Related Research Articles

1588 (MDLXXXVIII) was a leap year starting on Friday of the Gregorian calendar and a leap year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar, the 1588th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 588th year of the 2nd millennium, the 88th year of the 16th century, and the 9th year of the 1580s decade. As of the start of 1588, the Gregorian calendar was 10 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.

Charles Howard, 1st Earl of Nottingham, 2nd Baron Howard of Effingham, KG, known as Lord Howard of Effingham, was an English statesman and Lord High Admiral under Elizabeth I and James I. He was commander of the English forces during the battles against the Spanish Armada and was chiefly responsible for the victory that saved England from invasion by the Spanish Empire.

Revenge was an English race-built galleon of 46 guns, built in 1577 and captured by the Spanish in 1591, sinking soon afterwards. She was the first of 13 English and Royal Navy ships to bear the name.
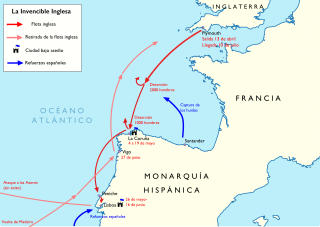
The English Armada, also known as the Counter Armada or the Drake–Norris Expedition, was an attack fleet sent against Spain by Queen Elizabeth I of England that sailed on 28 April 1589 during the undeclared Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604) and the Eighty Years' War. Led by Sir Francis Drake as admiral and Sir John Norris as general, it failed to drive home the advantage that England had gained resulting from the failure of the Spanish Armada in the previous year. The Spanish victory marked a revival of Philip II's naval power through the next decade.

The naval Battle of Vila Franca do Campo, also known as Battle of Ponta Delgada and Naval Battle of Terceira Island, took place on 26 July 1582, off the coast of the island of São Miguel in the Portuguese archipelago of the Azores, during the War of the Portuguese Succession. A combined corsair expedition, mainly French, sailed against a Spanish naval force made up of Portuguese and Castilian ships, to preserve control of the Azores under the pretender António, Prior of Crato and to defend the islands from incorporation into the Iberian Union, the largest French force sent overseas before the age of Louis XIV.

The Spanish Armada was a Spanish fleet that sailed from Lisbon in late May 1588, commanded by the Alonso de Guzmán, Duke of Medina Sidonia, an aristocrat without previous naval experience appointed by Philip II of Spain. His orders were to sail up the English Channel, join with the Duke of Parma in Flanders, and escort an invasion force that would land in England and overthrow Elizabeth I. Its purpose was to reinstate Catholicism in England, end support for the Dutch Republic, and prevent attacks by English and Dutch privateers against Spanish interests in the Americas.
The Spanish Armada in Ireland refers to the landfall made upon the coast of Ireland in September 1588 of a large portion of the 130-strong fleet sent by Philip II to invade England.

The siege of Bergen op Zoom was a siege that took place between September 23 - November 13, 1588, during the Eighty Years' War and the Anglo–Spanish War. The siege took place in the aftermath of the Spanish Armada when famed commander Alexander Farnese, the Duke of Parma attempted to use his forces to besiege Bergen op Zoom, which was held by an Anglo-Dutch force under Thomas Morgan and Peregrine Bertie. An English officer named Grimstone, claiming to be a disaffected Catholic, had set up a trap during which a large Spanish assault was bloodily repulsed. An Anglo-Dutch relief column under the command Maurice of Orange arrived soon after and forced the Duke of Parma to retreat, thus ending the siege.

Laurens Cornelis Boudewijn de Graaf was a Dutch pirate, mercenary, and naval officer in the service of the French colony of Saint-Domingue during the late 17th and early 18th century.

Charles Paget was a Roman Catholic conspirator, involved in the Babington Plot to assassinate Queen Elizabeth I of England.
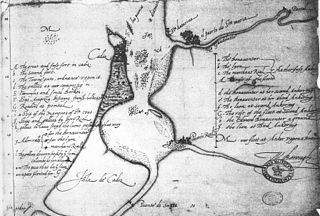
Singeing the King of Spain's Beard is the derisive name given to a series of attacks by the English privateer Francis Drake against the Spanish in the summer of 1587, beginning in April with a raid on Cádiz. This was an attack on the Spanish naval forces assembling in the Bay of Cádiz in preparation for the planned expedition against England. Much of the Spanish fleet was destroyed, and substantial supplies were destroyed or captured. There followed a series of raiding parties against several forts along the Portuguese coast. A Spanish treasure ship, returning from the Indies, was also captured. The damage caused by the English delayed Spanish preparations for the Armada by at least a year.

Sir Edward Osborne (1530?–1591), was one of the principal merchants of London in the later sixteenth century, and Lord Mayor of London in 1583.

The Sea Dogs were a group of English privateers and explorers authorised by Queen Elizabeth I to raid England's enemies, whether they were formally at war with them or not. Active from 1560 until Elizabeth's death in 1603, the Sea Dogs primarily attacked Spanish targets both on land and at sea, particularly during the Anglo-Spanish War. Members of the Sea Dogs, including Sir John Hawkins and Sir Francis Drake, also engaged in illicit slave trading with Spanish colonies in the Americas.

The Battle of Berlengas Islands was a naval battle which took place off the Portuguese coast on 15 July 1591, during the war between Elizabeth I of England and Philip II of Spain. It was fought between an English privateer squadron under George Clifford, 3rd Earl of Cumberland, who had set out his fortunes by large-scale privateering, and a squadron of 5 Spanish galleys commanded by Francisco Coloma tasked with patrolling the Portuguese coast against privateers. While anchored off the Berlengas, the English ships were surprised by the Spanish galleys, which succeeded in taking one English ship and rescuing two prizes.

The Battle of Flores was a naval engagement during the Brittany Campaign of the Anglo-Spanish War of 1585 fought off the Island of Flores between an English fleet of 22 ships under Lord Thomas Howard and a Spanish fleet of 55 ships under Alonso de Bazán. Sent to the Azores to capture the annual Spanish treasure convoy, when a stronger Spanish fleet appeared off Flores, Howard ordered his ships to flee to the north, saving all of them except the galleon Revenge commanded by Admiral Sir Richard Grenville.

The Conquest of the Azores, but principally involving the conquest of the island of Terceira, occurred on 2 August 1583, in the Portuguese archipelago of the Azores, between forces loyal to the claimant D. António, Prior of Crato, supported by the French and English troops, and the Spanish and Portuguese forces loyal to King Philip II of Spain, commanded by the Admiral Don Álvaro de Bazán, Marquis of Santa Cruz, during the War of the Portuguese Succession. The victory of the Marquis of Santa Cruz resulted in the rapid Spanish conquest of the Azores, facilitating the integration of the Kingdom of Portugal and its colonial possessions into the Spanish Empire.
Rowland York or Yorke was an English soldier of fortune and defector to Spain.
Vice-Admiral Sir Richard Stayner (1625–1662) was an English naval officer who supported the Parliamentary cause during the English Civil War and the Interregnum. During the First Anglo-Dutch War he commanded the Foresight in actions at Portland, the Gabbard and in the Battle of Scheveningen. During the Anglo-Spanish War (1654–1660), he won renown and a fortune in prize money when he captured a great part of the Spanish West Indian treasure fleet off Cadiz in 1656. He was knighted by the Lord Protector Oliver Cromwell for services in Admiral Robert Blake's destruction of Spanish ships at Santa Cruz, 1657. He was a rear-admiral of the fleet which brought Charles II to England in 1660. He was again knighted at the Restoration. He died at Lisbon, while serving as vice-admiral of the Mediterranean fleet.

The 3rd Spanish Armada, also known as the Spanish Armada of 1597, was involved in a major naval event that took place between 18 October and 15 November 1597 as part of the Anglo–Spanish War. The attack of the armada, which was the third attempt by Spain to invade or raid the British Isles during the war, was ordered by King Philip II of Spain in revenge for the English attack on Cadiz following the failure of the 2nd Spanish Armada the previous year due to a storm. The Armada was executed by the Adelantado, Martín de Padilla, who was hoping to intercept and destroy the English fleet under Robert Devereux the 2nd Earl of Essex as it returned from the failed Azores expedition. When this was achieved, the Armada would go on to capture either the important port of Falmouth or Milford Haven and use those places as a base for invasion.
John Cecil, alias John Snowden was an English Roman Catholic priest, diplomat, spy and political adventurer.
References
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Laughton, John Knox (1899). "Tomson, Richard". In Lee, Sidney (ed.). Dictionary of National Biography . Vol. 57. London: Smith, Elder & Co.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Laughton, John Knox (1899). "Tomson, Richard". In Lee, Sidney (ed.). Dictionary of National Biography . Vol. 57. London: Smith, Elder & Co.