
River monitors are military craft designed to patrol rivers.

The Romanian Naval Forces is the principal naval branch of the Romanian Armed Forces and operates in the Black Sea and on the Danube. It traces its history back to 1860.

A spar torpedo is a weapon consisting of a bomb placed at the end of a long pole, or spar, and attached to a boat. The weapon is used by running the end of the spar into the enemy ship. Spar torpedoes were often equipped with a barbed spear at the end, so it would stick to wooden hulls. A fuse could then be used to detonate it.

The Romanian War of Independence is the name used in Romanian historiography to refer to the Russo-Turkish War (1877–78), following which Romania, fighting on the Russian side, gained independence from the Ottoman Empire. On April 16 [O.S. April 4] 1877, Romania and the Russian Empire signed a treaty at Bucharest under which Russian troops were allowed to pass through Romanian territory, with the condition that Russia respected the integrity of Romania. Consequently, the mobilization of the Romanian troops also began, and about 120,000 soldiers were massed in the south of the country to defend against an eventual attack of the Ottoman forces from south of the Danube. On April 24 [O.S. April 12] 1877, Russia declared war on the Ottoman Empire and its troops entered Romania through the newly built Eiffel Bridge, on their way to the Ottoman Empire. Due to great losses, the Russian Empire asked Romania to intervene. On July 24 [O.S. July 12] 1877, the first Romanian Army units crossed the Danube and joined forces with the Russian Army.

The Kingdom of Romania was neutral for the first two years of World War I, entering on the side of the Allied powers from 27 August 1916 until Central Power occupation led to the Treaty of Bucharest in May 1918, before reentering the war on 10 November 1918. It had the most significant oil fields in Europe, and Germany eagerly bought its petroleum, as well as food exports.

Naval warfare in the Mediterranean during World War I took place between the naval forces of the Entente and the Central Powers in the Mediterranean Sea between 1914 and 1918.

The Flămânda Offensive, which took place during World War I between 29 September and 5 October 1916, was an offensive across the Danube mounted by the Romanian 3rd Army supported by Romanian coastal artillery. Named after the hamlet of Flămânda, the battle represented a consistent effort by the Romanian Army to stop the Central Powers' southern offensive led by August von Mackensen. The battle ended as a tactical victory for the Central Powers.
The Royal Romanian Navy during World War I (1914–1918) was divided into two fleets and fought against the forces of the Central Powers. When Romania entered the war in August 1916, the Romanian Navy was officially divided as follows :

The Yugoslav monitor Drava was a river monitor operated by the Royal Yugoslav Navy between 1921 and 1941. She was originally built for the Austro-Hungarian Navy as the name ship of the Enns-class river monitors. As SMS Enns, she was part of the Danube Flotilla during World War I, and fought against the Serbian and Romanian armies from Belgrade to the lower Danube. In October 1915, she was covering an amphibious assault on Belgrade when she was holed below the waterline by a direct hit, and had to be towed to Budapest for repairs. After brief service with the Hungarian People's Republic at the end of the war, she was transferred to the newly created Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, and renamed Drava. She remained in service throughout the interwar period, but was not always in full commission due to budget restrictions.

The Yugoslav monitor Sava is a Temes-class river monitor that was built for the Austro-Hungarian Navy as SMS Bodrog. She fired the first shots of World War I just after 01:00 on 29 July 1914, when she and two other monitors shelled Serbian defences near Belgrade. She was part of the Danube Flotilla, and fought the Serbian and Romanian armies from Belgrade to the mouth of the Danube. In the closing stages of the war, she was the last monitor to withdraw towards Budapest, but was captured by the Serbs when she grounded on a sandbank downstream from Belgrade. After the war, she was transferred to the newly created Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, and renamed Sava. She remained in service throughout the interwar period, although budget restrictions meant she was not always in full commission.

Vardar was a Sava-class river monitor built for the Austro-Hungarian Navy as SMS Bosna, but was renamed SMS Temes (II) before she went into service. During World War I, she was the flagship of the Danube Flotilla, and fought the Serbian Army, the Romanian Navy and Army, and the French Army. She reverted to the name Bosna in May 1917, after the original SMS Temes was raised and returned to service. After brief service with the Hungarian People's Republic at the end of the war, she was transferred to the newly created Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, and renamed Vardar. She remained in service throughout the interwar period, although budget restrictions meant she was not always in full commission.

SMS Körös was the name ship of the Körös-class river monitors built for the Austro-Hungarian Navy. Completed in 1892, the ship was part of the Danube Flotilla, and fought various Allied forces from Belgrade down the Danube to the Black Sea during World War I. After brief service with the Hungarian People's Republic at the end of the war, she was transferred to the newly created Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, and renamed Morava. She remained in service throughout the interwar period, although budget restrictions meant she was not always in full commission.
The Danube Delta Campaign was a series of naval engagements between the Soviet Danube Flotilla and its Romanian counterpart in late June 1941, during the first days of Operation Barbarossa.

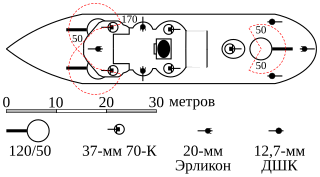
NMS Mihail Kogălniceanu was a Brătianu-class river monitor of the Romanian Navy. She saw service in both world wars, being the most successful vessel in her class of four ships. Like her three sisters, she was initially built as a river monitor, but in early 1918, she was converted to a sea-going monitor. During the Second Balkan War, she supported the Romanian crossing of the Danube into Bulgaria. During World War I, she carried out numerous bombardments against the Central Powers forces advancing along the shore of the Danube and carried out the last action of the Romanian Navy before the 11 November 1918 armistice. She later fought successfully against Bolshevik naval forces during the early months of the Russian Civil War, helping secure the Budjak region. During the interwar period, she contributed to the suppression of the Tatarbunary Uprising and was rearmed with longer main guns towards the end of the 1930s. During World War II, she fought several engagements against the Soviet Navy in the first month of the Eastern Front, but was ultimately sunk by Soviet aircraft shortly after Romania ceased hostilities against the Soviet Union, on 24 August 1944.

NMS Rândunica was the first torpedo boat of the Romanian Navy. A small British-built spar torpedo boat, she was commissioned in 1875 and fought during the Romanian War of Independence and during World War I.

The action of 26 June 1941 consisted in an engagement between the navies of the Soviet Union and the Kingdom of Romania, taking place on the Chilia branch of the Danube Delta, near the commune of Ceatalchioi. The action resulted in a Romanian victory and the withdrawal of the Soviet vessels, one of them being damaged and later captured.

The action off Măcin was a naval engagement between a torpedo boat of the Romanian Navy with a mixed Romanian-Russian crew, together with another 3 Russian torpedo boats, and a monitor of the Ottoman Navy which took place during the 1877-1878 Russo-Turkish War. It was the first time in history that a torpedo craft sank its target without being sunk itself.
The second Romanian campaign of World War I was one of the shortest military operations of the war, taking place during the last two days of the war, 10 and 11 November 1918. With no significant battles, it yielded important territorial as well as material gains for the Romanians, and was a prelude to the Hungarian–Romanian War, which would start two days later, on 13 November.
The Romanian Danube Flotilla is the oldest extant naval force on the Danube, dating since 1860, when the Romanian Navy was founded. It saw service during most of the wars involving Romania, and was the most powerful river naval force in the world during the Interwar period.

During World War I, the Black Sea Fleet of the Romanian Navy fought against the Central Powers forces of the German Empire, the Ottoman Empire and Austria-Hungary. The Romanian warships succeeded in defending the coast of the Danube Delta, corresponding to an area around the port of Sulina, while also aiding in the Delta's defense from inland Central Powers forces.

















