
Arunachal Pradesh is a state in Northeastern India. It was formed from the erstwhile North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and became a state on 20 February 1987. It borders the states of Assam and Nagaland to the south. It shares international borders with Bhutan in the west, Myanmar in the east, and a disputed border with China in the north at the McMahon Line. Itanagar is the state capital of Arunachal Pradesh. Arunachal Pradesh is the largest of the Seven Sister States of Northeast India by area. Arunachal Pradesh shares a 1,129 km border with China's Tibet Autonomous Region.

Assam is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of 78,438 km2 (30,285 sq mi). The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur to the east; Meghalaya, Tripura, Mizoram and Bangladesh to the south; and West Bengal to the west via the Siliguri Corridor, a 22 kilometres (14 mi) wide strip of land that connects the state to the rest of India. Assamese and Bodo are the official languages of Assam, while Bengali is official in the Barak Valley.

Indian architecture is rooted in its history, culture and religion. Among a number of architectural styles and traditions, the best-known include the many varieties of Hindu temple architecture, Indo-Islamic architecture, especially Mughal architecture, Rajput architecture and Indo-Saracenic architecture. Much early Indian architecture was in wood, which has not survived. Instead the earliest survivals are from the many sites with Indian rock-cut architecture, most Buddhist but some Hindu and Jain.

Pichhwai, literally meaning 'that which hangs from the back' from the Sanskrit words "Pichh" means back and "wais" means hanging, are large devotional Hindu painted pictures, normally on cloth, which portray Krishna. They are mainly made to hang in Hindu temples of the Pushtimarg devotional tradition, especially the Shrinathji Temple in Nathdwara, Rajasthan, built around 1672. They are hung behind the idol of Shrinathji, a local form of Krishna and the centre of Pushtimarg worship, to depict his leelas. Aurangabad was another area associated with them. The purpose of pichhwais, other than artistic appeal, is to narrate tales of Krishna to the illiterate. Temples have sets with different images, which are changed according to the calendar of festivals celebrating the deity.

The Bengal Presidency, officially the Presidency of Fort William and later Bengal Province, was a subdivision of the British Empire in India. At the height of its territorial jurisdiction, it covered large parts of what is now South Asia and Southeast Asia. Bengal proper covered the ethno-linguistic region of Bengal. Calcutta, the city which grew around Fort William, was the capital of the Bengal Presidency. For many years, the Governor of Bengal was concurrently the Viceroy of India and Calcutta was the de facto capital of India until 1911.

Sonitpur district [Pron: ˌsə(ʊ)nɪtˈpʊə or ˌʃə(ʊ)nɪtˈpʊə] is an administrative district in the state of Assam in India. The district headquarters is located at Tezpur.

Hinduism is practised by 1.7% of the population of Myanmar. Hinduism is practised by about 890,000 people in Myanmar, and has been influenced by elements of Buddhism, with many Hindu temples in Myanmar housing statues of the Buddha. There are also a large population of Hindus in which the Myanmar Tamils and minority Bengali Hindus having the biggest population share.

Indian painting has a very long tradition and history in Indian art, though because of the climatic conditions very few early examples survive. The earliest Indian paintings were the rock paintings of prehistoric times, such as the petroglyphs found in places like Bhimbetka rock shelters. Some of the Stone Age rock paintings found among the Bhimbetka rock shelters are approximately 10,000 years old.

The history of Bengal is intertwined with the history of the broader Indian subcontinent and the surrounding regions of South Asia and Southeast Asia. It includes modern-day Bangladesh and the Indian states of West Bengal and Assam's Karimganj district, located in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent, at the apex of the Bay of Bengal and dominated by the fertile Ganges delta. The region was known to the ancient Greeks and Romans as Gangaridai, a powerful kingdom whose war elephant forces led the withdrawal of Alexander the Great from India. Some historians have identified Gangaridai with other parts of India. The Ganges and the Brahmaputra rivers act as a geographic marker of the region, but also connects the region to the broader Indian subcontinent. Bengal, at times, has played an important role in the history of the Indian subcontinent.

Nagarjunakonda is a historical town, now an island located near Nagarjuna Sagar in Guntur district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh, near the state border with Telangana. It is 160 km west of another important historic site Amaravati Stupa.

Eastern Bengal and Assam was an administrative subdivision (province) of the British India between 1905 and 1912. Headquartered in the city of Dacca, it covered territories in what are now Bangladesh, Northeast India and Northern West Bengal.

The People of Assam inhabit a multi-ethnic, multi-linguistic and multi-religious society. They speak languages that belong to four main language groups: Tibeto-Burman, Indo-Aryan, Tai-Kadai, and Austroasiatic. The large number of ethnic and linguistic groups, the population composition, and the peopling process in the state has led to it being called an "India in miniature".

The Barak Valley is located in the southern region of the Indian state of Assam. The main city of the valley is Silchar. The region is named after the Barak river. The Barak valley consists of three administrative districts of Assam - namely Cachar, Karimganj, and Hailakandi.

Richard Lawrence Bartholomew was an Indian art critic, photographer, painter, poet, and writer.

Bengali Hindus are an ethnoreligious population who make up the majority in the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Jharkhand, and Assam's Barak Valley region. In Bangladesh, they form the largest minority. They are adherents of Hinduism and are native to the Bengal region in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent. Bengali Hindus speak Bengali, which belongs to the Indo-Aryan language family and adhere to Shaktism or Vaishnavism of their native religion Hinduism with some regional deities. There are significant numbers of Bengali-speaking Hindus in different Indian states. According to the census in 1881, 12.81 percent of Bengali Hindus belonged to the upper castes.
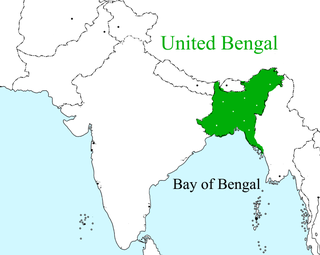
Greater Bangladesh is a conspiracy theory circulated by a number of far-right Indian politicians and writers that the People's Republic of Bangladesh has aspirations of territorial expansion, to include the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura and Assam as part of its own territory. Some proponents also claim that Mamata Banerjee, Chief minister of West Bengal, is involved in trying to create Greater Bangladesh. The theory is principally based on the large number of illegal Bangladeshi Muslim immigrants that reside in Indian territory.
The Bengali Hindu diaspora is the worldwide population of the Bengali Hindus of Indian and Bangladeshi origin.

Vrindavani Vastra is a drape woven by Assamese weavers led by Mathuradas Burha Aata during 16th century under the guidance of Srimanta Sankardeva, a Vaishnavite saint and scholar who lived in present-day Assam. The lead weaver Mathuradas Burha Aata a disciple of Sri Sri Madhabdev was the first Satradhikar of the great Barpeta satra. Mathuradas Burha Aata along with his 12 assistant weavers wove the Brindavani Bastra. The large drape illustrates the childhood activities of Lord Krishna in Vrindavan. Parts of the original Vrindavani vastra are presently owned by the Victoria and Albert Museum in London and Musee Guimet in Paris. The piece of cloth demonstrates the skillful weaving methods developed during medieval times and such complexity is rarely seen in present-day Assam.

Northeast India consists of the eight states Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim and Tripura. Tourism in this area is based around the unique Himalayan landscape and culture distinct from the rest of India.

Eastern South Asia is a subregion of South Asia. It includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, and Nepal. Geographically, it lies between the Eastern Himalayas and the Bay of Bengal. Two of the world's largest rivers, the Ganges and the Brahmaputra, flow into the sea through Eastern South Asia. The region includes the world's highest mountainous terrain and the world's largest delta, and has a climate ranging from alpine and subalpine to subtropical and tropical. Since Nepal, Bhutan, and northeast India are landlocked, the coastlines of Bangladesh and East India serve as the principal gateways to the region.


















