The New Zealand falcon or kārearea in Māori is New Zealand's only falcon. Other common names for the bird are bush hawk and sparrow hawk. It is frequently mistaken for the larger and more common swamp harrier. It is the country's most threatened bird of prey, with only around 3000–5000 breeding pairs remaining.

The leafscale gulper shark is a dogfish of the family Centrophoridae. C. squamosus is reported to have a lifespan of approximately 70 years, based on otolith ring counts. It was the first described species in the genus Centrophorus, which now contains 13 species.
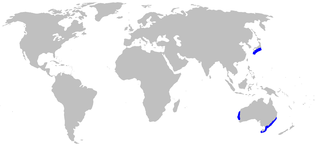
The bareskin dogfish is a little-known, deepwater dogfish shark of the family Etmopteridae. This species is found in the western Pacific from southern Japan to western and southeastern Australia as well as in New Zealand waters.
Captain Frederick Wollaston Hutton, FRS, was an English-New Zealand scientist who applied the theory of natural selection to explain the origins and nature of the natural history of New Zealand. An army officer in early life, he then had an academic career in geology and biology. He became one of the most able and prolific nineteenth century naturalists of New Zealand.

New Zealand is a sovereign island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. The country has two main landmasses—the North Island, and the South Island —and around 600 smaller islands. It has a total land area of 268,000 square kilometres (103,500 sq mi). New Zealand is about 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi) east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and 1,000 kilometres (600 mi) south of the Pacific island areas of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. Because of its remoteness, it was one of the last lands to be settled by humans. During its long period of isolation, New Zealand developed a distinct biodiversity of animal, fungal, and plant life. The country's varied topography and its sharp mountain peaks, such as the Southern Alps, owe much to the tectonic uplift of land and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland.

Corylophidae is a family of minute hooded beetles, sometimes called minute fungus beetles, in the order Coleoptera. There are about 18 genera and at least 120 described species in Corylophidae.

Nepticulidae is a family of very small moths with a worldwide distribution. They are characterised by eyecaps over the eyes. These pigmy moths or midget moths, as they are commonly known, include the smallest of all living moths, with a wingspan that can be as little as 3 mm in the case of the European pigmy sorrel moth, but more usually 3.5–10 mm. The wings of adult moths are narrow and lanceolate, sometimes with metallic markings, and with the venation very simplified compared to most other moths.

Anthribidae is a family of beetles also known as fungus weevils. The antennae are not elbowed, may occasionally be longer than the body and thread-like, and can be the longest of any members of Curculionoidea. As in the Nemonychidae, the labrum appears as a separate segment to the clypeus, and the maxillary palps are long and projecting.

The Cryptorhynchinae is a large subfamily of weevils (Curculionidae), with some 6000 species. They are found in most zoogeographic regions although they are most diverse in the Neotropics, Australia and Oceania.

The Catalogue of Life is an online database that provides the world's most comprehensive and authoritative index of known species of animals, plants, fungi and micro-organisms. It was created in 2001 as a partnership between the global Species 2000 and the American Integrated Taxonomic Information System. The Catalogue interface is available in twelve languages and is used by research scientists, citizen scientists, educators, and policy makers. The Catalogue is also used by the Biodiversity Heritage Library, the Barcode of Life Data System, Encyclopedia of Life, and the Global Biodiversity Information Facility. The Catalogue currently compiles data from 168 peer-reviewed taxonomic databases, that are maintained by specialist institutions around the world. As of 2019, the Catalogue lists 1,837,565 of the world's 2.2m extant species known to taxonomists on the planet at present time.

The colossal squid, sometimes called the Antarctic squid or giant cranch squid, is believed to be the largest squid species in terms of mass. It is the only recognised member of the genus Mesonychoteuthis and is known from only a small number of specimens. The species is confirmed to reach a mass of at least 500 kilograms (1,100 lb), though the largest specimens—known only from beaks found in sperm whale stomachs—may perhaps weigh as much as 600–700 kilograms (1,300–1,500 lb), making it the largest-known invertebrate. Maximum total length has been estimated at 9–10 metres (30–33 ft).
Sepioloidea pacifica, also known as the Pacific bobtail squid, is a species of cuttlefish native to the southern Pacific Ocean; it occurs off New Zealand in the west and in the Nazca and Sala y Gomez submarine ridges in the east.

Iridoteuthis maoria is a species of bobtail squid native to the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It occurs in Cook Strait and Chatham Rise off North Island in New Zealand, and has also been recorded from the Nazca and Sala y Gomez submarine ridges in the eastern Pacific.

Nototodarus sloanii is a species of squid commonly known as the New Zealand arrow squid or Wellington flying squid. It is also known by its Māori name of Wheketere. It is a favoured prey species of a number of marine mammals and diving birds. It is an important food source for the New Zealand fur seal and the endangered species: New Zealand sea lion and yellow-eyed penguin. N. sloanii is sought by trawler fishermen for human consumption; in this trawling process, Australian sea lions are frequently killed, since they prey upon N. sloanii.

The Mycetophagidae or hairy fungus beetles are a family of beetles in the large suborder Polyphaga. The different species are between 1.0 and 6.5 mm in length. The larvae and adults live in decaying leaf litter, fungi, and under bark. Most species feed on fungi. Worldwide, the 18 genera contain around 200 species.
Schizopteridae is the largest family in the infraorder Dipsocoromorpha and comprises 56 genera and approximately 255 species. Schizopterids are some of the smallest (0.5–2.0 mm) true bugs. Members of this family can be distinguished by their small size, enlarged forecoxae and varying degree of abdominal and genitalic asymmetry in males. Schizopteridae exhibit a wide range of simple and complex wing venation patterns–some species even possess true elytra. The group is currently divided into three subfamilies: Schizopterinae, Ogeriinae and Hypselosomatinae.

Pseudowintera traversii, sometimes called Travers horopito, is a species of woody shrub in the family Winteraceae. The specific epithet traversii is in honor of naturalist Henry H. Travers (1844-1928), son of William Thomas Locke Travers.

Pharaxonotha is a genus of pleasing fungus beetles in the family Erotylidae. There are at least three described species in Pharaxonotha.

Acropteroxys is a genus of lizard beetles in the family Erotylidae. There are at least two described species in Acropteroxys.