
Arable land is any land capable of being ploughed and used to grow crops. Alternatively, for the purposes of agricultural statistics, the term often has a more precise definition:
Arable land is the land under temporary agricultural crops, temporary meadows for mowing or pasture, land under market and kitchen gardens and land temporarily fallow. The abandoned land resulting from shifting cultivation is not included in this category. Data for 'Arable land' are not meant to indicate the amount of land that is potentially cultivable.

The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security. Its Latin motto, fiat panis, translates to "let there be bread". It was founded on 16th October 1945.

The following international wheat production statistics come from the Food and Agriculture Organization figures from FAOSTAT database, older from International Grains Council figures from the report "Grain Market Report".
CountrySTAT is a Web-based information technology system for food and agriculture statistics at the national and subnational levels. It provides decision-makers access to statistics across thematic areas such as production, prices, trade and consumption. This supports analysis, informed policy-making and monitoring with the goal of eradicating extreme poverty and hunger.

Agriculture in Nigeria is a branch of the economy in Nigeria, providing employment for about 35% of the population as of 2020. As reported by the FAO, agriculture remains the foundation of the Nigerian economy, despite the presence of oil in the country. It is the main source of livelihood for most Nigerians. The Agricultural sector is made up of four sub-sectors: Crop Production, Livestock, Forestry and Fishing.
The Food and Agriculture Organization Corporate Statistical Database (FAOSTAT) website disseminates statistical data collected and maintained by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). FAOSTAT data are provided as a time-series from 1961 in most domains for 245 countries in English, Spanish and French.
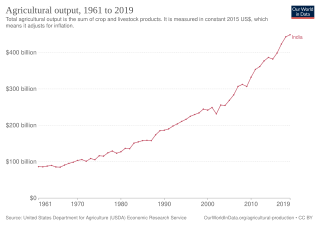
The history of agriculture in India dates back to the Indus Valley Civilization. India ranks second worldwide in farm outputs. As per 2018, agriculture employed more than 50% of the Indian work force and contributed 17–18% to country's GDP.

A crop is a plant that can be grown and harvested extensively for profit or subsistence. Crops may refer either to the harvested parts or to the harvest in a more refined state. Most crops are cultivated in agriculture or aquaculture. A crop may include macroscopic fungus, or macroscopic marine alga.

Agriculture in the Philippines is an important part of the economy of the Philippines with crops like rice, coconut and sugar dominating the production of crops and exports. It employs 23% of the Filipino workforce as of 2021, according to the World Bank.

Agricultural land is typically land devoted to agriculture, the systematic and controlled use of other forms of life—particularly the rearing of livestock and production of crops—to produce food for humans. It is generally synonymous with both farmland or cropland, as well as pasture or rangeland.

Georgia’s climate and soil have made agriculture one of its most productive economic sectors; the 18 percent of Georgian land that is arable provided 32 percent of the republic's NMP in 1990. In the Soviet period, swampy areas in the west were drained and arid regions in the east were salvaged by a complex irrigation system, allowing Georgian agriculture to expand production tenfold between 1918 and 1980. Production was hindered in the Soviet period, however, by the misallocation of agricultural land such as the assignment of prime grain fields to tea cultivation and excessive specialization. Georgia’s emphasis on labor-intensive crops such as tea and grapes kept the rural work force at an unsatisfactory level of productivity. Some 25 percent of the Georgian work force was engaged in agriculture in 1990; 37 percent had been so engaged in 1970.
The FAO geopolitical ontology is an ontology developed by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) to describe, manage and exchange data related to geopolitical entities such as countries, territories, regions and other similar areas.

Rice production in the Philippines is an important aspect of the country's food supply and economy. The Philippines is the 8th largest rice producer in the world, accounting for 2.8% of global rice production. The Philippines was also the world's largest rice importer in 2010.
The FAO Country Profiles are a multilingual web portal which repackages the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) vast archive of information on its global activities in agriculture and food security in a single area and catalogues it exclusively by country and thematic areas.
Mozambique has a variety of regional cropping patterns; agro-climatic zones range from arid and semi-arid to the sub-humid zones to the humid highlands. The most fertile areas are in the northern and central provinces, which have high agro-ecological potential and generally produce agricultural surpluses. Southern provinces have poorer soils and scarce rainfall, and are subject to recurrent droughts and floods.

The banana industry is an important part of the global industrial agrobusiness. About 15% of the global banana production goes to export and international trade for consumption in Western countries. They are grown on banana plantations primarily in the Americas.