
Tucson is a city in and the county seat of Pima County, Arizona, United States, and is home to the University of Arizona. It is the second largest city in Arizona, with a population of 520,116 in the 2010 United States Census, while the 2015 estimated population of the entire Tucson metropolitan statistical area (MSA) was 980,263. The Tucson MSA forms part of the larger Tucson-Nogales combined statistical area (CSA), with a total population of 1,010,025 as of the 2010 Census. Current (2021) city of Tucson population is estimated at 554,503 with Tucson MSA of 1,068,730. Tucson is the second most-populated city in Arizona behind Phoenix, both of which anchor the Arizona Sun Corridor. The city is 108 miles (174 km) southeast of Phoenix and 60 mi (97 km) north of the U.S.–Mexico border. Tucson is the 33rd largest city and the 58th largest metropolitan area in the United States (2014).

Pima County is a county in the south central region of the U.S. state of Arizona. As of the 2010 census, the population was 980,263, making it Arizona's second-most populous county. The county seat is Tucson, where most of the population is centered. The county is named after the Pima Native Americans who are indigenous to this area.

Marana is a town in Pima County, Arizona, United States, located northwest of Tucson, with a small portion in Pinal County. According to the 2010 census, the population of the town is 34,961. From 1990 to 2000, Marana was the fourth fastest-growing place among all cities and towns in Arizona of any size.

Tanque Verde is a suburban census-designated place (CDP) in Pima County, Arizona, United States, northeast of Tucson. The population was 16,195 at the 2000 census.

The Rincon Mountains are a significant mountain range east of Tucson, Pima County, Arizona, in the United States. The Rincon Mountains are one of five mountain ranges surrounding the Tucson valley. The other ranges include the most prominent, the Santa Catalina Mountains to the north, the Santa Rita Mountains to the south, the Tucson Mountains to the west, and the Tortolita Mountains to the northwest. Redington Pass separates the Rincon Mountains from the Santa Catalina Mountains. The Rincon Mountains are generally less rugged than the Santa Catalina Mountains and Santa Rita Mountains. The Rincon Mountains are also included in the Madrean sky island mountain ranges of southeast Arizona, extreme southwest New Mexico, and northern Sonora Mexico.

Amphitheater Public Schools, also known as Amphi or District 10, is the third largest public school district in Tucson, Arizona, in terms of enrollment, with about 13,500 students and a staff of about 2000 employees Amphi was established on July 3, 1893. With its headquarters in Flowing Wells, presently serves segments of North Tucson, Casas Adobes, Catalina Foothills, and the communities of Oro Valley, eastern Tortolita, and Catalina northwest of the city.
Redington Pass is a high mountain pass between the Santa Catalina Mountains and the Rincons in northeast Pima County, Arizona. It is located just east of Tucson. Historically, it was the connection between the farming and ranching areas of Redington along the San Pedro River on the east side of the pass and Tucson on the west side.
In the U.S. state of Arizona, Interstate 10 (I‑10), the major east–west Interstate Highway in the United States Sun Belt, runs east from California, enters Arizona near the town of Ehrenberg and continues through Phoenix and Tucson and exits at the border with New Mexico near San Simon. The highway also runs through the cities of Casa Grande, Eloy and Marana. Segments of the highway are referred to as either the Papago Freeway, Inner Loop or Maricopa Freeway within the Phoenix area and the Pearl Harbor Memorial Highway outside metro Phoenix.

Pima Canyon is a major canyon located in the Santa Catalina Mountains, north of Catalina Foothills and Tucson, Arizona, USA. Pusch Ridge forms the northwestern cliffs of Pima Canyon, dramatically rising from Pima Creek on the canyon floor. Pima Canyon varies greatly in elevation, from 2,900 feet (880 m) above sea level at Pima Creek to 6,350 feet (1,940 m) at Pima Saddle. Mount Kimball is the highest peak in the vicinity of the canyon.
Tanque Verde Falls are a series of waterfalls in Tanque Verde Canyon east of Tanque Verde, Arizona and Tucson, Arizona. Tanque Verde Ridge of the Rincon Mountains lies to the south and Agua Caleinte Hill to the north. The falls lie south of Redington Road which connects the Tucson Valley to the southwest with the San Pedro River valley to the east.

Saguaro National Park is an American national park in Pima County, southeastern Arizona. The 92,000-acre (37,000 ha) park consists of two separate areas—the Tucson Mountain District (TMD) about 10 miles (16 km) west of the city of Tucson and the Rincon Mountain District (RMD) about 10 miles (16 km) east of the city—that preserve Sonoran Desert landscapes, fauna, and flora, including the giant saguaro cactus.

Fort Lowell was a United States Army post active from 1873 to 1891 on the outskirts of Tucson, Arizona. Fort Lowell was the successor to Camp Lowell, an earlier Army installation. The Army chose a location just south of the confluence of the Tanque Verde and Pantano creeks, at the point where they form the Rillito River, due to the year-round supply of water during that period. The Hohokam natives had chosen the site centuries earlier, presumably for the same reason. To this day, shards of Hohokam pottery can still be found in the area. The Army claimed a military reservation that encompassed approximately eighty square miles and extended east toward the Rincon Mountains.
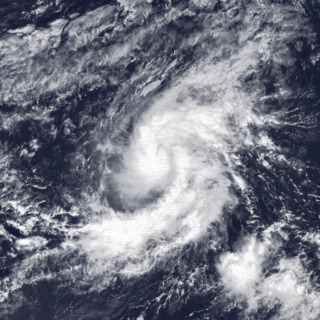
Tropical Storm Octave was considered the worst tropical cyclone in the history of Arizona, whose remnants caused devastating and record-breaking flooding in the state. The nineteenth tropical cyclone and fifteenth named storm of the 1983 Pacific hurricane season, the origins of Tropical Storm Octave were from a tropical disturbance that formed south of the Gulf of Tehuantepec on September 23, 1983. Steered by a deep layer high over Mexico, the disturbance moved west for four days before becoming a tropical depression on September 27 off the southwest coast of Mexico. Over an area of warm sea surface temperatures, it was able to quickly strengthen to peak winds of 50 mph (85 km/h), through wind shear prevented much further development. By September 30, Octave was accelerating to the northeast, steadily weakening due to cooler waters. That day it weakened to tropical depression status, and on October 2, Octave dissipated.

The Little Rincon Mountains are a small range of mountains, lying to the east of the Rincon Mountains, at Tucson, of eastern Pima County, Arizona. The range is located in northwest Cochise County and is part of the western border of the San Pedro River and Valley, the major valley and river of western Cochise County. The river is northward flowing to meet the Gila River; its headwaters are south of the US-Mexico border in northern Sonora. A small part of the Little Rincon range's southwest lies in Pima County.

Brawley Wash is an ephemeral stream, tributary to the Santa Cruz River, located in Pima County. Its source is in the Altar Valley between the Sierrita and Coyote Mountains at 31°58′20″N111°23′29″W, at the confluence of the Altar and Alambre washes along Arizona State Route 286. It flows north-north east through the Altar Valley and turns north as it enters Avra Valley near Robles Junction where Arizona State Route 86 crosses the streambed. The wash traverses the Avra Valley between the Roskruge Mountains and the Tucson Mountains. It joins the Santa Cruz east of the Samaniego Hills of the Silver Bell Mountains. The wash is known as the Los Robles Wash near its junction with the Santa Cruz approximately six miles west of Avra and Interstate 10.

Ciénega Creek is an intermittent stream located in the Basin and Range region of southern Arizona, and is one of the most intact riparian corridors left in the state. It originates in the Canelo Hills and continues northwest about 50 miles (80 km) to an area just outside Tucson, where it becomes known as Pantano Wash. Pantano Wash continues through Tucson and eventually connects with the Rillito River.
Pima County Natural Resources, Parks and Recreation is the agency within Pima County, Arizona that manages the natural resources, parks, and recreation offerings within Pima County including Tucson, AZ.

The Rillito River is a river in Pima County, Arizona. It flows from east to west across the northern boundary of the City of Tucson from the confluence of Tanque Verde Creek and Pantano Wash to the Santa Cruz River 12.2 miles (19.6 km) away. The Rillito River Park runs along the north and south banks of the river from Interstate 10 to North Craycroft Road.
The Loop is a network of shared-use paths in metropolitan Tucson, Arizona maintained by Pima County. Once complete it will comprise 131 miles (211 km) of paved trails dedicated to cyclist, pedestrian, and equestrian use. By 2014, the network was 85% complete, with over one hundred miles in place. Pima County estimates the Loop is used by an average of 2,000 visitors each weekday and more than 5,000 on weekends.














