Related Research Articles
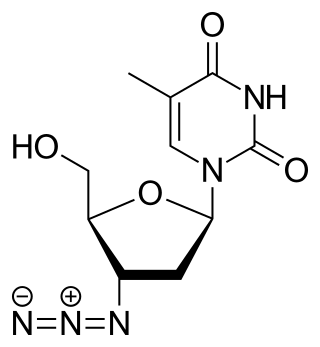
Zidovudine (ZDV), also known as azidothymidine (AZT), is an antiretroviral medication used to prevent and treat HIV/AIDS. It is generally recommended for use in combination with other antiretrovirals. It may be used to prevent mother-to-child spread during birth or after a needlestick injury or other potential exposure. It is sold both by itself and together as lamivudine/zidovudine and abacavir/lamivudine/zidovudine. It can be used by mouth or by slow injection into a vein.
The management of HIV/AIDS normally includes the use of multiple antiretroviral drugs as a strategy to control HIV infection. There are several classes of antiretroviral agents that act on different stages of the HIV life-cycle. The use of multiple drugs that act on different viral targets is known as highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). HAART decreases the patient's total burden of HIV, maintains function of the immune system, and prevents opportunistic infections that often lead to death. HAART also prevents the transmission of HIV between serodiscordant same-sex and opposite-sex partners so long as the HIV-positive partner maintains an undetectable viral load.
Virus latency is the ability of a pathogenic virus to lie dormant within a cell, denoted as the lysogenic part of the viral life cycle. A latent viral infection is a type of persistent viral infection which is distinguished from a chronic viral infection. Latency is the phase in certain viruses' life cycles in which, after initial infection, proliferation of virus particles ceases. However, the viral genome is not eradicated. The virus can reactivate and begin producing large amounts of viral progeny without the host becoming reinfected by new outside virus, and stays within the host indefinitely.
The Division of Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (DAIDS) is a division of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, which is part of the National Institutes of Health. It was formed in 1986 as a part of the initiative to address the national research needs created by the advent and spread of the HIV/AIDS epidemic. Specifically, the Division's mission is to increase basic knowledge of the pathogenesis, natural history, and transmission of HIV disease and to support research that promotes progress in its detection, treatment, and prevention. DAIDS accomplishes this through planning, implementing, managing, and evaluating programs in (1) fundamental basic research, (2) discovery and development of therapies for HIV infection and its complications, and (3) discovery and development of vaccines and other prevention strategies.
Douglas D. Richman is an American infectious diseases physician and medical virologist. Richman's work has focused on the HIV/AIDS pandemic, since its appearance in the early 1980s. His major contributions have been in the areas of treatment, drug resistance, and pathogenicity.

Janice Ellen Clements is vice dean for faculty at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine and the Mary Wallace Stanton Professor of Faculty Affairs. She is a professor in the departments of Molecular and Comparative Pathobiology, Neurology, and Pathology, and has a joint appointment in molecular biology and genetics. Her molecular biology and virology research examines lentiviruses and how they cause neurological diseases.
M. Christine "Chris" Zink is the director of the Department of Molecular and Comparative Pathobiology at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine. She also holds professorships in the Department of Pathology at Johns Hopkins and in the Department of Molecular Microbiology and Immunology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. Zink researches the response of the immune system to retroviruses such as HIV and is currently investigating an animal model of antiretroviral therapy and the potential of a common antibiotic to prevent HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders.
Joel N. Blankson is a professor at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine in the Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases. Blankson is an expert on HIV infection, particularly HIV latency and long-term control of HIV infection. He is a lead investigator in studies on these topics and is frequently interviewed in the scientific and popular press. Blankson also practices internal and infectious diseases medicine in Lutherville, Maryland.
Stuart C. Ray is an American physician. He is Vice Chair of Medicine for Data Integrity and Analytics, Associate Director of the Infectious Diseases Fellowship Training Program at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, and a Professor in the Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases. Ray also holds appointments in Viral Oncology and the Division of Health Sciences Informatics. He is affiliated with the Institute for Computational Medicine at Johns Hopkins and is licensed to practice medicine in Maryland.

HIV/AIDS research includes all medical research that attempts to prevent, treat, or cure HIV/AIDS, as well as fundamental research about the nature of HIV as an infectious agent and AIDS as the disease caused by HIV.
Deborah Persaud is a Guyanese-born American virologist who primarily works on HIV/AIDS at Johns Hopkins Children's Center.
The Mississippi baby is a Mississippi girl who in 2013 was thought to have been cured of HIV. She had contracted HIV at birth from her HIV-positive mother. Thirty hours after the baby was born, she was treated with intense antiretroviral therapy. When the baby was about 18 months old, the mother did not bring the child in for scheduled examinations for the next five months. When the mother returned with the child, doctors expected to find high levels of HIV, but instead the HIV levels were undetectable. The Mississippi baby was thought to be the other person, after the "Berlin patient," to have been cured of HIV. As a result, the National Institutes of Health planned to conduct a worldwide study on aggressive antiretroviral treatment of newborn infants of mothers with HIV infections. It was thought that aggressive antiretroviral therapy on newborn infants might be a cure for HIV. On July 10, 2014, however, it was reported that the child was found to be infected with HIV.
Leor S. Weinberger is an American virologist and quantitative biologist. He is credited with discovering the HIV virus latency circuit, which provided the first experimental evidence that stochastic fluctuations ('noise') in gene expression are used for cell fate decisions. He has also pioneered the concept of therapeutic interfering particles, or “TIPs”, which are resistance-proof antivirals. His TED talk on this novel antiviral approach 20 years in the making has been called a "highlight" of TED and received a standing ovation from the live audience.

Michel C. Nussenzweig is a professor and head of the Laboratory of Molecular Immunology at The Rockefeller University and a Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigator. He is a member of both the US National Academy of Medicine and the US National Academy of Sciences.

Sharon Ruth Lewin, FRACP, FAHMS is the inaugural Director of The Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity. She is also a Professor of Medicine at The University of Melbourne, a National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Practitioner Fellow, Director of the Cumming Global Centre for Pandemic Therapeutics, and President of the International AIDS Society (IAS).
Ya-Chi Ho is a Taiwanese infectious disease researcher and Associate Professor of Microbial Pathogenesis and Medicine at Yale University. Her research centers on the interaction between HIV and the host's immune system with the ultimate goal of curing HIV/AIDS.
Melanie Ott is a German virologist who is a senior investigator of The Ott Lab, Director the Gladstone Institute of Virology, and Senior Vice President of Gladstone Institutes. She is also a Professor of Medicine at the University of California, San Francisco.

Amanda Brown is an American immunologist and microbiologist as well as an associate professor of neurology and neuroscience at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, Maryland. Brown is notable for cloning one of the first recombinant HIV viruses and developing a novel method to visualize HIV infected cells using GFP fluorescence.

Charles Williams Flexner is an American physician, clinical pharmaceutical scientist, academic, author and researcher. He is a Professor of Medicine at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
Howard E. Gendelman is an American physician-scientist whose research intersects the disciplines of neuroimmunology, pharmacology, and infectious diseases. Gendelman was born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. His research is focused on harnessing immune responses for therapeutic gain in HIV/AIDS and Neurodegenerative disease. He is the Margaret R. Larson Professor of infectious diseases and internal medicine at the University of Nebraska Medical Center (UNMC) in Omaha.