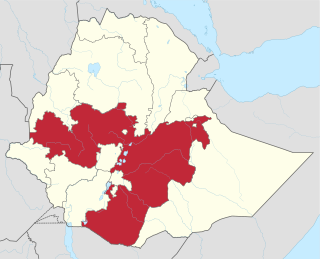
The Hachalu Hundessa riots were a series of civil unrest that occurred in the Oromia Region of Ethiopia, more specifically in the hot spot of Addis Ababa, Shashamene and Ambo following the killing of the Oromo musician Hachalu Hundessa on 29 June 2020. The riots lead to the deaths of at least 239 people according to initial police reports. Peaceful protests against Hachalu's killing have been held by Oromos abroad as well. The Ethiopian Human Rights Commission (EHRC) found in its 1 January 2021 full report that part of the killings were a crime against humanity, with deliberate, widespread systematic killing of civilians by organised groups. The EHRC counted 123 deaths, 76 of which it attributed to security forces.

Opposition to Haile Selassie relied largely of internal administration of his country. While Haile Selassie made attempt to modernize the country and brought to global power since Italy's occupation in 1936–41, the later administration met with negative public attitude especially among educated people in universities and peasants.

On 12 September 1974, Emperor Haile Selassie was deposed by the Coordinating Committee of the Armed Forces, Police, and Territorial Army, a Soviet-backed military junta that consequently ruled Ethiopia as the Derg until 28 May 1991.

Radio in Ethiopia was introduced during Emperor Haile Selassie regime in 1933 where the first radio station was built in 1931. On 31 January 1935, with assistance of the Italian contractor firm Ansaldo, the largest and more powerful station was built and the Emperor delivered the first speech in the broadcast.
Woizero Elleni Mekuria or Ellene Mocria (1941–2021) was an Ethiopian radio and television journalist. After joining the External Service of the Voice of Ethiopia in 1962, she was Ethiopia's first female radio newscaster and producer. In 1964, when Ethiopian Television began broadcasting, she became Ethiopia's first woman television journalist.














