
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In amplitude modulation, the amplitude of the wave is varied in proportion to that of the message signal, such as an audio signal. This technique contrasts with angle modulation, in which either the frequency of the carrier wave is varied, as in frequency modulation, or its phase, as in phase modulation.

Frequency modulation (FM) is the encoding of information in a carrier wave by varying the instantaneous frequency of the wave. The technology is used in telecommunications, radio broadcasting, signal processing, and computing.
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a separate signal called the modulation signal that typically contains information to be transmitted. For example, the modulation signal might be an audio signal representing sound from a microphone, a video signal representing moving images from a video camera, or a digital signal representing a sequence of binary digits, a bitstream from a computer. The carrier is higher in frequency than the modulation signal. In radio communication the modulated carrier is transmitted through space as a radio wave to a radio receiver. Another purpose is to transmit multiple channels of information through a single communication medium, using frequency-division multiplexing (FDM). For example in cable television which uses FDM, many carrier signals, each modulated with a different television channel, are transported through a single cable to customers. Since each carrier occupies a different frequency, the channels do not interfere with each other. At the destination end, the carrier signal is demodulated to extract the information bearing modulation signal.

In radio communications, single-sideband modulation (SSB) or single-sideband suppressed-carrier modulation (SSB-SC) is a type of modulation used to transmit information, such as an audio signal, by radio waves. A refinement of amplitude modulation, it uses transmitter power and bandwidth more efficiently. Amplitude modulation produces an output signal the bandwidth of which is twice the maximum frequency of the original baseband signal. Single-sideband modulation avoids this bandwidth increase, and the power wasted on a carrier, at the cost of increased device complexity and more difficult tuning at the receiver.
A Compatible sideband transmission, also known as amplitude modulation equivalent (AME) or Single sideband reduced-carrier (SSB-RC), is a type of single sideband RF modulation in which the carrier is deliberately reinserted at a lower level after its normal suppression to permit reception by conventional AM receivers. The general convention is to filter the lower-sideband, and communicate using only the upper-sideband and a partial carrier.
Double-sideband suppressed-carrier transmission (DSB-SC) is transmission in which frequencies produced by amplitude modulation (AM) are symmetrically spaced above and below the carrier frequency and the carrier level is reduced to the lowest practical level, ideally being completely suppressed.
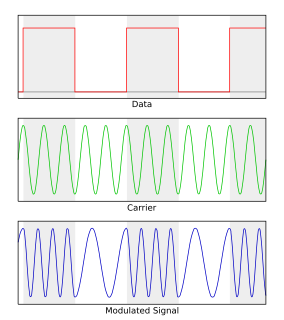
Frequency-shift keying (FSK) is a frequency modulation scheme in which digital information is transmitted through discrete frequency changes of a carrier signal. The technology is used for communication systems such as telemetry, weather balloon radiosondes, caller ID, garage door openers, and low frequency radio transmission in the VLF and ELF bands. The simplest FSK is binary FSK (BFSK). BFSK uses a pair of discrete frequencies to transmit binary information. With this scheme, the 1 is called the mark frequency and the 0 is called the space frequency.
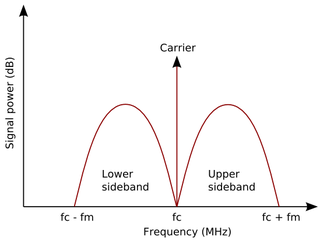
In radio communications, a sideband is a band of frequencies higher than or lower than the carrier frequency, that are the result of the modulation process. The sidebands carry the information transmitted by the radio signal. The sidebands comprise all the spectral components of the modulated signal except the carrier. The signal components above the carrier frequency constitute the upper sideband (USB), and those below the carrier frequency constitute the lower sideband (LSB). All forms of modulation produce sidebands.
Demodulation is extracting the original information-bearing signal from a carrier wave. A demodulator is an electronic circuit that is used to recover the information content from the modulated carrier wave. There are many types of modulation so there are many types of demodulators. The signal output from a demodulator may represent sound, images or binary data.
8VSB is the modulation method used for broadcast in the ATSC digital television standard. ATSC and 8VSB modulation is used primarily in North America; in contrast, the DVB-T standard uses COFDM.

In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a waveform that is modulated (modified) with an information-bearing signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave usually has a much higher frequency than the input signal does. The purpose of the carrier is usually either to transmit the information through space as an electromagnetic wave, or to allow several carriers at different frequencies to share a common physical transmission medium by frequency division multiplexing. The term originated in radio communication, where the carrier wave creates the waves which carry the information (modulation) through the air from the transmitter to the receiver. The term is also used for an unmodulated emission in the absence of any modulating signal.
C-QUAM is the method of AM stereo broadcasting used in Canada, the United States and most other countries. It was invented in 1977 by Norman Parker, Francis Hilbert, and Yoshio Sakaie, and published in an IEEE journal.
Independent sideband (ISB) is an AM single sideband mode which is used with some AM radio transmissions. Normally each sideband carries identical information, but ISB modulates two different input signals — one on the upper sideband, the other on the lower sideband. This is used in some kinds of AM stereo.

In a radio receiver, a beat frequency oscillator or BFO is a dedicated oscillator used to create an audio frequency signal from Morse code radiotelegraphy (CW) transmissions to make them audible. The signal from the BFO is mixed with the received signal to create a heterodyne or beat frequency which is heard as a tone in the speaker. BFOs are also used to demodulate single-sideband (SSB) signals, making them intelligible, by essentially restoring the carrier that was suppressed at the transmitter. BFOs are sometimes included in communications receivers designed for short wave listeners; they are almost always found in communication receivers for amateur radio, which often receive CW and SSB signals.
Amplitude-companded single-sideband (ACSB) is a narrowband modulation method using a single-sideband with a pilot tone, allowing an expander in the receiver to restore the amplitude that was severely compressed by the transmitter. The pilot tone serves as a frequency reference for the receiver, eliminating the signal distortion that would occur with single-sideband suppressed carrier modulation when the receiver is off frequency.
A radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves with frequencies between about 30 Hz and 300 GHz. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating current, the antenna radiates radio waves. Transmitters are necessary parts of all systems that use radio: radio and television broadcasting, cell phones, wireless networks, radar, two way radios like walkie talkies, radio navigation systems like GPS, remote entry systems, among numerous other uses.

In radio, a detector is a device or circuit that extracts information from a modulated radio frequency current or voltage. The term dates from the first three decades of radio (1888-1918). Unlike modern radio stations which transmit sound on an uninterrupted carrier wave, early radio stations transmitted information by radiotelegraphy. The transmitter was switched on and off to produce long or short periods of radio waves, spelling out text messages in Morse code. Therefore, early radio receivers had only to distinguish between the presence or absence of a radio signal. The device that performed this function in the receiver circuit was called a detector. A variety of different detector devices, such as the coherer, electrolytic detector, magnetic detector and the crystal detector, were used during the wireless telegraphy era until superseded by vacuum tube technology.
Dynamic carrier control (DCC) is a method of reducing power consumption in radio transmitters during periods of low audio activity or silence. It is a type of Modulation-Dependent Carrier Level control, or MDCL. All modern high-power (>50 kW) shortwave radio transmitters incorporate DCC of some kind, as well as some mediumwave (MW) transmitters.
A Nyquist filter is an electronic filter used in TV receivers to equalize the video characteristics. The filter is named after the Swedish–US engineer Harry Nyquist (1889–1976).






