Related Research Articles

Wuxing, usually translated as Five Phases, is a fivefold conceptual scheme that many traditional Chinese fields used to explain a wide array of phenomena, from cosmic cycles to the interaction between internal organs, and from the succession of political regimes to the properties of medicinal drugs. The "Five Phases" are Fire, Water, Wood, Metal or Gold, and Earth or Soil. This order of presentation is known as the "Days of the Week" sequence. In the order of "mutual generation", they are Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water. In the order of "mutual overcoming", they are Wood, Earth, Water, Fire, and Metal.

An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of their environment, interacting as a system. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the system through photosynthesis and is incorporated into plant tissue. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and other microbes.

Geotechnical engineering, also known as geotechnics, is the branch of civil engineering concerned with the engineering behavior of earth materials. It uses the principles and methods of soil mechanics and rock mechanics for the solution of engineering problems and the design of engineering works. It also relies on knowledge of geology, hydrology, geophysics, and other related sciences.

Overgrazing occurs when plants are exposed to intensive grazing for extended periods of time, or without sufficient recovery periods. It can be caused by either livestock in poorly managed agricultural applications, game reserves, or nature reserves. It can also be caused by immobile, travel restricted populations of native or non-native wild animals. However, "overgrazing" is a controversial concept, based on equilibrium system theory. A strong indicator of overgrazing is where additional feed needs to be brought in from outside the farm, often to support livestock through the winter. Traditionally this feed was sourced on the farm, with fewer animals being kept and some fields being used for hay and silage production. Modern farm businesses often choose to keep more animals than their land can support alone; buying in external feed to offset this.

Physical geography is one of the two fields of geography. Physical geography is the branch of natural science which deals with the processes and patterns in the natural environment such as the atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and geosphere, as opposed to the cultural or built environment, the domain of human geography.
Soil retrogression and degradation are two regressive evolution processes associated with the loss of equilibrium of a stable soil. Retrogression is primarily due to soil erosion and corresponds to a phenomenon where succession reverts the land to its natural physical state. Degradation is an evolution, different from natural evolution, related to the local climate and vegetation. It is due to the replacement of primary plant communities by the secondary communities. This replacement modifies the humus composition and amount, and affects the formation of the soil. It is directly related to human activity. Soil degradation may also be viewed as any change or ecological disturbance to the soil perceived to be deleterious or undesirable.

Pedology is a discipline within soil science which focuses on understanding and characterizing soil formation, evolution, and the theoretical frameworks through which we understand a soil body(s), often in the context of the natural environment. Pedology is often seen as one of two main branches of soil inquiry, the other being edaphology which is traditionally more agronomically oriented and focuses on how soil properties influence plant communities. In studying the fundamental phenomenology of soils, e.g. soil formation, pedologists pay particular attention to observing soil morphology and the geographic distributions of soils, and the placement of soil bodies into larger temporal and spatial contexts. In so doing, pedologists develop systems of soil classification, soil maps, and theories for characterizing temporal and spatial interrelations among soils. There are a few noteworthy sub-disciplines of pedology; namely pedometrics and soil geomorphology. Pedometrics focuses on the development of techniques for quantitative characterization of soils, especially for the purposes of mapping soil properties whereas soil geomorphology studies the interrelationships between geomorphic processes and soil formation.
In economics, capital consists of human-created assets that can enhance one's power to perform economically useful work. For example, a stone arrowhead is capital for a hunter-gatherer who can use it as a hunting instrument; similarly, roads are capital for inhabitants of a city. Capital is distinct from land and other non-renewable resources in that it can be increased by human labor, and does not include certain durable goods like homes and personal automobiles that are not used in the production of saleable goods and services. Adam Smith defined capital as "that part of man's stock which he expects to afford him revenue". In economic models, capital is an input in the production function.
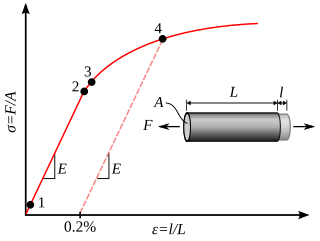
In physics and materials science, plasticity, also known as plastic deformation, is the ability of a solid material to undergo permanent deformation, a non-reversible change of shape in response to applied forces. For example, a solid piece of metal being bent or pounded into a new shape displays plasticity as permanent changes occur within the material itself. In engineering, the transition from elastic behavior to plastic behavior is known as yielding.

Ecological succession is the process of change in the species structure of an ecological community over time. The time scale can be decades, or even millions of years after a mass extinction.
Liebig law of the minimum, often simply called Liebig's law or the law of the minimum, is a principle developed in agricultural science by Carl Sprengel (1840) and later popularized by Justus von Liebig. It states that growth is dictated not by total resources available, but by the scarcest resource. The law has also been applied to biological populations and ecosystem models for factors such as sunlight or mineral nutrients.
Humic substances are organic compounds that are important components of humus, the major organic fraction of soil, peat, and coal. For a long era in the 19th and 20th centuries, humic substances were often viewed through a lens of acid–base theory that described humic acids, as organic acids, and their conjugate bases, humates, as important components of organic matter. Through this viewpoint humic acids were defined as organic substances extracted from soil that coagulate when a strong-base extract is acidified, whereas fulvic acids are organic acids that remain soluble when a strong-base extract is acidified.

Soil mechanics is a branch of soil physics and applied mechanics that describes the behavior of soils. It differs from fluid mechanics and solid mechanics in the sense that soils consist of a heterogeneous mixture of fluids and particles but soil may also contain organic solids and other matter. Along with rock mechanics, soil mechanics provides the theoretical basis for analysis in geotechnical engineering, a subdiscipline of civil engineering, and engineering geology, a subdiscipline of geology. Soil mechanics is used to analyze the deformations of and flow of fluids within natural and man-made structures that are supported on or made of soil, or structures that are buried in soils. Example applications are building and bridge foundations, retaining walls, dams, and buried pipeline systems. Principles of soil mechanics are also used in related disciplines such as geophysical engineering, coastal engineering, agricultural engineering, hydrology and soil physics.
Soil survey, soil mapping, is the process of classifying soil types and other soil properties in a given area and geo-encoding such information. It applies the principles of soil science, and draws heavily from geomorphology, theories of soil formation, physical geography, and analysis of vegetation and land use patterns. Primary data for the soil survey are acquired by field sampling and by remote sensing. Remote sensing principally uses aerial photography, but LiDAR and other digital techniques are steadily gaining in popularity. In the past, a soil scientist would take hard-copies of aerial photography, topo-sheets, and mapping keys into the field with them. Today, a growing number of soil scientists bring a ruggedized tablet computer and GPS into the field with them. The tablet may be loaded with digital aerial photos, LiDAR, topography, soil geodatabases, mapping keys, and more.

Caliche is a sedimentary rock, a hardened natural cement of calcium carbonate that binds other materials—such as gravel, sand, clay, and silt. It occurs worldwide, in aridisol and mollisol soil orders—generally in arid or semiarid regions, including in central and western Australia, in the Kalahari Desert, in the High Plains of the western USA, in the Sonoran Desert and Mojave Desert, and in Eastern Saudi Arabia at Al-Hasa. Caliche is also known as calcrete or kankar. It belongs to the duricrusts. The term caliche is Spanish and is originally from the Latin calx, meaning lime.

Sonication is the act of applying sound energy to agitate particles in a sample, for various purposes such as the extraction of multiple compounds from plants, microalgae and seaweeds. Ultrasonic frequencies (>20 kHz) are usually used, leading to the process also being known as ultrasonication or ultra-sonication.
Soil morphology is the study of the formation and description of soil types within various soil horizons. C.F. Marbut championed reliance on soil morphology instead of on theories of pedogenesis for soil classification because theories of soil genesis are both ephemeral and dynamic.

Shear strength is a term used in soil mechanics to describe the magnitude of the shear stress that a soil can sustain. The shear resistance of soil is a result of friction and interlocking of particles, and possibly cementation or bonding at particle contacts. Due to interlocking, particulate material may expand or contract in volume as it is subject to shear strains. If soil expands its volume, the density of particles will decrease and the strength will decrease; in this case, the peak strength would be followed by a reduction of shear stress. The stress-strain relationship levels off when the material stops expanding or contracting, and when interparticle bonds are broken. The theoretical state at which the shear stress and density remain constant while the shear strain increases may be called the critical state, steady state, or residual strength.
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure the "accessible void", the total amount of void space accessible from the surface.

An oedometer test is a kind of geotechnical investigation performed in geotechnical engineering that measures a soil's consolidation properties. Oedometer tests are performed by applying different loads to a soil sample and measuring the deformation response. The results from these tests are used to predict how a soil in the field will deform in response to a change in effective stress.
References
- ↑ Woods, R. (1978). Measurements of Dynamic Soil Properties. Proc. Earthquake Engineering and Soil Dynamics. 1, pp. 91-178. Pasadena: ASCE Specialty Conference.