
Oomycota or oomycetes form a distinct phylogenetic lineage of fungus-like eukaryotic microorganisms. They are filamentous, microscopic, absorptive organisms that reproduce both sexually and asexually. Sexual reproduction of an oospore is the result of contact between hyphae of a male antheridia and female oogonia; this spore can overwinter and is known as a resting spore. Asexual reproduction is the formation of chlamydospore and sporangia producing zoospores. Oomycetes occupy both saprophytic and pathogenic lifestyles, and include some of the most notorious pathogens of plants, causing devastating diseases such as late blight of potato and sudden oak death. One oomycete, the mycoparasite Pythium oligandrum, is used for biocontrol, attacking plant pathogenic fungi. The oomycetes are also often referred to as water molds, although the water-preferring nature which led to that name is not true of most species, which are terrestrial pathogens. The Oomycota have a very sparse fossil record. A possible oomycete has been described from Cretaceous amber.

Quercus suber, commonly called the cork oak, is a medium-sized, evergreen oak tree in the section Quercus sect. Cerris. It is the primary source of cork for wine bottle stoppers and other uses, such as cork flooring and as the cores of cricket balls. It is native to southwest Europe and northwest Africa. In the Mediterranean basin the tree is an ancient species with fossil remnants dating back to the Tertiary period.
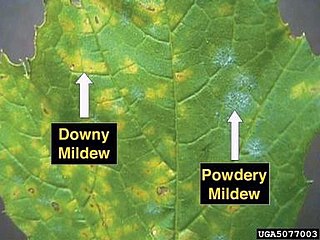
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease that affects a wide range of plants. Powdery mildew diseases are caused by many different species of fungi in the order Erysiphales, with Podosphaera xanthii being the most commonly reported cause. Erysiphe cichoracearum was formerly reported to be the primary causal organism throughout most of the world. Powdery mildew is one of the easier plant diseases to identify, as its symptoms are quite distinctive. Infected plants display white powdery spots on the leaves and stems. The lower leaves are the most affected, but the mildew can appear on any above-ground part of the plant. As the disease progresses, the spots get larger and denser as large numbers of asexual spores are formed, and the mildew may spread up and down the length of the plant.
In mycology, the terms teleomorph, anamorph, and holomorph apply to portions of the life cycles of fungi in the phyla Ascomycota and Basidiomycota:

Beauveria bassiana is a fungus that grows naturally in soils throughout the world and acts as a parasite on various arthropod species, causing white muscardine disease; it thus belongs to the entomopathogenic fungi. It is being used as a biological insecticide to control a number of pests such as termites, thrips, whiteflies, aphids and different beetles. Its use in the control of bedbugs and malaria-transmitting mosquitos is under investigation.

Uncinula necator is a fungus that causes powdery mildew of grape. It is a common pathogen of Vitis species, including the wine grape, Vitis vinifera. The fungus is believed to have originated in North America. European varieties of Vitis vinifera are more or less susceptible to this fungus. Uncinula necator infects all green tissue on the grapevine, including leaves and young berries. It can cause crop loss and poor wine quality if untreated. The sexual stage of this pathogen requires free moisture to release ascospores from its cleistothecia in the spring. However, free moisture is not needed for secondary spread via conidia; high atmospheric humidity is sufficient. Its anamorph is called Oidium tuckeri.

Erysiphales are an order of ascomycete fungi. The order contains one family, Erysiphaceae. Many of them cause plant diseases called powdery mildew.
Pichia is a genus of yeasts in the family Saccharomycetaceae with spherical, elliptical, or oblong acuminate cells. Pichia is a teleomorph, and forms hat-shaped, hemispherical, or round ascospores during sexual reproduction. The anamorphs of some Pichia species are Candida species. The asexual reproduction is by multilateral budding.
The fungal genus Pyrenophora includes 191 species, including the following plant pathogenic species: P. teres, P. graminea and P. tritici-repentis.

Rhizoctonia solani is a plant pathogenic fungus with a wide host range and worldwide distribution. It was discovered more than 100 years ago. R. solani frequently exists as thread-like growth on plants or in culture, and is considered a soil-borne pathogen. R. solani is best known to cause various plant diseases such as collar rot, root rot, damping off, and wire stem. R. solani attacks its hosts when they are in their early stages of development, such as seeds and seedlings, which are typically found in the soil. The pathogen is known to cause serious plant losses by attacking primarily the roots and lower stems of plants. Although it has a wide range of hosts, its main targets are herbaceous plants. R. solani would be considered a basidiomycete fungus if the teleomorph stage were more abundant. The pathogen is not currently known to produce any asexual spores (conidia), though it is considered to have an asexual lifecycle. Occasionally, sexual spores (basidiospores) are produced on infected plants. The disease cycle of R. solani is important in management and control of the pathogen.

Beauveria is a genus of asexually-reproducing fungi allied with the ascomycete family Cordycipitaceae. Its several species are typically insect pathogens. The sexual states (teleomorphs) of Beauveria species, where known, are species of Cordyceps.

Moniliophthora roreri is a basidiomycete fungus that causes frosty pod rot disease, one of the most serious problems for cacao production in Latin America. This disease and together with witches’ broom disease and black pod rot constitute the cacao disease trilogy. It causes serious losses in southwestern parts of South America; spores are dry and powdery and are spread easily by water movement, wind, or movement of pods; disease spread is highest during periods of high rainfall.

Quercus × warei is a hybrid oak tree in the genus Quercus. The tree is a hybrid of Quercus roburL. f. fastigiata(Lam.) O. Schwarz and Quercus bicolorWilld. . The hybrid is named for the American dendrologist George Ware, former Research Director at the Morton Arboretum, Illinois.

Chorioactis is a genus of fungus that contains the single species Chorioactis geaster. The mushroom is commonly known as the devil's cigar or the Texas star in the United States, while in Japan it is called kirinomitake( キリノミタケ). This extremely rare mushroom is notable for its unusual appearance and disjunct distribution: it is found only in select locales in Texas and Japan. The fruit body, which grows on the stumps or dead roots of cedar elms or dead oaks, somewhat resembles a dark brown or black cigar before it splits open radially into a starlike arrangement of four to seven leathery rays. The interior surface of the fruit body bears the spore-bearing tissue known as the hymenium, and is colored white to brown, depending on its age. The fruit body opening can be accompanied by a distinct hissing sound and the release of a smoky cloud of spores.

Erysiphe alphitoides is a species of fungus which causes powdery mildew on oak trees.
Phyllonorycter rostrispinosa is a moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is known from the islands of Kyūshū and Honshū in Japan.
Bucculatrix tsurubamella is a moth in the family Bucculatricidae. It was described by Kobayashi, Hirowatari and Kuroko in 2010. It is found on Honshu, the main island of Japan.
Homonopsis illotana is a species of moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found in China, Korea, Japan and the Russian Far East.
Hypatima teramotoi is a moth in the family Gelechiidae. It was described by Ueda in 2012. It is found in Japan.














