Related Research Articles

The leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula. There are 60 bones in each leg.

In human anatomy, the fibularis longus is a superficial muscle in the lateral compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body (eversion) and to extend the foot downward away from the body at the ankle.
The ankle, the talocrural region or the jumping bone (informal) is the area where the foot and the leg meet. The ankle includes three joints: the ankle joint proper or talocrural joint, the subtalar joint, and the inferior tibiofibular joint. The movements produced at this joint are dorsiflexion and plantarflexion of the foot. In common usage, the term ankle refers exclusively to the ankle region. In medical terminology, "ankle" can refer broadly to the region or specifically to the talocrural joint.

The extensor hallucis longus muscle is a thin skeletal muscle, situated between the tibialis anterior and the extensor digitorum longus. It extends the big toe and dorsiflects the foot. It also assists with foot eversion and inversion.
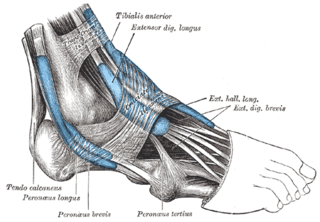
The extensor digitorum longus is a pennate muscle, situated at the lateral part of the front of the leg.

The extensor digitorum brevis muscle is a muscle on the upper surface of the foot that helps extend digits 2 through 4.

In human anatomy, the fibularis tertius is a muscle in the anterior compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body (eversion) and to pull the foot upward toward the body (dorsiflexion).

In human anatomy, the abductor digiti minimi is a skeletal muscle situated on the ulnar border of the palm of the hand. It forms the ulnar border of the palm and its spindle-like shape defines the hypothenar eminence of the palm together with the skin, connective tissue, and fat surrounding it. Its main function is to pull the little finger away from the other fingers.
The palmar carpal ligament is a thickened portion of antebrachial fascia on anterior/palmar side of the wrist which - together with the flexor retinaculum of the hand - retains the tendons of most of the flexor muscles of the hand.

The flexor retinaculum is a fibrous band on the palmar side of the hand near the wrist. It arches over the carpal bones of the hands, covering them and forming the carpal tunnel.

The fibular retinacula are fibrous retaining bands that bind down the tendons of the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis muscles as they run across the side of the ankle.

The inferior extensor retinaculum of the foot is a Y-shaped band placed in front of the ankle-joint, the stem of the Y being attached laterally to the upper surface of the calcaneus, in front of the depression for the interosseous talocalcaneal ligament; it is directed medialward as a double layer, one lamina passing in front of, and the other behind, the tendons of the peroneus tertius and extensor digitorum longus.
A transverse ligament is a ligament on a transverse plane, orthogonal to the anteroposterior or oral-aboral axiscan of the body.

The extensor retinaculum is a thickened portion of the antebrachial fascia that holds the tendons of the extensor muscles in place. It is located on the back of the forearm, just proximal to the hand. It is continuous with the palmar carpal ligament.

The superior extensor retinaculum of the foot is the upper part of the extensor retinaculum of foot which extends from the ankle to the heelbone.

The anterior compartment of the leg is a fascial compartment of the lower leg. It contains muscles that produce dorsiflexion and participate in inversion and eversion of the foot, as well as vascular and nervous elements, including the anterior tibial artery and veins and the deep fibular nerve.

The posterior compartment of the thigh is one of the fascial compartments that contains the knee flexors and hip extensors known as the hamstring muscles, as well as vascular and nervous elements, particularly the sciatic nerve.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:
Retinaculum may refer to:
Retinaculum of foot may refer to
References
- ↑ "UAMS Department of Neurobiology and Developmental Sciences - Fascia and Membrane Tables". anatomy.uams.edu. Retrieved 2019-04-13.
- ↑ "Definition of RETINACULUM".