Related Research Articles
Dieting is the practice of eating food in a regulated way to decrease, maintain, or increase body weight, or to prevent and treat diseases such as diabetes and obesity. As weight loss depends on calorie intake, different kinds of calorie-reduced diets, such as those emphasising particular macronutrients, have been shown to be no more effective than one another. As weight regain is common, diet success is best predicted by long-term adherence. Regardless, the outcome of a diet can vary widely depending on the individual.

Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin and contains essential nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is ingested by an organism and assimilated by the organism's cells to provide energy, maintain life, or stimulate growth. Different species of animals have different feeding behaviours that satisfy the needs of their metabolisms and have evolved to fill a specific ecological niche within specific geographical contexts.

In nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.

"Junk food" is a term used to describe food that is high in calories from macronutrients such as sugar and/or fat, and possibly sodium, making it hyperpalatable, but with insufficient dietary fiber, protein, or micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals. It is also known as HFSS food. The term junk food is a pejorative dating back to the 1950s. Many variations of junk food can be easily found in most supermarkets and fast food restaurants. Due to easy accessibility, commercially-oriented packaging, and often-low prices, people are most likely to consume it.

Chocolate milk is a type of flavoured milk made by mixing cocoa solids with milk. It is a food pairing in which the milk's mouthfeel masks the dietary fibres of the cocoa solids.

A food pyramid is a representation of the optimal number of servings to be eaten each day from each of the basic food groups. The first pyramid was published in Sweden in 1974. The 1992 pyramid introduced by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) was called the "Food Guide Pyramid" or "Eating Right Pyramid". It was updated in 2005 to "MyPyramid", and then it was replaced by "MyPlate" in 2011.

The Paleolithic diet, Paleo diet, caveman diet, or Stone Age diet is a modern fad diet consisting of foods thought by its proponents to mirror those eaten by humans during the Paleolithic era.

Convenience food is food that is commercially prepared for ease of consumption, and is usually ready to eat without further preparation. It may also be easily portable, have a long shelf life, or offer a combination of such convenient traits. Convenience foods include ready-to-eat dry products, frozen food such as TV dinners, shelf-stable food, prepared mixes such as cake mix, and snack food. Food scientists now consider most of these products to be ultra-processed foods and link them to poor health outcomes.

Olestra is a fat substitute that adds no metabolizable calories to products. It has been used in the preparation of otherwise high-fat foods, thereby lowering or eliminating their fat content. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) originally approved olestra for use in the US as a replacement for fats and oils in prepackaged ready-to-eat snacks in 1996, concluding that such use "meets the safety standard for food additives, reasonable certainty of no harm". In the late 2000s, olestra lost its popularity due to supposed side effects and has been largely phased out, but products containing the ingredient can still be purchased at grocery stores in some countries. As of 2024, no products using olestra are sold in the United States.

Low-carbohydrate diets restrict carbohydrate consumption relative to the average diet. Foods high in carbohydrates are limited, and replaced with foods containing a higher percentage of fat and protein, as well as low carbohydrate foods.

A chocoholic is a person who craves or compulsively consumes chocolate. The word "chocoholic" was first used in 1961, according to Merriam-Webster. It is a portmanteau of "chocolate" and "alcoholic". The term is used loosely or humorously to describe a person who is inordinately fond of chocolate; however, there is medical evidence to support the existence of actual addiction to chocolate. Psychoactive constituents of chocolate that trigger a ‘feel-good’ reaction for the consumer include tryptophan and phenylethylamine, which may contribute to cravings and addiction-like responses, particularly in people with specific genetic alleles. The quantity of sugars used in chocolate confections also impacts the psychoactive effects of chocolate.

A healthy diet is a diet that maintains or improves overall health. A healthy diet provides the body with essential nutrition: fluid, macronutrients such as protein, micronutrients such as vitamins, and adequate fibre and food energy.
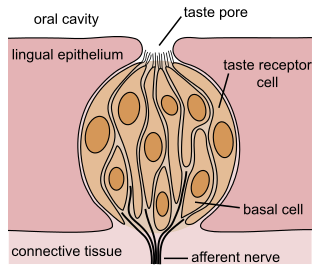
The gustatory system or sense of taste is the sensory system that is partially responsible for the perception of taste (flavor). Taste is the perception stimulated when a substance in the mouth reacts chemically with taste receptor cells located on taste buds in the oral cavity, mostly on the tongue. Taste, along with the sense of smell and trigeminal nerve stimulation, determines flavors of food and other substances. Humans have taste receptors on taste buds and other areas, including the upper surface of the tongue and the epiglottis. The gustatory cortex is responsible for the perception of taste.
Diet plays an important role in the genesis of obesity. Personal choices, food advertising, social customs and cultural influences, as well as food availability and pricing all play a role in determining what and how much an individual eats.
Research into food choice investigates how people select the food they eat. An interdisciplinary topic, food choice comprises psychological and sociological aspects, economic issues and sensory aspects.

Criticism of fast food includes claims of negative health effects, animal cruelty, cases of worker exploitation, children-targeted marketing and claims of cultural degradation via shifts in people's eating patterns away from traditional foods. Fast food chains have come under fire from consumer groups, such as the Center for Science in the Public Interest, a longtime fast food critic over issues such as caloric content, trans fats and portion sizes. Social scientists have highlighted how the prominence of fast food narratives in popular urban legends suggests that modern consumers have an ambivalent relationship with fast food, particularly in relation to children.
Only two essential fatty acids are known to be essential for humans: alpha-linolenic acid and linoleic acid. The biological effects of the ω-3 and ω-6 fatty acids are mediated by their mutual interactions. Closely related, these fatty acids act as competing substrates for the same enzymes. The biological effects of the ω-3 and ω-6 fatty acids are largely mediated by essential fatty acid interactions. The proportion of omega-3 to omega-6 fatty acids in a diet may have metabolic consequences. Unlike omega-3 fatty acids and omega-6 fatty acids, omega-9 fatty acids are not classed as essential fatty acids because they can be created by the human body from monounsaturated and saturated fatty acids, and are therefore not essential in the diet.
Barry Michael Popkin is an American nutrition and obesity researcher at the Carolina Population Center and the W.R. Kenan Jr. Distinguished Professor of Nutrition at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Public Health, where he is the director of the Global Food Research Program. He developed the concept of "nutrition transition". He is the author of over 650 journal articles and a book, The World is Fat, translated into a dozen languages.

Pure, White and Deadly is a 1972 book by John Yudkin, a British nutritionist and former Chair of Nutrition at Queen Elizabeth College, London. Published in New York, it was the first publication by a scientist to anticipate the adverse health effects, especially in relation to obesity and heart disease, of the public's increased sugar consumption. At the time of publication, Yudkin sat on the advisory panel of the British Department of Health's Committee on the Medical Aspects of Food and Nutrition Policy (COMA). He stated his intention in writing the book in the last paragraph of the first chapter: "I hope that when you have read this book I shall have convinced you that sugar is really dangerous."

Trans fat, also called trans-unsaturated fatty acids, or trans fatty acids, is a type of unsaturated fat that occurs in foods. Trace concentrations of trans fats occur naturally, but large amounts are found in some processed foods. Since consumption of trans fats is unhealthy, artificial trans fats are highly regulated or banned in many nations. However, they are still widely consumed in developing nations, resulting in hundreds of thousands of deaths each year. The World Health Organization (WHO) had set a goal to make the world free from industrially produced trans fat by the end of 2023. The goal was not met, and the WHO announced another goal "for accelerated action till 2025 to complete this effort" along with associated support on 1 February 2024.
References
- 1 2 "Richard (Rick) Mattes". Purdue University. Retrieved 31 August 2015.
- 1 2 Moss, Michael (18 December 2013). "Are Nuts a Weight-Loss Aid?". New York Times. Retrieved 31 August 2015.
- ↑ Mourao, D M; Bressan, J; Campbell, W W; Mattes, R D (19 June 2007). "Effects of food form on appetite and energy intake in lean and obese young adults". International Journal of Obesity. 31 (11): 1688–1695. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0803667 . PMID 17579632.
- ↑ Martinez, Chelsea (9 July 2007). "Liquid or solid food: Maybe it matters". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 31 August 2015.
- ↑ Running, Cordelia A.; Craig, Bruce A.; Mattes, Richard D. (September 2015). "Oleogustus: The Unique Taste of Fat". Chemical Senses. 40 (7): 507–516. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjv036 . PMID 26142421.
- ↑ Oaklander, Mandy (28 July 2015). "A New Taste Has Been Added to the Human Palate". Time. Retrieved 31 August 2015.