
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires, were one of the two main coalitions that fought in World War I (1914–1918). It consisted of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Bulgaria; this was also known as the Quadruple Alliance.

The Treaty of Trianon often referred to as the Peace Dictate of Trianon or Dictate of Trianon in Hungary, was prepared at the Paris Peace Conference and was signed on the one side by Hungary and, on the other, by the Allied and Associated Powers, in the Grand Trianon château in Versailles on 4 June 1920. It formally terminated the state of war issued from World War I between most of the Allies of World War I and the Kingdom of Hungary. The treaty is mostly famous due to the territorial changes induced on Hungary and recognizing its new international borders after the First World War.
Following the termination of hostilities in World War II, the Allies were in control of the defeated Axis countries. Anticipating the defeat of Germany, Italy and Japan, they had already set up the European Advisory Commission and a proposed Far Eastern Advisory Commission to make recommendations for the post-war period. Accordingly, they managed their control of the defeated countries through Allied Commissions, often referred to as Allied Control Commissions (ACC), consisting of representatives of the major Allies.

The Eastern Front or Eastern Theater, of World War I, was a theater of operations that encompassed at its greatest extent the entire frontier between Russia and Romania on one side and Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, the Ottoman Empire, and Germany on the other. It ranged from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Black Sea in the south, involved most of Eastern Europe, and stretched deep into Central Europe. The term contrasts with the Western Front, which was being fought in Belgium and France. Unlike the static warfare on the Western Front, the fighting on the geographically larger Eastern Front was more dynamic, often involving the flanking and encirclement of entire formations, and resulted in over 100,000 square miles of territory becoming occupied by a foreign power.

The Treaty of Bucharest (1918) was a peace treaty between Romania and the opposing Central Powers following the stalemate reached after the campaign of 1917. This left Romania isolated after Russia's unilateral exit from World War I.

Artur or Arthur Văitoianu was a Romanian general who served as a Prime Minister of Romania for about two months in 1919. During his mandate, the first elections of Greater Romania were held.

Ion Ionel Constantin Brătianu was a Romanian politician, leader of the National Liberal Party (PNL), Prime Minister of Romania for five terms, and Foreign Minister on several occasions; he was the eldest son of statesman and PNL leader Ion Brătianu, the brother of Vintilă and Dinu Brătianu, and the father of Gheorghe I. Brătianu. Ion I. C. Brătianu's political activities after World War I, including part of his third and fourth term, saw the unification of the Old Romanian Kingdom with Transylvania, Bukovina and Bessarabia. In 1923, he was elected an honorary member of the Romanian Academy.

The Treaty of Bucharest of 1916 was signed between Romania and the Entente Powers on 4 /17 August 1916 in Bucharest. The treaty stipulated the conditions under which Romania agreed to join the war on the side of the Entente, particularly territorial promises in Austria-Hungary. The signatories bound themselves to keep secret the contents of the treaty until a general peace was concluded.

The Kingdom of Romania was neutral for the first two years of World War I, entering on the side of the Allied powers from 27 August 1916 until Central Power occupation led to the Treaty of Bucharest in May 1918, before reentering the war on 10 November 1918. It had the most significant oil fields in Europe, and Germany eagerly bought its petroleum, as well as food exports.

The union of Transylvania with Romania was declared on 1 December [O.S. 18 November] 1918 by the assembly of the delegates of ethnic Romanians held in Alba Iulia. The Great Union Day, celebrated on 1 December, is a national holiday in Romania that celebrates this event. The holiday was established after the Romanian Revolution, and celebrates the unification not only of Transylvania, but also of Bessarabia and Bukovina and parts of Banat, Crișana and Maramureș with the Romanian Kingdom. Bessarabia and Bukovina had joined with the Kingdom of Romania earlier in 1918.

The Armistice of Salonica was the armistice signed at 10:50 p.m. on 29 September 1918 between Bulgaria and the Allied Powers at the General Headquarters of the Allied Army of the Orient in Thessaloniki. The armistice came into force at noon on 30 September 1918. The armistice would remain in effect until the conclusion of the Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine, the final general peace treaty, in November 1919.

The Kingdom of Bulgaria participated in World War I on the side of the Central Powers from 14 October 1915, when the country declared war on Serbia, until 30 September 1918, when the Armistice of Salonica came into effect.

The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was signed on 9 February 1918 between the Ukrainian People's Republic (UPR) and the Central Powers, ending Ukraine's involvement in World War I and recognizing the UPR's sovereignty. The treaty, which followed the armistice on the Eastern Front in December 1917, was signed at Brest-Litovsk. The peace delegation from Soviet Russia, led by Leon Trotsky, did not recognize the UPR delegation, which had been sent from the Central Rada in Kiev, instead recognizing a delegation from the Ukrainian People's Republic of Soviets in Kharkov.

The Hungarian–Romanian War was fought between Hungary and Romania from 13 November 1918 to 3 August 1919. The conflict had a complex background, with often contradictory motivations for the parties involved.
The Second Army was a field army of the Romanian Land Forces, created on 18 August 1916. Its successor is the 2nd Infantry Division.

The Armistice of Focșani was an agreement that ended the hostilities between Romania and the Central Powers in World War I. It was signed on 9 December 1917 in Focșani in Romania.
Events from the year 1917 in Romania.

On 15 December [O.S. 2 December] 1917, an armistice was signed between the Russian Republic led by the Bolsheviks on the one side, and the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Kingdom of Bulgaria, the German Empire and the Ottoman Empire—the Central Powers—on the other. The armistice took effect two days later, on 17 December [O.S. 4 December]. By this agreement, Russia de facto exited World War I, although fighting would briefly resume before the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was signed on 3 March 1918, and Russia made peace.
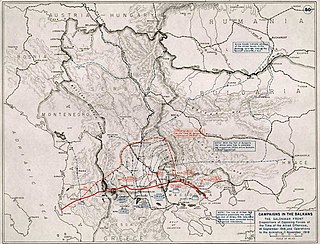
The Liberation of Serbia, Albania and Montenegro was a military action in the Balkans in the final weeks of World War I. Between 29 September and 11 November 1918, the Allied Army of the Orient liberated these three countries from occupation by the Central Powers.

The territorial evolution of Romania includes all the changes in the country's borders from its formation to the present day. The precedents of Romania as an independent state can be traced back to the 14th century, when the principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia were founded. Wallachia during its history lost several portions of its territory, either to the Ottomans or the Habsburgs. However, this land would be later essentially recovered in its entirety. Moldavia, on the other hand, suffered great territorial losses. In 1774, the Habsburgs invaded Bukovina and annexed it one year later, and in 1812, the Russian Empire took control of Bessarabia. Both territories were later exposed to powerful colonization policies. The principalities declared unification in 1859 as the Principality of Romania. This new state sought independence from the Ottoman Empire's vassalage, and in 1878, it fought a war against it alongside Russia. However, the latter would annex Southern Bessarabia, which was recovered decades before. Romania received Northern Dobruja as compensation, and would wage a war for the southern part against Bulgaria in 1913.

















