Related Research Articles

Barge typically refers to a flat-bottomed vessel which does not have its own means of mechanical propulsion. Original use was on inland waterways, while modern use is on both inland and marine water environments. The first modern barges were pulled by tugs, but on inland waterways, most are pushed by pusher boats, or other vessels. The term barge has a rich history, and therefore there are many types of barges.

A waterway is any navigable body of water. Broad distinctions are useful to avoid ambiguity, and disambiguation will be of varying importance depending on the nuance of the equivalent word in other ways. A first distinction is necessary between maritime shipping routes and waterways used by inland water craft. Maritime shipping routes cross oceans and seas, and some lakes, where navigability is assumed, and no engineering is required, except to provide the draft for deep-sea shipping to approach seaports (channels), or to provide a short cut across an isthmus; this is the function of ship canals. Dredged channels in the sea are not usually described as waterways. There is an exception to this initial distinction, essentially for legal purposes, see under international waters.

A ship canal is a canal especially intended to accommodate ships used on the oceans, seas, or lakes to which it is connected.

The Intracoastal Waterway (ICW) is a 3,000-mile (4,800 km) inland waterway along the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico coasts of the United States, running from Massachusetts southward along the Atlantic Seaboard and around the southern tip of Florida, then following the Gulf Coast to Brownsville, Texas. Some sections of the waterway consist of natural inlets, saltwater rivers, bays, and sounds, while others are artificial canals. It provides a navigable route along its length without many of the hazards of travel on the open sea.

The Gulf Intracoastal Waterway (GIWW) is the portion of the Intracoastal Waterway located along the Gulf Coast of the United States. It is a navigable inland waterway running approximately 1,300 mi (2,100 km) from Saint Marks, Florida, to Brownsville, Texas.
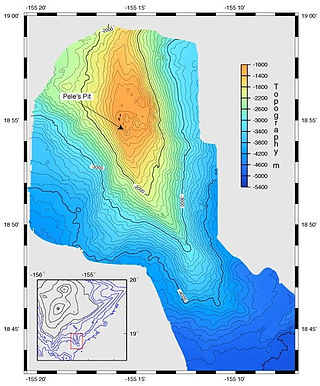
A bathymetric chart is a type of isarithmic map that depicts the submerged bathymetry and physiographic features of ocean and sea bottoms. Their primary purpose is to provide detailed depth contours of ocean topography as well as provide the size, shape and distribution of underwater features.
The head of navigation is the farthest point above the mouth of a river that can be navigated by ships. Determining the head of navigation can be subjective on many streams, as the point may vary greatly with the size or the draft of the ship being contemplated for navigation and the seasonal water level. On others, it is quite objective, being caused by a waterfall, a low bridge that is not a drawbridge, or a dam without navigation locks. Several rivers in a region may have their heads of navigation along a line called the fall line.

In geography, hydrography, and fluvial geomorphology, a thalweg or talweg is the line or curve of lowest elevation within a valley or watercourse. Its vertical position in maps is the nadir in the stream profile.

A riverboat is a watercraft designed for inland navigation on lakes, rivers, and artificial waterways. They are generally equipped and outfitted as work boats in one of the carrying trades, for freight or people transport, including luxury units constructed for entertainment enterprises, such as lake or harbour tour boats. As larger water craft, virtually all riverboats are especially designed and constructed, or alternatively, constructed with special-purpose features that optimize them as riverine or lake service craft, for instance, dredgers, survey boats, fisheries management craft, fireboats and law enforcement patrol craft.

In physical geography and hydrology, a channel is a landform on which a relatively narrow body of water is situated, such as a river, river delta or strait. While channel typically refers to a natural formation, the cognate term canal denotes a similar artificial structure.
Bathymetry is the study of underwater depth of ocean floors, lake floors, or river floors. In other words, bathymetry is the underwater equivalent to hypsometry or topography. The first recorded evidence of water depth measurements are from Ancient Egypt over 3000 years ago.

A body of water, such as a river, canal or lake, is navigable if it is deep, wide and calm enough for a water vessel to pass safely. Navigability is also referred to in the broader context of a body of water having sufficient under keel clearance for a vessel.
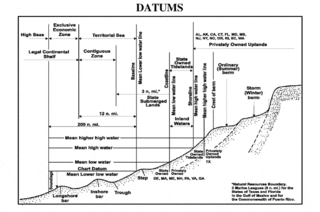
A chart datum is the water level surface serving as origin of depths displayed on a nautical chart and for reporting and predicting tide heights. A chart datum is generally derived from some tidal phase, in which case it is also known as a tidal datum. Common chart datums are lowest astronomical tide (LAT) and mean lower low water (MLLW). In non-tidal areas, e.g. the Baltic Sea, mean sea level (MSL) is used. A chart datum is a type of vertical datum and must not be confused with the horizontal datum for the chart.
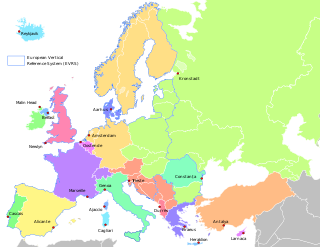
An ordnance datum (OD) is a vertical datum used by an ordnance survey as the basis for deriving altitudes on maps. A spot height may be expressed as above ordnance datum (AOD). Usually mean sea level (MSL) at a particular place is used for the datum.

River engineering is a discipline of civil engineering which studies human intervention in the course, characteristics, or flow of a river with the intention of producing some defined benefit. People have intervened in the natural course and behaviour of rivers since before recorded history—to manage the water resources, to protect against flooding, or to make passage along or across rivers easier. Since the Yuan Dynasty and Ancient Roman times, rivers have been used as a source of hydropower. From the late 20th century, the practice of river engineering has responded to environmental concerns broader than immediate human benefit. Some river engineering projects have focused exclusively on the restoration or protection of natural characteristics and habitats.

In geodesy, surveying, hydrography and navigation, vertical datum or altimetric datum is a reference coordinate surface used for vertical positions, such as the elevations of Earth-bound features and altitudes of satellite orbits and in aviation. In planetary science, vertical datums are also known as zero-elevation surface or zero-level reference.

The Eurasia Canal is a proposed 700-kilometre-long (430 mi) canal connecting the Caspian Sea to the Black Sea along the Kuma-Manych Depression. Currently, a chain of lakes and reservoirs and the shallow irrigation Kuma–Manych Canal are found along this route. If completed the canal would also link several landlocked countries in Asia with the open seas through the Bosphorus. If completed, the Eurasian Canal will become the second longest canal in the world after the Grand Canal in China.
This glossary of geography terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts used in geography and related fields, including Earth science, oceanography, cartography, and human geography, as well as those describing spatial dimension, topographical features, natural resources, and the collection, analysis, and visualization of geographic data. It is split across two articles:

The Kaub gauging station is a stream gauge located on the Rhine river in the German city of Kaub. It is a "decisive" water level measurement site for the Rhine, as Kaub is located at the shallowest part of the Middle Rhine and ships with freight from North Sea ports have to pass Kaub on their way to the industrial southwest of Germany. The gauge level does not directly correspond to the actual depth of the river ; instead, as is the case with most Rhine gauges, the actual depth of the navigation channel is defined as:
Fairway is a part of a water body containing the navigable channel, a route suitable for ships of the larger size.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Muilerman et al. 2018, p. 63.
- ↑ Wang, Lu; Xie, Ping; Xu, Chong-Yu; Sang, Yan-Fang; Chen, Jie; Yu, Tao (2 August 2021). "A framework for determining lowest navigable water levels with nonstationary characteristics" (PDF). Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment. 36 (2): 583–608. doi:10.1007/s00477-021-02058-1. eISSN 1436-3259. hdl:10852/92995. ISSN 1436-3240. S2CID 236780910.
- 1 2 3 4 Muilerman et al. 2018, p. 64.
- ↑ Muilerman et al. 2018, p. 14.
- ↑ UNECE 2017, p. 15.
- ↑ Muilerman et al. 2018, p. 67.