
Mass production, also known as flow production or continuous production, is the production of large amounts of standardized products, including and especially on assembly lines. Together with job production and batch production, it is one of the three main production methods.

A factory,manufacturing plant or a production plant is an industrial site, usually consisting of buildings and machinery, or more commonly a complex having several buildings, where workers manufacture goods or operate machines processing one product into another.
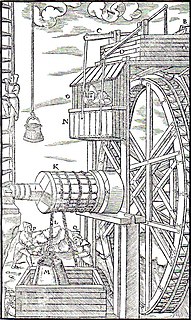
Mechanization is the process of changing from working largely or exclusively by hand or with animals to doing that work with machinery. In an early engineering text a machine is defined as follows:
Every machine is constructed for the purpose of performing certain mechanical operations, each of which supposes the existence of two other things besides the machine in question, namely, a moving power, and an object subject to the operation, which may be termed the work to be done.
Machines, in fact, are interposed between the power and the work, for the purpose of adapting the one to the other.
Portable sawmills are sawmills small enough to be moved easily and set up in the field. They have existed for over 100 years but grew in popularity in the United States starting in the 1970s, when the 1973 oil crisis and the back-to-the-land movement had led to renewed interest in small woodlots and in self-sufficiency. Their popularity has grown exponentially since 1982, when the portable bandsaw mill was first commercialized.

The Škoda Works was one of the largest European industrial conglomerates of the 20th century, founded by Czech engineer Emil Škoda in 1859 in Plzeň, then in the Kingdom of Bohemia, Austrian Empire. It is the predecessor of today's Škoda Auto and Škoda Transportation companies.
UralVagonZavod is a Russian machine building company located in Nizhny Tagil, Russia.

A line shaft is a power driven rotating shaft for power transmission that was used extensively from the Industrial Revolution until the early 20th century. Prior to the widespread use of electric motors small enough to be connected directly to each piece of machinery, line shafting was used to distribute power from a large central power source to machinery throughout a workshop or an industrial complex. The central power source could be a water wheel, turbine, windmill, animal power or a steam engine. Power was distributed from the shaft to the machinery by a system of belts, pulleys and gears known as millwork.

A machine shop is a room, building, or company where machining, a form of subtractive manufacturing, is done. In a machine shop, machinists use machine tools and cutting tools to make parts, usually of metal or plastic. A machine shop can be a small business or a portion of a factory, whether a toolroom or a production area for manufacturing. The parts produced can be the end product of the factory, to be sold to customers in the machine industry, the car industry, the aircraft industry, or others. In other cases, companies in those fields have their own machine shops.

An overhead crane, commonly called a bridge crane, is a type of crane found in industrial environments. An overhead crane consists of parallel runways with a traveling bridge spanning the gap. A hoist, the lifting component of a crane, travels along the bridge. If the bridge is rigidly supported on two or more legs running on a fixed rail at ground level, the crane is called a gantry crane or a goliath crane.
The Husqvarna Group is a Swedish manufacturer of outdoor power products including chainsaws, trimmers, brushcutters, cultivators, garden tractors, mowers, and sewing machines. Headquartered in Stockholm, Sweden, the Group also produces consumer watering products, cutting equipment and diamond tools for the construction and stone industries.
Foundry products operations was a subsidiary operation of the Cincinnati Milling Machine Company (CMM), a company which no longer exists. Some parts of the company evolved into the present Milacron, Inc. and Cincinnati Machine. CMM relied heavily on castings for the manufacturing of its machine tool products. The castings were produced at Cincinnati foundries owned by CMM and at foundries independent of CMM, between 1907 and 1988.
KUKA Systems GmbH, a division of KUKA Aktiengesellschaft, Augsburg, is an international supplier of engineering services and flexible automated manufacturing solutions with around 3,900 employees in twelve countries globally.

Sampson Moore (1812-1877) was an English engineer and inventor based in Liverpool, England during the industrial revolution. His company, Sampson Moore & Co. produced a number of notable inventions.
Huta Ludwików is one of the oldest and best-known Polish factories of metal parts. Currently owned by a Kielce-based Zakłady Wyrobów Metalowych „SHL” joint-stock company, it is a major producer of, among other things, automotive parts for most European markets. In the past the name of the factory was primarily associated with various types of military equipment produced for the Polish Army, ranging from the wz. 34 sabres and wz. 31 helmet to SHL motorcycles. It was also the main sponsor of the now-defunct SHL Kielce sports club.
Agricultural engineering in the Soviet Union - Soviet machine building industry.

Lilpop, Rau i Loewenstein was a Polish engineering company. Established in 1818 as an iron foundry, with time it rose to become a large holding company specialising in iron and steel production, as well as all sorts of machinery and metal products.
The Yamabiko Corporation is a Japanese manufacturer of power tools formed with the September 2008 merger of the Kioritz and Shindaiwa corporations. The brands owned and distributed by Yamabiko are Kioritz, Shindaiwa and ECHO. The Yamabiko Corporation is based in Ome, Japan.

The machine industry or machinery industry is a subsector of the industry, that produces and maintains machines for consumers, the industry, and most other companies in the economy.

A machine factory is a company, that produces machines. These companies traditionally belong to the heavy industry sector in comparison to a more consumer oriented and less capital intensive light industry. Today many companies make more sophisticated smaller machines, and they belong to the light industry. The economic sector of machine factories is called the machine industry.

Carl and Wilhelm Blumwe were successful German entrepreneurs, industrialists and businessmen in Bromberg from the second half of the 19th century. Their buildings and realizations are still standing today in the city.





















